中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (16): 2461-2466.doi: 10.12307/2023.134
• 纳米生物材料 nanobiomaterials • 下一篇
负载柳氮磺吡啶缓释纳米粒的制备及体外评价
钟文静1,周子涵1,王浩宇2,李尚勇2,夏玉军1
- 1青岛大学基础医学院特种医学系,山东省青岛市 266000;2青岛大学基础医学院,山东省青岛市 266000
Preparation and in vitro evaluation of sustained-release nanoparticles loaded with sulfasalazine
Zhong Wenjing1, Zhou Zihan1, Wang Haoyu2, Li Shangyong2, Xia Yujun1
- 1Department of Special Medicine, Basic Medical College, Qingdao University, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China; 2Basic Medical College, Qingdao University, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
柳氮磺吡啶:是水杨酸与磺胺吡啶的偶氮化合物,为磺胺类抗菌药,具有抗菌和免疫抑制作用,在肠道内被该处细菌分解为磺胺吡啶与5-氨基水杨酸。缓释系统:是指通过适宜的方法延缓药物在体内的释放、吸收、代谢以及排泄的过程,从而延长药物作用时间或者减轻其毒副作用的给药系统。
背景:柳氮磺吡啶是治疗溃疡性结肠炎的常用药,传统给药方式吸收差、利用度低,且常伴随严重的毒副反应。与传统给药方式相比,基于结肠靶向纳米给药能够保护药物免受不良环境的影响,改善药物的局部吸收和生物利用度。
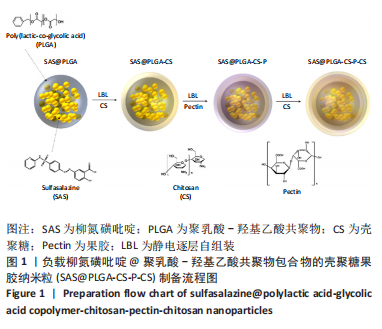
目的:制备柳氮磺吡啶@聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物-壳聚糖-果胶-壳聚糖纳米粒,对其进行表征和体外评价,并在细胞水平验证纳米颗粒用作药物载体的安全性。
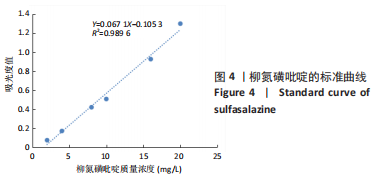
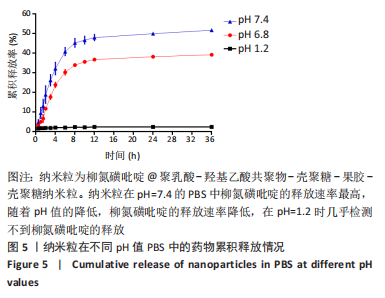
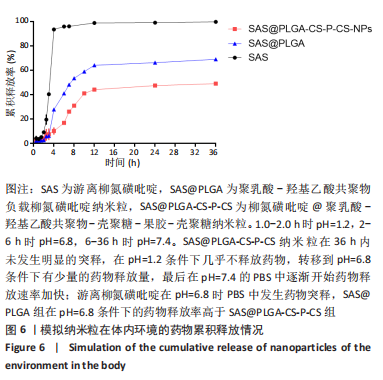
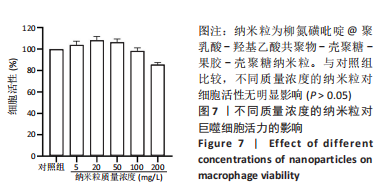
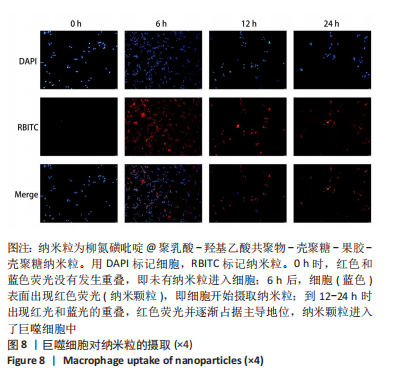
方法:采用O/W乳液法和静电逐层自组装技术制备柳氮磺吡啶@聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物-壳聚糖-果胶-壳聚糖纳米粒,利用透射电镜观察了纳米粒的形态,激光粒度仪检测了纳米粒的电位与粒径,紫外分光光度计法检测其载药率和包封率。将纳米粒溶解于不同pH值(1.2,6.8,7.4)PBS中,检测纳米粒对柳氮磺吡啶的释放情况。将不同质量浓度(10,20,50,100,200 mg/L)的纳米粒溶液与巨噬细胞共培养,48 h后,采用CCK8法检测细胞活性;将20 mg/L的纳米粒溶液与巨噬细胞共培养,24 h后,罗丹明荧光染色细胞摄取纳米粒情况。
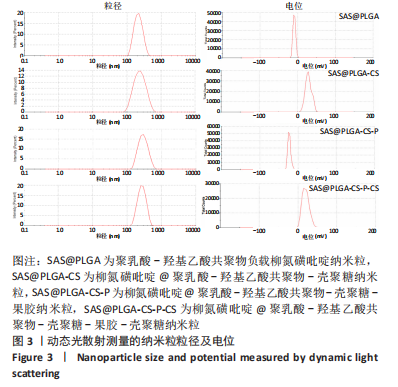
结果与结论:①透射电镜下可见,纳米粒呈椭球形,粒径大小均一;纳米粒粒径为290.9 nm,电位为19.8 mV,分散指数为0.295,单个纳米颗粒具有良好的分散性;纳米粒的包封率为75.68%,载药量为22.24%;②体外药物释放实验显示,在36 h内,随着PBS pH值的升高,纳米粒的释放速率加快,纳米粒在pH=1.2的PBS中几乎不释放柳氮磺吡啶,在pH=7.4的PBS中可以缓慢持续释放柳氮磺吡啶,表明纳米粒具有pH值依赖性和良好的缓释特征;③不同质量浓度的米粒浓度对巨噬细胞的活性未造成明显影响,未表现细胞毒性作用;④细胞摄取实验显示,培养6 h后,细胞开始摄取纳米粒,12-24 h纳米颗粒进入了巨噬细胞;⑤柳氮磺吡啶@聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物-壳聚糖-果胶-壳聚糖纳米粒具有良好的的缓释特性与细胞相容性,能被巨噬细胞摄取且摄取效率高。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7169-8261(钟文静)
中图分类号: