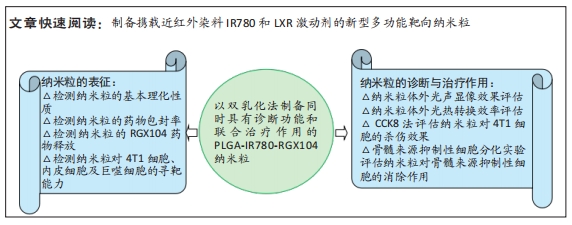
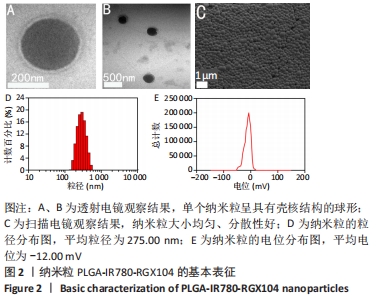
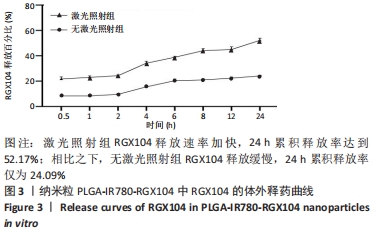
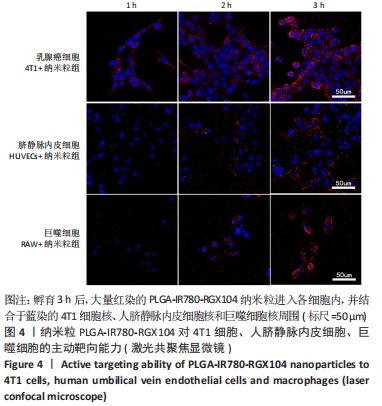
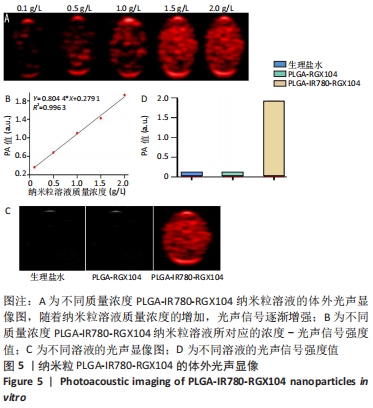
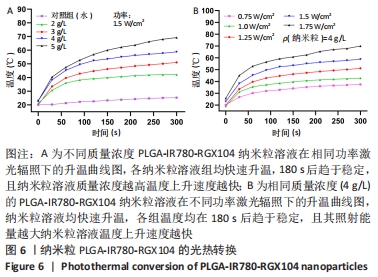
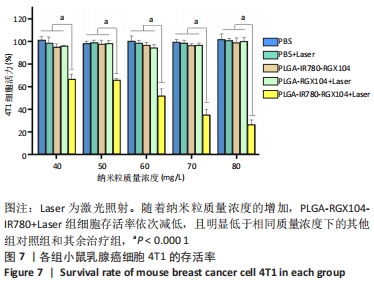
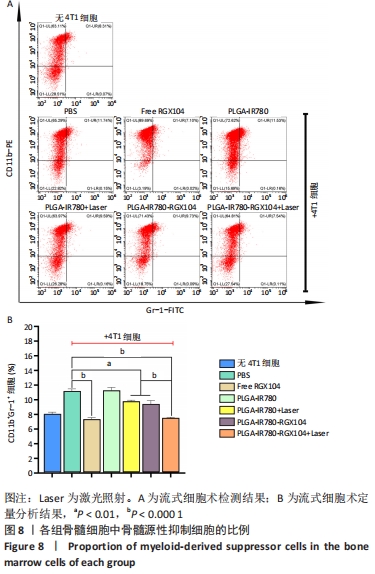
[1] 师金,梁迪,李道娟,等.全球女性乳腺癌流行情况研究[J].中国肿瘤,2017,26(9):683-690.
[2] 罗水莲,吴猛,白姣,等.赫赛汀靶向载阿霉素/印度墨水多功能分子探针的制备及其对乳腺癌成像诊断及治疗的实验研究[J].中华医学超声杂志(电子版),2020,17(6):566-573.
[3] Ge XQ, SONG ZM, SUN LN, et al. Lanthanide (Gd3+ and Yb3+) functionalized gold nanoparticles for in vivo imaging and therapy. Biomaterials. 2016;108(12):35-43.
[4] ZHANG B, WANG HF, SHEN S, et al. Fibrin-targeting peptide CREKA-conjugated multi-walled carbon nanotubes for self-amplified photothermal therapy of tumor. Biomaterials. 2016;79(2):46-55.
[5] WANG WY, JING T, XIA XR, et al. Melanin-loaded biocompatible photosensitive nanoparticles for controlled drug release in combined photothermal-chemotherapy guided by photoacoustic/ultrasound dual-modality imaging. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(10):4060-4074.
[6] SOFIA Fk, ELEFTHERIOS P, DIAMANDIS, et al. Cancer immunotherapy: the beginning of the end of cancer. BMC Med. 2016;14(73):1-18.
[7] KOKATE R. A systematic overview of cancer immunotherapy: an emerging therapy. Pharm Pharmacol Int. 2017;5(2):31-35.
[8] ZHOU J, WANG MY, HAN YN, et al. Multistage-Targeted Gold/Mesoporous Silica Nanocomposite Hydrogel as In Situ Injectable Drug Release System for Chemophotothermal Synergistic Cancer Therapy. Bio Mater. 2020;3(1):421-431.
[9] CHEN WR, ADAMS RL, CARUBELLI R, et al. Laser-photosensitizer assisted immunotherapy: A novel modality in cancer treatment. Cancer Lett. 1997;115(1):25-30.
[10] CARMEN MG, RIZVI I, CHANG Y, et al. Synergism of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Targeted Immunotherapy With Photodynamic Treatment of Ovarian Cancer In Vivo. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97(20): 1516-1524.
[11] CHEN WR, SINGHAL AK, LIU H, et al. Antitumor Immunity Induced by Laser Immunotherapy and Its Adoptive Transfer. Cancer Res. 2001; 61(2):459-461.
[12] SUN HT, YU TZ, LI X, et al. Second near-infrared photothermal-amplified immunotherapy using photoactivatable composite nanostimulators. J Nanobiotechnol. 2021;19:433.
[13] JEON M, KIM G, LEE W, et al. Development of theranostic dual-layered Au-liposome for effective tumor targeting and photothermal therapy. J Nanobiotechnol. 2021;19:262.
[14] ZHOU ZG, JIANG N, CHEN JS, et al. Selectively down-regulated PD-L1 by albumin-phenformin nanoparticles mediated mitochondrial dysfunction to stimulate tumor-specific immunological response for enhanced mild-temperature photothermal efficacy. J Nanobiotechnol. 2021;19:375.
[15] HUANG LP, LI YN, DU YN, et al. Mild photothermal therapy potentiates anti-PD-L1 treatment for immunologically cold tumors via an all-in-one and all-in-control strategy. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):4871.
[16] 江琼超,周泊阳,许燕妮,等.PEG修饰载NaHCO3产气纳米脂质微泡激活树突状细胞增强抗肿瘤能力的初步研究[J].中国超声医学杂志,2021,37(5):591-593.
[17] CHEN L, ZHOU LL, WANG CH, et al. Tumor-T argeted drug and CpG delivery system for phototherapy and docetaxel-enhanced immunotherapy with polarization toward M1-type macrophages on triple negative breast cancers. Adv Mater. 2019;31(52):1904997.
[18] PENG JR, XIAO Y, LI WT, et al. Photosensitizer Micelles Together with IDO Inhibitor Enhance Cancer Photothermal Therapy and Immunotherapy. Adv Sci. 2018;5(5):145.
[19] NOWIKIEWIC ZT, KURYLCIO A, POLKOWSKI W, et al. Imaging methods for the local lymphatic system of the axilla in early breast cancer in patients qualified for sentinel lymph node biopsy. Prz Menopauzalny. 2016;31(52):52-55.
[20] ROBINSON JT, TABAKMAN SM, LIANG Y, et al. Ultrasmall reduced graphene oxide with high near-infrared absorbance for photothermal therapy. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133(17):6825-6831.
[21] 王文渊,敬婷,王志刚,等.载黑色素/全氟戊烷的光致相变型纳米粒用于增强体内超声/光声显影及光热治疗的实验研究[J].中国超声医学杂志,2019,35(7):653-655.
[22] MICHEL O, ANTOINE T, FRANCOIS G, et al.Calreticulin exposure dictates the immunogenicity of cancer cell death. Nat Med. 2007;13:54-61.
[23] CHEN Q, XU LG, LIANG C, et al. Photothermal therapy with immune-adjuvant nanoparticles together with checkpoint blockade for effective cancer immunotherapy. Nat Com. 2016;7:13193.
[24] SLOVAK R, LUDWIG JM, GETTINGER SN, et al. Immuno-thermal ablation–boosting the anticancer immune response. J Immuno Ther Cancer. 2017;5(1):1-15.
[25] NAM J, SON S, OCHYL LJ, et al. Chemo-photothermal therapy combination elicits anti-tumor immunity against advanced metastatic cancer. Nat Commun. 2018;9:1074.
[26] TESSA G, CHRISTO SN, HERCUS TR, et al. In vitroGM-CSF signalling blockade and chemotherapeutic agents act in concert to inhibit the function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Clin Transl Immunology. 2016;5(12):e119.
[27] RAJENDRAKUMAR SK, UTHAMAN S, CHO CS, et al. Nanoparticle-Based Phototriggered Cancer Immunotherapy and Its Domino Effect in the Tumor Microenvironment. Biomacromolecules. 2018;19(6):1869-1887.
[28] NAMKOONG H, ISHII M, FUJII H, et al. Clarithromycin expands CD11b+Gr-1+ cells via the STAT3/Bv8 axis to ameliorate lethal endotoxic shock and post-influenza bacterial pneumonia. PLoS Pathog. 2018;14(4):e1006955.
[29] WAN DD, YANG YL, LIU YY, et al. Sequential Depletion of Myeloid-derived Suppressor Cells and Tumor Cells with a Dual-pH-Sensitive Conjugated Micelle System for Cancer Chemoimmunotherapy. J Control Release. 2020;317:43-56.
[30] TAVAZOIE MF, POLLACK I, TANQUECO R, et al. LXR/ApoE Activation Restricts Innate Immune Suppression in Cancer. Cell. 2018;172:1-16.
[31] SUN JH, XU W, Li LP, et al. Ultrasmall Endogenous Biopolymer Nanoparticles for Magnetic Resonance /Photoacoustic Dual-Modal Imaging-Guided Photothermal Therapy. Nanoscale. 2018;10:10584-10595.
[32] GUO Y, WANG XY, CHEN YL, et al.a light-controllable specific drug delivery nanoplatform for targeted bimodal imaging-guided photothermal/chemo synergistic cancer therapy. Acta Biomater. 2018; 80:308-326.
[33] LIU YJ, BHATTARAI P, DAI ZF, et al. Photothermal therapy and photoacoustic imaging via nanotheranostics in fighting cancer. Chem Soc Rev. 2019;48(7):2053-2108.
[34] SHENG D, LIU T, DENG L, et al. Perfluorooctyl bromide & indocyanine green co-loaded nanoliposomes for enhanced multimodal imaging-guided phototherapy. Biomaterials. 2018;165(1):1-13.
[35] REN H, LIU JQ, SU FH, et al. Relighting Photosensitizers by Synergistic Integration of Albumin and Perfluorocarbon for Enhanced Photodynamic Therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(4):3463-3473.
[36] ZHANG EL, ZHANG C, SU OP, et al.Newly developed strategies for multifunctional mitochondria-targeted agents in cancer therapy.Drug Discovery Today. 2011;16(3):140-146.
[37] BARNETT BP, RUIZ-CABELLO J, HOTA P, et al. Fluorocapsules for Improved Function, Immunoprotection, and Visualization of Cellular Therapeutics with MR,US,and CT Imaging. Radiology. 2011;258(1):182-191.
[38] ZHANG L, WANG D, YANG K, et al. Mitochondria-targeted artificial“Nano-RBCs” for amplified synergistic cancer phototherapy by a single NIR irradiation. Adv Sci. 2018;5(8):1800049.
[39] 刘姝伶,郭大静,冉海涛,等.诊疗一体化胶质瘤靶向纳米粒增效声动力治疗及多模态显像:体外实验研究[J].中国医学影像技术, 2021,37(5):641-647.
[40] LIU MZ, ZHANG P, DENG LM, et al. IR780-based light-responsive nanocomplexes combining phase transition for enhancing multimodal imaging-guided photothermal therapy. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(3):1132-1146.
|