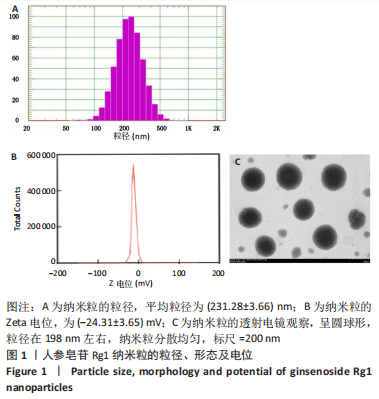
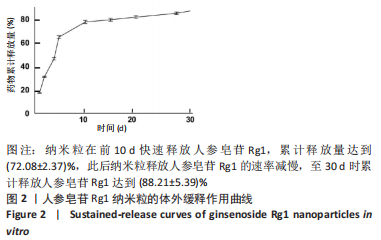
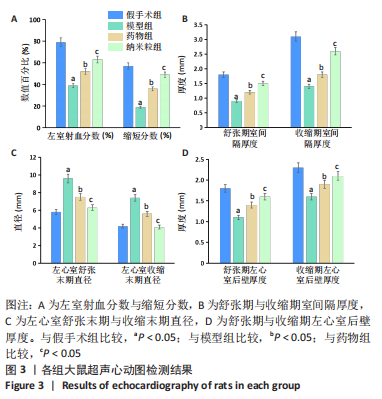
[1] CHEN R, XIAO Y, CHEN M, et al. A traditional Chinese medicine therapy for coronary heart disease after percutaneous coronary intervention: a meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(5):BSR20180973.
[2] 中国心血管健康与疾病报告2019 概要 [J].心脑血管病防治,2020, 20(5):437-450.
[3] YANAMANDALA M, ZHU W, GARRY DJ, et al. Overcoming the roadblocks to cardiac cell therapy using tissue engineering. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017; 70(6):766-775.
[4] BLANCO-FERNANDEZ B, CASTAÑO O, MATEOS-TIMONEDA MÁ, et al. Nanotechnology Approaches in Chronic Wound Healing. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2021;10(5):234-256.
[5] LUO Y, WANG Q, ZHANG Y. Biopolymer-Based Nanotechnology Approaches To Deliver Bioactive Compounds for Food Applications: A Perspective on the Past, Present, and Future. J Agric Food Chem. 2020;68(46):12993-13000.
[6] BAYDA S, ADEEL M, TUCCINARDI T, et al.The History of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology: From Chemical-Physical Applications to Nanomedicine. Molecules. 2019;25(1):112.
[7] TIBURCIUS S, KRISHNAN K, YANG JH, et al. Silica-Based Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Vehicles for Prostate Cancer Treatment. Chem Rec. 2021;21(6):1535-1568.
[8] TALAT A, KHAN AU. Patents in chemotherapy: nanoparticles as drug-delivery vehicles. Pharm Pat Anal. 2020;9(4):117-119.
[9] LUO M, YAN D, SUN Q, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates cardiomyocyte apoptosis and inflammation via the TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2020;121(4):2994-3004.
[10] LU ML, WANG J, SUN Y, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates mechanical stress-induced cardiac injury via calcium sensing receptor-related pathway.J Ginseng Res. 2021;45(6):683-694.
[11] HUANG L, CAI HA, ZHANG MS, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 promoted the wound healing in diabetic foot ulcers via miR-489-3p/Sirt1 axis. J Pharmacol Sci. 2021;147(3):271-283.
[12] 金岩,刘闺男.人参皂苷Rg1对急性心肌梗死大鼠血管新生的作用[J].中国医科大学学报,2007,36(5):517-519.
[13] MARUYAMA K, NAEMURA K, YOSHIHARA K, et al. Surgical protocol for permanent ligation of the left anterior descending coronary artery in mice to generate a model of myocardial infarction. STAR Protoc. 2021;2(3):100775.
[14] BORGHI C, BENTIVENGA C, COSENTINO ER. Uric acid and risk of myocardial infarction. A dynamic duo. Int J Cardiol. 2020;320:23-24.
[15] CRITCHER CR, SIEGEL M. Re-examining the Association Between E-Cigarette Use and Myocardial Infarction: A Cautionary Tale. Am J Prev Med. 2021;61(4):474-482.
[16] PEET C, IVETIC A, BROMAGE DI, et al. Cardiac monocytes and macrophages after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res. 2020;116(6): 1101-1112.
