| [1] 胡亮,郑昌琼,冉均国.医用粘合剂研究进展[J].国外医学:生物医学工程分册,1998,21(1):26.[2] Pfister WR.Silicone PSAS of ferflexibility for medical,pharmaceutical use.Adhesives Age.1990;33(3):2.[3] Han JM,Hong G,Hayashida K,et al.Influence of composition on the adhesive strength and initial viscosity of denture adhesives.Dent Mater J.2014;33(1):98-103.[4] Imazato S,Ma S,Chen JH,et al.Therapeutic polymers for dental adhesives: loading resins with bio-active components.Dent Mater. 2014;30(1):97-104.[5] Avre WN,Denver SP,Evans SL.Ageing and moisture uptake in polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) bone cements.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2013;32C:76-88.[6] Howe N,Cherpelis B.Obtaining rapid and effective hemostasis: Part 1. Update And review of topical hemostatic agents.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69(5):659.e1-659.e17.[7] Duarte AP,Coelho JF,Bordado JC,et al.Surgical adhesives: systematic review of the main types and development forecast.Prog Polymer Sci. 2012;37:1031-1050.[8] Sanders L,Nagatomi J.Clinical applications of surgical adhesives and sealants.Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2014;42(3-4):271-292.[9] Amosi N,Zarzhitsky S,Gilsohn E,et al.Acidic Peptide Hydro-gel Scaffolds Enhance Calcium Phosphate Mineral Turnover intoBone Tissue.Acta Biomaterialia. 2012;8(7):2466-2475.[10] Li S,Wang J,Song L,et al.Injectable PAMAM/ODex double-crosslinked hydrogels with high mechanical strength.Biomed Mater. 2016;12(1): 015012.[11] Bae KH,Wang LS,Kurisawa M.Injectable biodegradable hydrogels: progress and challenges.J Mater Chem B. 2013;1(40):5371-5388.[12] Shekaran A,Garcia JR,Clark AY,et al.Bone regeneration using an alpha 2 beta 1 integrin-specific hydrogel as a BMP2delivery vehicle. Biomaterials.2014;35(21):5453-5461.[13] Balakrishnan B,Joshi N,Banerjee R.Borate aided Schiff's base formation yields in situ gelling hydrogels for cartilage regeneration.J Mater Chem B.2013;1:5564-5577.[14] Yuan L,Wu Y,Gu QS,et al.Injectable photo crosslinked enhanced double-network hydrogelsfrom modified sodium alginate and gelatin. Int J Biol Macromol.2017;96:569-577. [15] Geng X,Yuan L,Mo X.Oxidized dextran/amino gelatin/hyaluronic acid semi- interpenetrating network hydrogels for tissue engineering application.Adv Mater Res. 2013;627:745-750.[16] Weng L,Romanov A,Rooney J,et al.Non-cytotoxic, in situ gelable hydrogels composed of N-carboxyethyl chitosan and oxidized dextran. Biomaterials.2008;29(29):3905-3913.[17] Balakrishnan B,Mohanty M,Umashankar PR,et al.Evaluation of an in situ forming hydrogel wound dressing based on oxidized alginate and gelatin.Biomaterials. 2005;26(32):6335-6342.[18] Mo X,Iwata H,Matsuda S,et al.Soft tissue adhesive composed of modified gelatin and polysaccharides. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2000; 11(4):341-351.[19] Nowakowska M,Zapotoczny S,Sterzel M,et al. Novel Water-Soluble Photosensitizers from Dextrans. Biomacromolecules. 2004;5(3): 1009-1014.[20] Maia J,Ferreira L,Carvalho R,et al.Synthesis and characterization of new injectable and degradable dextran-based hydrogels.Polymer. 2005;46(23):9604-9614.[21] Schacht E,Bogdanov B,Bulcke AVD,et al.Hydrogels prepared by crosslinking of gelatin with dextran dialdehyde.React Functl Polym. 1997;33(2-3):109-116.[22] Massia SP,Stark J,LetbetterDS.Surface-immobilized dextran limits cell adhesion and spreading.Biomaterials.2000;21(22):2253-2261.[23] Wang T,Mu X,Li H, et al.The photocrosslinkable tissue adhesive based on copolymeric dextran/HEMA. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;5;92(2):1423-1431.[24] 崔莉,贾军芳,熊子豪,等.羧甲基壳聚糖/藻酸钠半互穿网络水凝胶的制备及性能研究[J].高分子学报,2014, 58(3):361-368.[25] Dodane V,Vilivalam VD.Pharmaceutical applications of chitosan. Pharm Sci Tech Today.1998;1(6): 246-253.[26] 孙立苹,杜予民,陈凌云,等.羧甲基壳聚糖水凝胶制备及其在药物控释中的应用[J].高分子学报,2004,48(2):191-195.[27] Zhao SP,Ma D,Zhang LM.New semi-interpenetrating network hydrogels: Synthesis, characterization and properties. Macromol Biosci.2006;6(6):445-451.[28] Sarem M,Moztarzadeh F,Mozafari M.How can genipin assist gelatin/carbohydrate chitosan scaffolds to act as replacements of load-bearing soft tissues? Carbohydr Polym. 2013; 93(2):635-643.[29] Tseng HJ,Tsou TL,Wang HJ.Characterization of chitosan-gelatin scaffolds for dermal tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2013; 7(1):20-31.[30] 王琴梅,廖燕红,滕伟,等.盐酸羟胺-电位滴定法测定氧化海藻酸钠上的醛基浓度[J].分析试验室,2008,27(s1):83-86.[31] Zhao H,Heindel ND.Determination of degree of substitution of formyl groups in polyaldehyde dextran by the hydroxylamine hydrochloride method.Pharm Res.1991;8(3):400-402.[32] 马有香,焦淑婷,张金生,等.分光光度法测定核黄素碘盐碘含量方法的研究[J].中国卫生检验,2008,18(3):460-461.[33] 李人宇,李咏梅,张成燕.分光光度法测定食盐中碘含量方法的评述[J].中国地方病防治杂志, 2008,28(2):105-107.[34] 孙言蓓.新型海藻酸盐-明胶水凝胶的研究[D].天津大学硕士学位论文,2007.[35] 韦广辉.电位滴定法测定胺茶碱片中乙二胺的含量[J].中国药房, 2011, 22(12):1136-1137.[36] 陈赞民,陈颖江.气相色谱法测定胺茶碱及其制剂中乙二胺的含量[J].药物分析杂志,2012,32(9):1673-1676.[37] YY/T 0729.1-2009,组织粘合剂粘接性能试验方法 第1部分:搭接-剪切拉伸承载强度.[38] YY/T 0729.2-2009,组织粘合剂粘接性能试验方法 第2部分:T-剥离拉伸承载强度.[39] YY/T 0729.3-2009,组织粘合剂粘接性能试验方法 第3部分:拉伸强度.[40] YY/T 0729.4-2009,组织粘合剂粘接性能试验方法 第4部分:伤口闭合强度.[41] 王艳红,顾汉卿.医用粘合剂的发展及临床应用进展[J].透析与人工器官, 2008,19(3):23.[42] 侯彪,谢松林.医用粘合剂在血管吻合及修复中应用的研究进展[J].岭南现代临床外科,2016,16(1):1115-120.[43] 张国栋.关于对医用粘合剂的研究[J].化学工程与装备, 2016,45(3): 167-169.[44] 刘加鹏,蒋臻,杨丙晔,等.海洋贻贝粘附蛋白类的结构与功能[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2007,23(11):899-904.[45] Neha T,Manohar V.Enhanced drug release by selective cleavage of cross-links in a double-cross-linked hydrogel.RSC Adv. 2016;6: 102453-102461.[46] Bao D,Chen M,Wang H,et al.Preparation and characterization of double cross-linked hydrogel films from carboxymethyl chitosan and carboxymethyl cellulose.Carbohydr Polym. 2014;110:113-120.[47] Ye MM,Jiang R,Zhao J,et al.In situ formation of adhesive hydrogels based on PL with laterally grafted catechol groups and their bonding efficacy to wet organic substrates.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2015;26:273. [48] Yu F,Cao XD,Du J,et al.Multifunctional Hydrogel with Good Structure Integrity, Self-Healing, and Tissue-Adhesive Property Formed by Combining Diels-Alder Click Reaction and Acylhydrazone Bond ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7:24023-24031. |
.jpg)
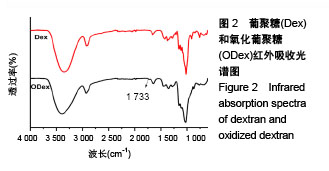
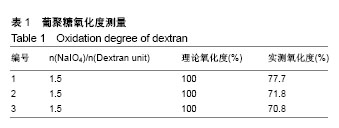
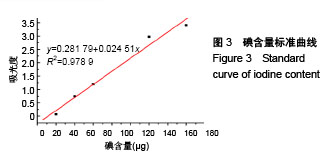
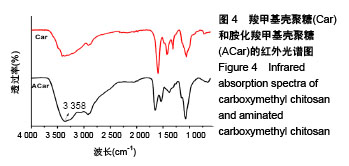
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)