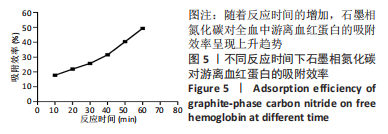
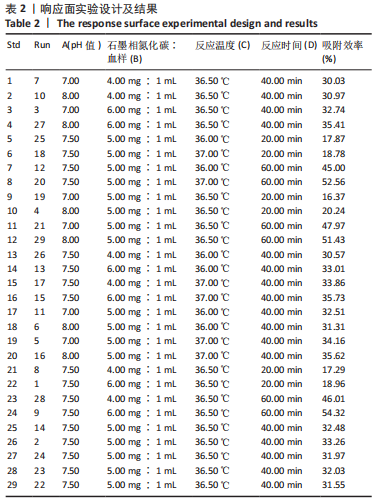
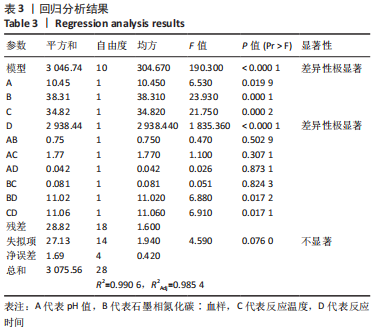
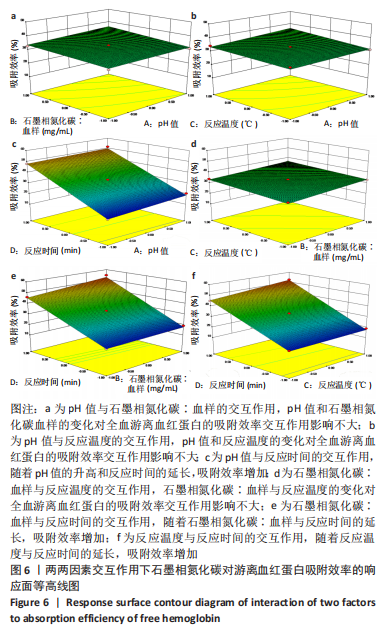
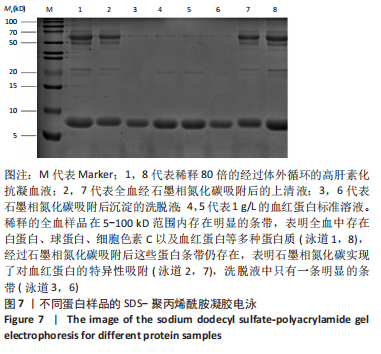
[1] 仇冰梅,王康,张雷,等.胸腹主动脉置换术中股静脉-股动脉转流的体外循环管理[J].医学研究生学报,2022,35(1):79-81.
[2] GOVENDER K, JANI V P, CABRALES P. The Disconnect Between Extracorporeal Circulation and the Microcirculation: A Review. ASAIO J. 2022;68(7):881-889.
[3] 段正伟,刘云霏.常规供心与边缘供心在终末期心脏病心脏移植中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(26):4211-4215.
[4] 高国栋,胡强,胡金晓,等.体外循环冠状动脉搭桥术中不同停跳液灌注方法的心肌保护作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2015,19(7):1112-1116.
[5] BAUDYS M, PAUŠOVá Š, PRAUS P, et al. Graphitic Carbon Nitride for Photocatalytic Air Treatment. Materials (Basel). 2020;13(13):3038.
[6] LIU Y, LIU Y, XU Y, et al. Phenanthroline bridging graphitic carbon nitride framework and Fe (II) ions to promote transfer of ph otogenerated electrons for selective photocatalytic reduction of Nitrophenols. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022;608(Pt 2):2088-2099.
[7] CUI Y, WANG Z, ZHENG J, et al. Fabrication of silver vanadate quantum dots/reduced graphene oxide/graphitic carbon nitride Z-scheme heterostructure modified polyvinylidene fluoride self-cleaning membrane for enhancing photocatalysis and mechanism insight. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022;614: 677-689.
[8] JALILI R, CHENAGHLOU S, KHATAEE A, et al. An Electrochemiluminescence Biosensor for the Detection of Alzheimer’s Tau Protein Based on Gold Nano star Decorated Carbon Nitride Nanosheets. Molecules. 2022;27(2):431.
[9] ALIZADEH T, RAFIEI F, AKHOUNDIAN M. A novel chloride selective potentiometric sensor based on graphitic carbon nitride/silver chloride (g -C3N4/AgCl) composite as the sensing element. Talanta. 2022;237:122895.
[10] KITTE SA, BUSHIRA FA, XU C, et al. Plasmon-Enhanced Nitrogen Vacancy-Rich Carbon Nitride Electrochemiluminescence Aptasensor for Highly Sensitive Detection of miRNA. Anal Chem. 2022;94(2):1406-1414.
[11] LI J, ZHANG K, ZHAO Y, et al. High-Efficiency and Stable Li-CO2 Battery Enabled by Carbon Nanotube/Carbon Nitride Heterostructured Photocathode. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022;61(4):e202114612.
[12] YE C, LIU M. A computational study on the potential application of carbon nitride nanosheets in Na-ion batteries. J Mol Model. 2022;28(2):40.
[13] LIU X, ZHANG H, CAI Z, et al. Fluorescent graphitic carbon nitride with photocatalytic oxidase-like activity for anti-counterfeitin g application. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2022;268:120685.
[14] CUI Y, AN X, ZHANG S, et al. Emerging graphitic carbon nitride-based membranes for water purification. Water Res. 2021;200:117207.
[15] TAO L, ZHANG H, LI G, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of pharmaceuticals by pore-structured graphitic carbon nitride with carbon vacancy in water: Identification of intermediate degradants and effects of active species. Sci Total Environ. 2022;824:153845.
[16] WANG J, LIAN X, CHEN S, et al. Effect of Bi(2)WO(6)/g-C(3)N(4) composite on the combustion and catalytic decomposition of energetic materials: An efficient catalyst with g-C(3)N(4) carrier. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022;610: 842-853.
[17] PATTANAYAK DS, PAL D, MISHRA J, et al. Doped graphitic carbon nitride (g-C(3)N(4)) catalysts for efficient photodegradation of tetracycline antibiotics in aquatic environments. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-19766-y.
[18] TIAN Y, ZHAO D, HUANG X, et al. Extended π-Conjugative Carbon Nitride for Single 1064 nm Laser-Activated Photodynamic/Photothermal Sy nergistic Therapy and Photoacoustic Imaging. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(6):7626-7635.
[19] ZHENG H, ZHAO Z, PHAN JB, et al. Highly Efficient Metal-Free Two-Dimensional Luminescent Melem Nanosheets for Bioimaging. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(2):2145-2151.
[20] ONG WJ, TAN LL, NG YH, et al. Graphitic Carbon Nitride (g-C3N4)-Based Photocatalysts for Artificial Photosynthesis and Environmental Remediation: Are We a Step Closer To Achieving Sustainability? Chem Rev. 2016;116(12):7159-7329.
[21] 张锐.石墨型氮化碳在蛋白质分离纯化中的应用研究[D].沈阳:东北大学,2014.
[22] 陈旭伟,郑旭,王晓峰,等.超高容量氧化石墨烯/碳纳米管气凝胶用于血红蛋白的吸附分离 [J]. 高等学校化学学报,2015,36(8):1498-1504.
[23] 孟媛媛.聚丙烯酸/石墨相氮化碳三维复合水凝胶的制备及其在血红蛋白分离中的应用[D].沈阳:东北大学,2018.
[24] ZHAO X, FAN X, SHAO X, et al. Modifying the physicochemical properties, solubility and foaming capacity of milk proteins by ultrasound-assisted alkaline pH-shifting treatment. Ultrason Sonochem. 2022;88:106089.
[25] 邵冬青,张群,姜舟婷.分子动力学模拟研究温度对蛋白质结构稳定性的影响[J].中国计量大学学报,2022,33(1):44-48+130.
[26] 袁玉琦,张巨源,王莉,等. 影响PVDF膜对蛋白吸附效率的主要因素[J].氨基酸和生物资源,2015,37(3):51-56.
[27] LI J, JIN H, HU Z. Application of Salvage Autologous Blood Transfusion for treating Massive Hemorrhage during Ectopic Pregnancy. Front Surg. 2022; 9:896526.
[28] SCHMIDBAUER SL, SEYFRIED TF. Cell Salvage at the ICU. J Clin Med. 2022; 11(13):3848.
[29] EROL K. Polychelated cryogels: hemoglobin adsorption from human blood. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2017;45(1):31-38.
[30] BAYDEMIR G, ANDAÇ M, PERÇIN I, et al. Molecularly imprinted composite cryogels for hemoglobin depletion from human blood. J Mol Recognit. 2014;27(9):528-536.
[31] ARMUTCU C, ÖZGüR E, ÇORMAN ME, et al. Interface imprinted polymers with well-oriented recognition sites for selective purification of hemoglobin. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021;197:111435.
[32] MOBASHERAT JAJROUD SY, FALAHATI M, ATTAR F, et al. Human hemoglobin adsorption onto colloidal cerium oxide nanoparticles: a new model based on zeta pote ntial and spectroscopy measurements. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2018;36(11):2908-2916.
[33] CHEN Q, WANG MM, ZHANG Y, et al. Selective Adsorption of Hemoglobin in Human Whole Blood with a Nickel Monosubstituted Silicotungstic Acid Hybrid. ACS Omega. 2022;7(26):22633-22638.
[34] LIU Y, WANG Y, YAN M, et al. Selective Removal of Hemoglobin from Blood Using Hierarchical Copper Shells Anchored to Magnetic Nano particles. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:7309481.
[35] LIU J, LIANG Y, LIANG Q, et al. Tunable composites prepared from graphene oxide and zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 for improved sel ective isolation of hemoglobin. Mikrochim Acta. 2018;185(8):361.
[36] WANG J, TAN S, LIANG Q, et al. Selective separation of bovine hemoglobin using magnetic mesoporous rare-earth silicate microspheres. Talanta. 2019; 204:792-801.
[37] WANG XM, HU ZJ, GUO PF, et al. Purification of hemoglobin by adsorption on nitrogen-doped flower-like carbon superstructures. Mikrochim Acta. 2020;187(3):162.
[38] ZHANG X, WU D, SHEN J, et al. Preparation of bottlebrush polymer-modified magnetic graphene as immobilized metal ion affinity adsor bent for purification of hemoglobin from blood samples. Mikrochim Acta. 2020; 187(8):472.
|