[17] TOMOAIA R, BEYER RS, SIMU G, et al. Understanding the role of echocardiography in remodeling after acute myocardial infarction and development of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Ultrason. 2019;21(1):69-76.
[18] JENČA D, MELENOVSKÝ V, STEHLIK J, et al. Heart failure after myocardial infarction: incidence and predictors. ESC Heart Fail. 2021;8(1):222-237.
[19] RUDDOX V, SANDVEN I, MUNKHAUGEN J, et al. Atrial fibrillation and the risk for myocardial infarction, all-cause mortality and heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2017;24(14): 1555-1566.
[20] TOMOAIA R, BEYER RS, SIMU G, et al. Understanding the role of echocardiography in remodeling after acute myocardial infarction and development of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.Med Ultrason. 2019;21(1):69-76.
[21] KOC L, ONDRUS T, FILA P, et al. Right ventricular myocardial infarction in the era of primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2021;122(10):700-707.
[22] XIAO M, LI Y, GUAN X. Community-Based Physical Rehabilitation After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention for Acute Myocardial Infarction. Tex Heart Inst J. 2021;48(2):e197103.
[23] FOKIN AA, KIREEV KA, NETISANOV SV. [Coronary artery bypass grafting in non-ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction]. Angiol Sosud Khir. 2020;26(3):142-149.
[24] WU X, REBOLL MR, KORF-KLINGEBIEL M, et al. Angiogenesis after acute myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res. 2021;117(5):1257-1273.
[25] MAHTTA D, SUDHAKAR D, KONERU S, et al. Targeting Inflammation After Myocardial Infarction. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2020;22(10):110.
[26] DENG Y, ZHANG X, SHEN H, et al. Application of the Nano-Drug Delivery System in Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;7:489.
[27] FORINI F, CANALE P, NICOLINI G, et al. Mitochondria-Targeted Drug Delivery in Cardiovascular Disease: A Long Road to Nano-Cardio Medicine. Pharmaceutics. 2020;12(11):1122.
[28] FU Y, TAN L, MENG L, et al. Therapeutic Effects of Paclitaxel Loaded Polyethylene Glycol-Polylactic Acid-Glycolic Acid Copolymer Nanoparticles on Pancreatic Cancer in Rats. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2020;20(12):7271-7275.
[29] HUA Y, SU Y, ZHANG H, et al. Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microsphere production based on quality by design: a review. Drug Deliv. 2021;28(1): 1342-1355.
[30] SONG F, CHEN L, LIN R, et al. Synthesis of carboxy-polyethylene glycol-amine (CA (PEG)n ) and [1-14 C]-CA (PEG)n via oxa-Michael addition of amino-polyethylene glycols to propiolates vs to acrylates. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm. 2020;63(1):15-24.
[31] YANG M, JIN L, WU Z, et al. PLGA-PEG Nanoparticles Facilitate In Vivo Anti-Alzheimer’s Effects of Fucoxanthin, a Marine Carotenoid Derived from Edible Brown Algae. J Agric Food Chem. 2021;69(34):9764-9777.
[32] 晏殊瑾,杨珂,王河,等.低强度脉冲超声靶向纳米粒控释SDF-1及BMP-2调节hPDLCs迁移和成骨分化[J].中国超声医学杂志,2022, 38(2):222-226.
[33] Wang B, Zhang C, Chu D, et al. Astragaloside IV improves angiogenesis under hypoxic conditions by enhancing hypoxia‑inducible factor‑1α SUMOylation. Mol Med Rep. 2021;23(4):244.
[34] DARDEN J, PAYNE LB, ZHAO H, et al. Excess vascular endothelial growth factor-A disrupts pericyte recruitment during blood vessel formation. Angiogenesis. 2019;22(1):167-183.
[35] JUBAN G, MOUNIER R.[Tissue repair: Key role of annexin A1 in the control of inflammatory response]. Med Sci (Paris). 2021;37(4):324-326.
[36] TOTLAND MZ, RASMUSSEN NL, KNUDSEN LM, et al. Regulation of gap junction intercellular communication by connexin ubiquitination: physiological and pathophysiological implications. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020;77(4):573-591.
[37] LAI Y, FOIS G, FLORES JR, et al. Inhibition of calcium-triggered secretion by hydrocarbon-stapled peptides. Nature. 2022;603(7903):949-956.
|