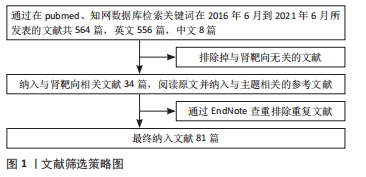
[1] KELLUM JA, BELLOMO R, RONCO C. Definition and classification of acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin Pract. 2008;109(4):c182-c187.
[2] XIAO Y-Q, CHENG W, WU X, et al. Novel risk models to predict acute kidney disease and its outcomes in a Chinese hospitalized population with acute kidney injury. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):15636.
[3] RILEY S, DIRO E, BATCHELOR P, et al. Renal impairment among acute hospital admissions in a rural Ethiopian hospital. Nephrology (Carlton). 2013;18(2):92-96.
[4] JHA V, GARCIA-GARCIA G, ISEKI K, et al. Chronic kidney disease: global dimension and perspectives. Lancet. 2013;382(9888):260-272.
[5] CORESH J, SELVIN E, STEVENS L A, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA. 2007;298(17):2038-2047.
[6] HAAS M, MOOLENAAR F, MEIJER DKF, et al. Specific drug delivery to the kidney. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2002;16(6):489-496.
[7] MURO S, GARNACHO C, J A,. et al. Control of endothelial targeting and intracellular delivery of therapeutic enzymes by modulating the size and shape of ICAM-1-targeted carriers. Mol Ther. 2008;16(8):1450-1458.
[8] CHEN Z, PENG H, ZHANG C. Advances in kidney-targeted drug delivery systems. Int J Pharm. 2020;587:119679.
[9] 郭苗苗,张芸,徐丹,等.肾靶向纳米给药系统的研究进展[J].医药导报, 2012,31(6):768-770.
[10] PETI-PETERDI J, KIDOKORO K, RIQUIER-BRISON A. Novel in vivo techniques to visualize kidney anatomy and function. Kidney Int. 2015;88(1):44-51.
[11] ICHIMURA K, STAN RV, KURIHARA H, et al. Glomerular endothelial cells form diaphragms during development and pathologic conditions. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;19(8):1463-1471.
[12] MINER JH. The glomerular basement membrane. Exp Cell Res. 2012; 318(9):973-978.
[13] ARMELLONI S, CORBELLI A, GIARDINO L, et al. Podocytes:recent biomolecular developments. Biomol Concepts. 2014;5(4):319-330.
[14] AKILESH S, HUBER T B, WU H, et al. Podocytes use FcRn to clear IgG from the glomerular basement membrane. P Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008; 105(3):967-972.
[15] LEVIDIOTIS V, POWER DA. New insights into the molecular biology of the glomerular filtration barrier and associated disease. Nephrology (Carlton). 2005; 10(2):157-166.
[16] SATCHELL SC, BRAET F. Glomerular endothelial cell fenestrations: an integral component of the glomerular filtration barrier. Am J Physiol-Renal. 2009;296(5): F947-F956.
[17] HIRONAKA K, MAKINO H, YAMASAKI Y, et al. Pores in the glomerular basement membrane revealed by ultrahigh-resolution scanning electron microscopy. Nephron. 1993;64(4):647-649.
[18] LEWIS E J, XU X. Abnormal glomerular permeability characteristics in diabetic nephropathy: implications for the therapeutic use of low-molecular weight heparin. Diabetes care. 2008;31 Suppl 2:S202-S207.
[19] TRYGGVASON K. Unraveling the mechanisms of glomerular ultrafiltration: nephrin, a key component of the slit diaphragm. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999;10(11):2440-2445.
[20] SAITO A, SATO H, IINO N, et al. Molecular mechanisms of receptor-mediated endocytosis in the renal proximal tubular epithelium. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010;2010:403272.
[21] SUBRAMANIAN VS, MARCHANT JS, SAID HM. Apical membrane targeting and trafficking of the human proton-coupled transporter in polarized epithelia. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008;294(1):C233-C240.
[22] WOOD I S, TRAYHURN P. Glucose transporters (GLUT and SGLT): expanded families of sugar transport proteins. Br J Nutr. 2003;89(1):3-9.
[23] HAGENBUCH B. Drug uptake systems in liver and kidney:a historic perspective. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2010;87(1):39-47.
[24] TERADA T, INUI KI. Physiological and pharmacokinetic roles of H+/organic cation antiporters (MATE/SLC47A). Biochem Pharmacol. 2008;75(9):1689-1696.
[25] ABBOUD HE. Mesangial cell biology. Exp Cell Res. 2012;318(9):979-985.
[26] ZHAO JH. Mesangial Cells and Renal Fibrosis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019; 1165:165-194.
[27] BAGAVANT H, KALANTARINIA K, SCINDIA Y, et al. Novel therapeutic approaches to lupus glomerulonephritis: translating animal models to clinical practice. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011;57(3):498-507.
[28] DUNCAN R, GASPAR R. Nanomedicine(s) under the microscope. Mol Pharm. 2011;8(6):2101-2141.
[29] AZARMI S, ROA W H, LöBENBERG R. Targeted delivery of nanoparticles for the treatment of lung diseases. Adv Drug Del Rev. 2008;60(8):863-875.
[30] CHOI HS, LIU W, MISRA P, et al. Renal clearance of quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25(10):1165-1170.
[31] ZUCKERMAN JE, DAVIS ME. Targeting therapeutics to the glomerulus with nanoparticles. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2013;20(6):500-507.
[32] CHOI CHJ, ZUCKERMAN J E, WEBSTER P, et al. Targeting kidney mesangium by nanoparticles of defined size. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108(16):6656-6661.
[33] GUO L, LUO S, DU Z, et al. Targeted delivery of celastrol to mesangial cells is effective against mesangioproliferative glomerulonephritis. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):878.
[34] LIANG X, WANG H, ZHU Y, et al. Short- and long-term tracking of anionic ultrasmall nanoparticles in kidney. ACS Nano. 2016;10(1):387-395.
[35] BORGMAN MP, COLEMAN T, KOLHATKAR RB, et al. Tumor-targeted HPMA copolymer-(RGDfK)-(CHX-A’’-DTPA) conjugates show increased kidney accumulation. J Control Release. 2008;132(3):193-199.
[36] KISSEL M, PESCHKE P, SUBR V, et al. Detection and cellular localisation of the synthetic soluble macromolecular drug carrier pHPMA. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imag. 2002;29(8):1055-1062.
[37] PIKE DB, GHANDEHARI H. HPMA copolymer-cyclic RGD conjugates for tumor targeting. Adv Drug Del Rev. 2010;62(2):167-183.
[38] MANIL L, DAVIN JC, DUCHENNE C, et al. Uptake of nanoparticles by rat glomerular mesangial cells in vivo and in vitro. Pharm Res. 1994;11(8):1160-1165.
[39] SANDOVAL RM, KENNEDY MD, LOW PS, et al. Uptake and trafficking of fluorescent conjugates of folic acid in intact kidney determined using intravital two-photon microscopy. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004;287(2):C517-C526.
[40] OROOJALIAN F, REZAYAN AH, MEHRNEJAD F, et al. Efficient megalin targeted delivery to renal proximal tubular cells mediated by modified-polymyxin Bpolyethylenimine based nano-gene-carriers. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;79:770-782.
[41] RICARD I, PAYET MD, DUPUIS G. VCAM-1 is internalized by a clathrin-related pathway in human endothelial cells but its alpha 4 beta 1 integrin counter-receptor remains associated with the plasma membrane in human T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1998;28(5):1708-1718.
[42] VISWESWARAN GRR, GHOLIZADEH S, RUITERS MHJ, et al. Targeting Rapamycin to Podocytes Using a Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (VCAM-1)-Harnessed SAINT-Based Lipid Carrier System. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0138870.
[43] BAINES RJ, BRUNSKILL NJ. The molecular interactions between filtered proteins and proximal tubular cells in proteinuria. Nephron Exp Nephrol. 2008;110(2):e67-e71.
[44] WANG G, LI Q, CHEN D, et al. Kidney-targeted rhein-loaded liponanoparticles for diabetic nephropathy therapy via size control and enhancement of renal cellular uptake. Theranostics. 2019;9(21):6191-6208.
[45] WANG J, MASEHI-LANO JJ, CHUNG EJ. Peptide and antibody ligands for renal targeting: nanomedicine strategies for kidney disease. Biomater Sci. 2017;5(8):1450-1459.
[46] BIDWELL G L, MAHDI F, SHAO Q, et al. A kidney-selective biopolymer for targeted drug delivery. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017;312(1):F54-F64.
[47] WISCHNJOW A, SARKO D, JANZER M, et al. Renal targeting: peptide-based drug delivery to proximal tubule cells. Bioconjug Chem. 2016;27(4):1050-1057.
[48] SHARMA P C, JAIN A, JAIN S, et al. Ciprofloxacin: review on developments in synthetic, analytical, and medicinal aspects. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2010;25(4):577-589.
[49] ALIDORI S, AKHAVEIN N, THOREK DLJ, et al. Targeted fibrillar nanocarbon RNAi treatment of acute kidney injury. J Urol. 2016;196(4):1313-1314.
[50] GENG Y, DALHAIMER P, CAI S, et al. Shape effects of filaments versus spherical particles in flow and drug delivery. Nat Nanotechnol. 2007; 2(4):249-255.
[51] JIANG D, GE Z, IM HJ, et al. DNA origami nanostructures can exhibit preferential renal uptake and alleviate acute kidney injury. Nat Biomed Eng. 2018;2(11):865-877.
[52] PONNUSWAMY N, BASTINGS MMC, NATHWANI B, et al. Oligolysine-based coating protects DNA nanostructures from low-salt denaturation and nuclease degradation. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15654.
[53] HE J, CHEN H, ZHOU W, et al. Kidney targeted delivery of asiatic acid using a FITC labeled renal tubular-targeting peptide modified PLGA-PEG system. Int J Pharm. 2020;584:119455.
[54] HU JB, KANG XQ, LIANG J, et al. E-selectin-targeted Sialic Acid-PEG-dexamethasone Micelles for enhanced anti-inflammatory efficacy for acute kidney injury. Theranostics. 2017;7(8):2204-2219.
[55] DAEMS N, PENNINCKX S, NELISSEN I, et al. Gold nanoparticles affect the antioxidant status in selected normal human cells. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:4991-5015.
[56] NIIDOME T, YAMAGATA M, OKAMOTO Y, et al. PEG-modified gold nanorods with a stealth character for in vivo applications. J Control Release. 2006;114(3):343-347.
[57] GREF, LüCK, QUELLEC, et al. ‘Stealth’ corona-core nanoparticles surface modified by polyethylene glycol (PEG): influences of the corona (PEG chain length and surface density) and of the core composition on phagocytic uptake and plasma protein adsorption. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2000;18(3-4):301-313.
[58] LI Y, PEI Y, ZHANG X, et al. PEGylated PLGA nanoparticles as protein carriers: synthesis, preparation and biodistribution in rats. J Control Release. 2001;71(2):203-211.
[59] CHERUKURI P, GANNON CJ, LEEUW TK, et al. Mammalian pharmacokinetics of carbon nanotubes using intrinsic near-infrared fluorescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(50):18882-18886.
[60] OLTRA NS, NAIR P, DISCHER DE. From stealthy polymersomes and filomicelles to “self” Peptide-nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng. 2014;5:281-299.
[61] PIAO JG, WANG L, GAO F, et al. Erythrocyte membrane is an alternative coating to polyethylene glycol for prolonging the circulation lifetime of gold nanocages for photothermal therapy. ACS Nano. 2014;8(10):10414-10425.
[62] HU CMJ, ZHANG L, ARYAL S, et al. Erythrocyte membrane-camouflaged polymeric nanoparticles as a biomimetic delivery platform. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011; 108(27):10980-10985.
[63] LUK BT, HU CM J, FANG RH, et al. Interfacial interactions between natural RBC membranes and synthetic polymeric nanoparticles. Nanoscale. 2014;6(5):2730-2737.
[64] SLACK JD, KANKE M, SIMMONS GH, et al. Acute hemodynamic effects and blood pool kinetics of polystyrene microspheres following intravenous administration. J Pharm Sci. 1981;70(6):660-664.
[65] TANG S, PENG C, XU J, et al. Tailoring renal clearance and tumor targeting of ultrasmall metal nanoparticles with particle density. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2016;55(52):16039-16043.
[66] WILLIAMS RM, SHAH J, TIAN HS, et al. Selective nanoparticle targeting of the renal tubules. Hypertension. 2018;71(1):87-94.
[67] BARUA S, MITRAGOTRI S. Challenges associated with penetration of nanoparticles across cell and tissue barriers: a review of current status and future prospects. Nano today. 2014;9(2):223-243.
[68] MATSUURA S, KATSUMI H, SUZUKI H, et al. l-Serine-modified polyamidoamine dendrimer as a highly potent renal targeting drug carrier. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(41):10511-10516.
[69] HAUGER O, DELALANDE C, DEMINIèRE C, et al. Nephrotoxic nephritis and obstructive nephropathy:evaluation with MR imaging enhanced with ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide-preliminary findings in a rat model. Radiology. 2000;217(3):819-826.
[70] SHIRAI T, KOHARA H, TABATA Y. Inflammation imaging by silica nanoparticles with antibodies orientedly immobilized. J Drug Targeting. 2012;20(6):535-543.
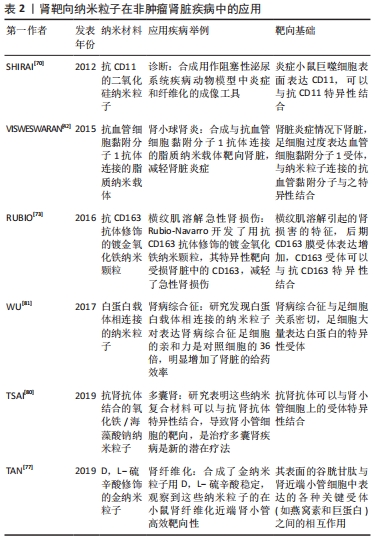
[71] MAROM O, NAKHOUL F, TISCH U, et al. Gold nanoparticle sensors for detecting chronic kidney disease and disease progression. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2012;7(5): 639-650.
[72] HU JB, LI SJ, KANG XQ, et al. CD44-targeted hyaluronic acid-curcumin prodrug protects renal tubular epithelial cell survival from oxidative stress damage. Carbohydr Polym. 2018;193:268-280.
[73] RUBIO-NAVARRO A, CARRIL M, PADRO D, et al. CD163-macrophages are involved in rhabdomyolysis-induced kidney injury and may be detected by MRI with targeted gold-coated iron oxide nanoparticles. Theranostics. 2016;6(6):896-914.
[74] CHEN J, VEMURI C, PALEKAR RU, et al. Antithrombin nanoparticles improve kidney reperfusion and protect kidney function after ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015;308(7):F765-F773.
[75] MANNE NDPK, ARVAPALLI R, NEPAL N, et al. Cerium oxide nanoparticles attenuate acute kidney injury induced by intra-abdominal infection in Sprague-Dawley rats. J Nanobiotechnol. 2015;13:75.
[76] TEEKAMP N, VAN DIJK F, BROESDER A, et al. Polymeric microspheres for the sustained release of a protein-based drug carrier targeting the PDGFβ-receptor in the fibrotic kidney. Int J Pharm. 2017;534(1-2):229-236.
[77] TAN L, LAI X, ZHANG M, et al. A stimuli-responsive drug release nanoplatform for kidney-specific anti-fibrosis treatment. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(4):1554-1564.
[78] QIAO H, SUN M, SU Z, et al. Kidney-specific drug delivery system for renal fibrosis based on coordination-driven assembly of catechol-derived chitosan. Biomaterials. 2014;35(25):7157-7171.
[79] GAO S, HEIN S, DAGNAES-HANSEN F, et al. Megalin-mediated specific uptake of chitosan/siRNA nanoparticles in mouse kidney proximal tubule epithelial cells enables AQP1 gene silencing. Theranostics. 2014;4(10):1039-1051.
[80] TSAI YC, TENG IL, JIANG ST, et al. Safe nanocomposite-mediated efficient delivery of microrna plasmids for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) therapy. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019; 8(5):e1801358.
[81] WU L, CHEN M, MAO H, et al. Albumin-based nanoparticles as methylprednisolone carriers for targeted delivery towards the neonatal Fc receptor in glomerular podocytes. Int J Mol Med. 2017;39(4):851-860.
|