中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (34): 5436-5441.doi: 10.12307/2022.452
• 组织工程骨材料 tissue-engineered bone • 上一篇 下一篇
多尺度羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖微管结构人工骨对兔骨缺损修复及成血管的影响
龙智生1,熊 龙2,龚飞鹏1,李经堂1,曾建华1,邓 颖1,兰 敏1,孔维豪1,陈 钢1
- 1南昌大学附属人民医院骨科,江西省南昌市 330006;2南昌大学第二附属医院骨科,江西省南昌市 330006
Effect of artificial bone with multi-scale hydroxyapatite/chitosan microtubule structure on rabbit bone defect repair and angiogenesis
Long Zhisheng1, Xiong Long2, Gong Feipeng1, Li Jingtang1, Zeng Jianhua1, Deng Ying1, Lan Min1, Kong Weihao1, Chen Gang1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Jiangxi Provincial People’s Hospital Affiliated to Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
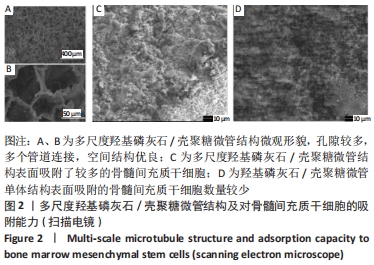
多尺度羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖微管结构:是指利用化学合成技术,构建以羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖为基础的多孔微管支架,该支架的空隙相通,具有多尺度的微观结构,该结构具有良好的细胞吸附能力和成骨及成血管功效。
材料不同层级的结构功能:小尺度结构(< 10 μm)更容易被组织液浸渍,提供更多的细胞吸附位点;中等尺度结构(20-40 μm)有利于原始巨噬细胞向M2型转化,并上调抗炎基因表达抑制宿主对移植物的免疫反应,这对于宿主细胞特别是间充质干细胞长入至关重要;大尺度(> 100 μm)有利于血管形成、细胞归巢、定植,为形成细胞集落提供场所。
背景:前期研究证实多尺度羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖微管成骨优良,而血管再生在成骨过程中较为关键,探索多尺度微管结构在其成血管中的作用及相关机制意义重大。
目的:探索多尺度羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖微管结构对兔骨缺损修复及成血管的影响。
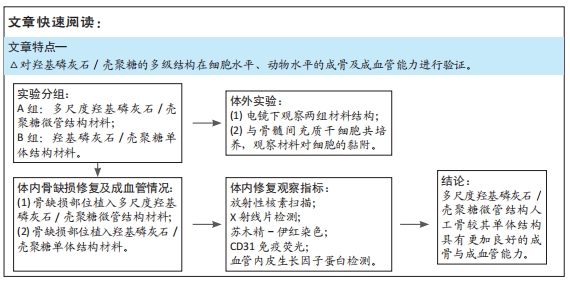
方法:构建多尺度羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖微管结构与羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖单体结构,将两种材料分别与骨髓间充质干细胞共培养,21 d后电镜下观察材料对细胞的吸附能力及细胞状态。在48只成年新西兰大白兔桡骨部位制作骨缺损模型,实验组(n=24)植入多尺度羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖微管结构材料,对照组(n=24)植入羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖单体结构材料,术后4,8,12周分别进行放射性核素骨显像、X射线片检查、组织形态学、CD31免疫组化染色及血管内皮生长因子蛋白检测。动物实验得到江西省人民医院伦理委员会批准。
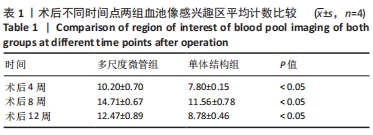
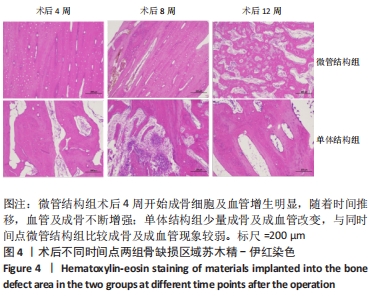
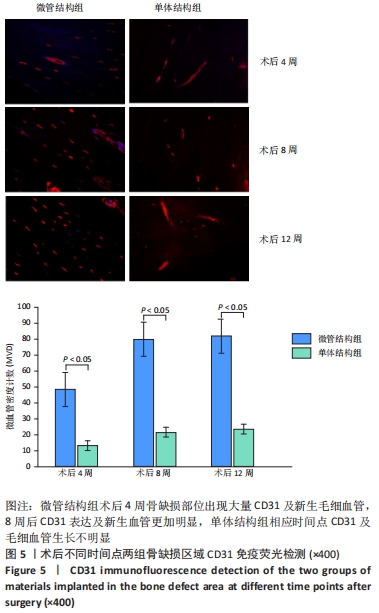
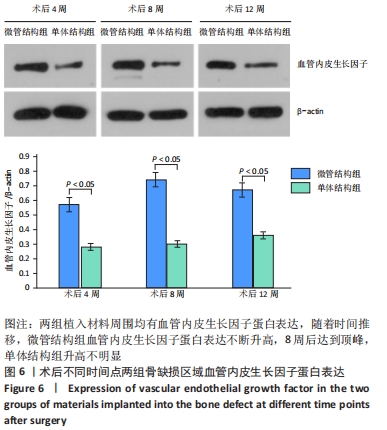
结果与结论:①电镜下可见,多尺度羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖微管结构材料孔隙相通,具有良好的空间结构,其表面吸附的骨髓间充质干细胞多于羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖单体结构材料。②放射性核素骨显像显示,实验组术后各时间点的血池成像均高于对照组(P < 0.05)。③X射线片显示,实验组各时间点的骨痂形成多于对照组。④苏木精-伊红染色显示,实验组术后12 周时骨缺损植骨区域内可见大量的新生血管及成骨,对照组术后12周时仅见骨折断端少许再生血管及成骨细胞附着;CD31免疫组化染色显示,实验组各时间点的微血管密度高于对照组(P < 0.05)。⑤Western Blot检测显示,实验组各时间点的血管内皮生长因子蛋白表达均高于对照组(P < 0.05)。⑥结果表明,多尺度羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖微管结构材料较其单体结构具有更加良好的成骨与成血管能力。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4899-6049 (龙智生)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: