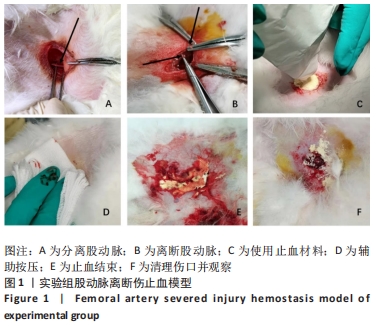
[1] LESTARI W, YUSRY WNSW, HARIS MS, et al. A glimpse on the function of chitosan as a dental hemostatic agent. Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 2020;56(1): 147-154.
[2] SAPAHN DR, BOUILLON B, CERNY V, DURANTEAU J, et al. The European guideline on management of major bleeding and coagulopathy following trauma: fifth edition. Crit Care. 2019;23(1): 98-99.
[3] 刘锐,李辉,杨俊峰,等.可吸收止血胶原海绵在心脏外科术中胸骨止血的应用体会[J].心肺血管病杂志,2014,33(5):719-721.
[4] YU W, XU J, SHENG H, et al. Clinical Evaluation of Absorbable Regenerated Oxidized Cellulose in Lung Cancer Surgery. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2020;23(6):492-495.
[5] CHEN XY, CUI CY, LIU Y, et al. A robust poly (N-acryloyl-2-glycine)- based sponge for rapid hemostasis. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(13):3760-3771.
[6] NADERI Z, AZIZIAN J. Synthesis and characterization of carboxymethyl chitosan/Fe3O4 and MnFe2O4 nanocomposites hydrogels for loading and release of curcumin. Photochem Photobiol B. 2018;18(5):206-214.
[7] YIN ML, WANG YF, ZHANG Y, et al. Novel quaternarized N-halamine chitosan and polyvinyl alcohol nanofibrous membranes as hemostatic materials with excellent antibacterial properties. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;232. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115823.
[8] BUKZEM ANDREA L, SIGNINI ROBERTA, DOS SANTOS DANILO M, et al. Optimization of carboxymethyl chitosan synthesis using response surface methodology and desirability function. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;85(1):615-624.
[9] FERNANDA GL, MEDEIROS BORSAGLI, ALEXANDRA AP, et al. O -carboxymethyl functionalization of chitosan: Complexation and adsorption of Cd (II) and Cr (VI) as heavy metal pollutant ions. React Funct Polym. 2015;97(1):37-47.
[10] GHOLAMALI I, ASNAASHARIISFAHANI M, ALIPOUR E. Silver Nanoparticles Incorporated in pH-Sensitive Nanocomposite Hydrogels Based on Carboxymethyl Chitosan-Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) for Use in a Drug Delivery System. Regen Eng Transl Med. 2020;6(2):138-153.
[11] DEMARCHI CA, SILVA L MD, NIEDZWIECKA A, et al. Nanoecotoxicology study of the response of magnetic O-Carboxymethylchitosan loaded silver nanoparticles on Artemia salina. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2020; 74(2):151-156.
[12] HATTORI H, ISHIHARA M. Changes in blood aggregation with differences in molecular weight and degree of deacetylation of chitosan. Biomed Mater. 2015;10(1):015014.
[13] WANG YM, XIAO DD, ZHONG Y, et al. Facile fabrication of carboxymethyl chitosan/paraffin coated carboxymethylated cotton fabric with asymmetric wettability for hemostatic wound dressing. Cellulose. 2020; 27(6):3443-3453.
[14] WANG LY, ZHONG YY, QIAN CT, et al. A natural polymer-based porous sponge with capillary-mimicking microchannels for rapid hemostasis. Acta Biomater. 2020;114:193-205.
[15] CHAO Y, LING X, YING Z, et al. A green fabrication approach of gelatin/CM-chitosan hybrid hydrogel for wound healing. Carbohydr Polym. 2010;82(4):1297-1305.
[16] 曾莉君,程刚毅,王赟,等.复合大孔聚多糖止血材料对肝脏钝挫伤止血的有效性研究[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2018,13(2): 88-93.
[17] HAO C, SHANG XQ, YU L, et al. Safety evaluation of a low-heat producing zeolite granular hemostatic dressing in a rabbit femoral artery hemorrhage model. J Biomater Appl. 2020;34(7):988-997.
[18] CHUNYU L, CHENYU L, SIMIAO Y, et al. Efficient antibacterial dextran-montmorillonite composite sponge for rapid hemostasis with wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;160:1130-1143.
[19] YANG WJ, SONG JC, ZHU YW, et al. Application of chain-based sponge dressing for gunshot wounds in the groin. Am J Emerg Med. 2021;39: 24-27.
[20] TANAKA SM, IMAMURA T, FUJIMOTO M, et al. Potent Hemostatic Efficacy of a Novel Recombinant Fibrin Sealant Patch (KTF-374) in Rabbit Bleeding Models. J Invest Surg. 2019;32(3):257-261.
[21] QIAO ZW, LV XL, HE SH, et al. A mussel-inspired supramolecular hydrogel with robust tissue anchor for rapid hemostasis of arterial and visceral bleedings. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(9):2829-2840.
[22] QIANQIAN OY, TINGTING H, CHENGPENG L, et al. Construction of a composite sponge containing tilapia peptides and chitosan with improved hemostatic performance. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;139(1): 719-729.
[23] 张爽,徐庆华,童琳,等.可吸收止血材料的研究现状与应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(10):1628-1634.
[24] ZHENG YX, PAN NY, LIU Y, et al. Novel porous chitosan/N-halamine structure with efficient antibacterial and hemostatic properties. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;253(1):117-205.
[25] HU Z, ZHANG DY, LU ST, et al. Chitosan-Based Composite Materials for Prospective Hemostatic Applications. Mar Drugs. 2018;16(8):273.
[26] ZHANG DY, HU Z, ZHANG LY, et al. Chitosan-Based Thermo-Sensitive Hydrogel Loading Oyster Peptides for Hemostasis Application. Materials (Basel, Switzerland). 2020;13(21):1-16.
[27] ZHENG W, CHEN CT, ZHANG XJ, et al. Layer-by-layer coating of carboxymethyl chitosan-gelatin-alginate on cotton gauze for hemostasis and wound healing. Surf Coat Technol. 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.126644.
[28] YONG Z, JZ L, FAN L, et al. Degradable porous carboxymethyl chitin hemostatic microspheres. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2020;31(11):1369-1384.
[29] WEI Z, YU X, BIN Y, et al. Synthesis and properties of crosslinked carboxymethyl chitosan and its hemostatic and wound healing effects on liver injury of rats. J Biomater Appl. 2019;34(3):442-450.
[30] ZHOU LB, DING RY, XU BX, et al. Application of microfibrillar collagen hemostat sponge for cartilage engineering. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2016; 9(3):6127-6132.
[31] 肖丹宇,卫骆云,俞俊峰,等.可吸收止血微球在腹腔镜胆囊切除术中的临床应用[J].中国内镜杂志,2014,20(4):398-400.
[32] GRUNKHORN R, BURNHAM R, WALTON G. Successful use of a military-grade haemostatic agent for a major head and neck bleed. J Laryngol Otol. 2013;127(10):1031-1033.
[33] POURSHAHRESTANI S, ZEIMARAN E, KADRI NA, et al. Polymeric Hydrogel Systems as Emerging Biomaterial Platforms to Enable Hemostasis and Wound Healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(20):e2000905.
[34] BIRANJE SS, MADIWALE PV, PATANKAR KC, et al. Cytotoxicity and hemostatic activity of chitosan/carrageenan composite wound healing dressing for traumatic hemorrhage. Carbohydr Poly. 2020;239. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116106.
[35] ZHANG DF, XU ZY, LI HF, et al. Fabrication of strong hydrogen-bonding induced coacervate adhesive hydrogels with antibacterial and hemostatic activities. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(5):1455-1463.
|