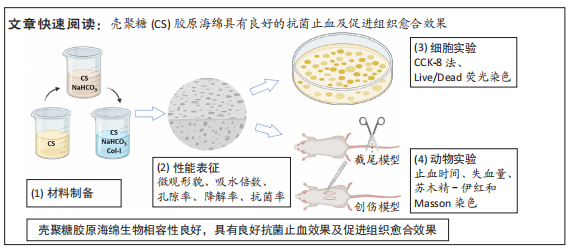
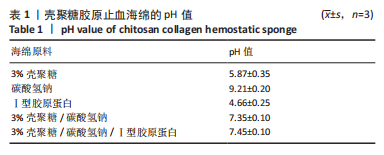
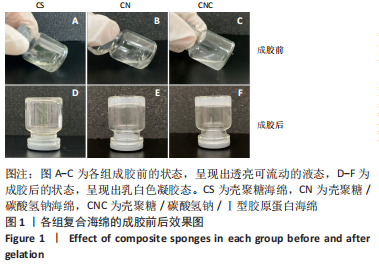
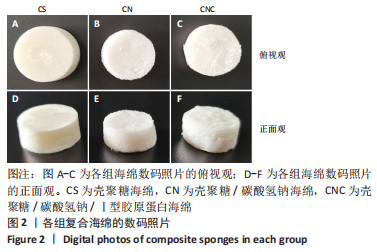
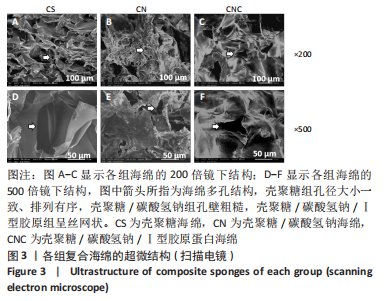
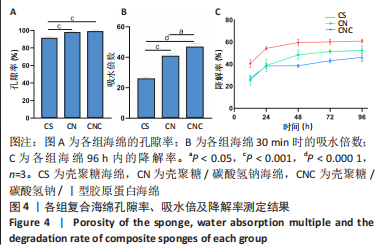
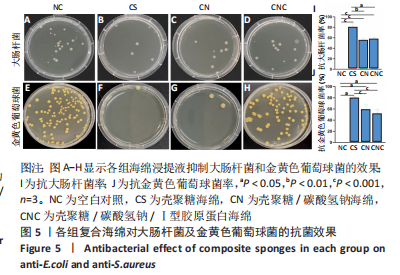
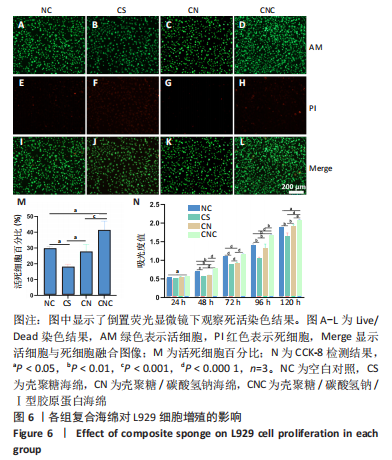
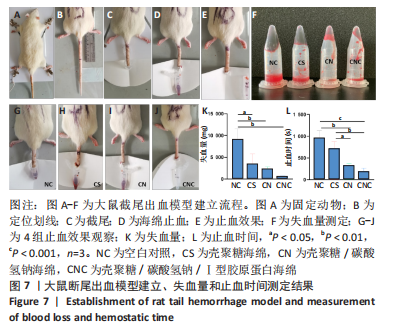
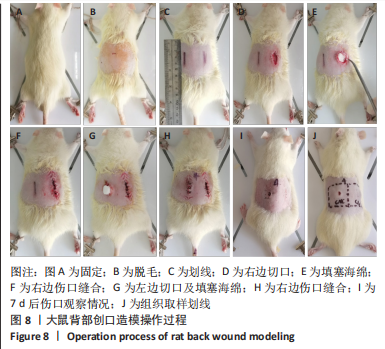
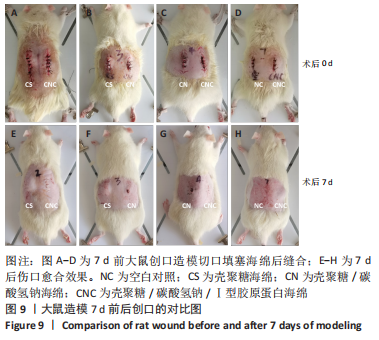
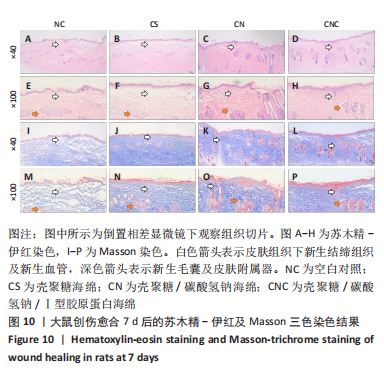
[1] CHENG H, SHI Z, YUE K, et al. Sprayable hydrogel dressing accelerates wound healing with combined reactive oxygen species-scavenging and antibacterial abilities. Acta Biomater. 2021;124:219-232.
[2] KUMBARGERE NAGRAJ S, PRASHANTI E, AGGARWAL H, et al. Interventions for treating post-extraction bleeding. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;3(3):Cd011930.
[3] 王静娟,胡开进,刘平,等.拔牙窝止血类覆盖及充填材料的选择及应用[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2017,10(10):586-589.
[4] YOSHIDA K, KODAMA Y, NAGAI T, et al. Clinico-statistical survey of oral antimicrobial prophylaxis and surgical site infection regarding ordinary tooth extraction and mandibular wisdom tooth extraction in the dental outpatient clinic. J Infect Chemother. 2021;27(2):192-197.
[5] HEMMINGSEN LM, JULIN K, AHSAN L, et al. Chitosomes-in-chitosan hydrogel for acute skin injuries: prevention and infection control. Mar Drugs. 2021;19(5):269.
[6] AGUILAR A, ZEIN N, HARMOUCH E, et al. Application of chitosan in bone and dental engineering. Molecules. 2019;24(16):3009.
[7] NARVAEZ-FLORES JJ, VILAR-PINEDA G, ACOSTA-TORRES LS, et al. Cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory effects of chitosan and hemostatic gelatin in oral cell culture. Acta Odontol Latinoam. 2021;34(2):98-103.
[8] KOU SG, PETERS LM, MUCALO MR. Chitosan: a review of sources and preparation methods. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;169:85-94.
[9] ABDELALLAH NH, GABER Y, ABDELGHANI S, et al. Chitosan and alginate salt as biomaterials are potential natural adjuvants for killed cholera vaccine. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2021;109(12):2462-2470.
[10] GAO X, LIU N, WANG Z, et al. Development and optimization of chitosan nanoparticle-based intranasal vaccine carrier. Molecules. 2021;27(1):204.
[11] CAO S, YANG Y, ZHANG S, et al. Multifunctional dopamine modification of green antibacterial hemostatic sponge. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;127:112227.
[12] HUANG Y, FENG L, ZHANG Y, et al. Hemostasis mechanism and applications of N-alkylated chitosan sponge. Polym Adv Tech. 2017; 28(9):1107-1114.
[13] VERLEE A, MINCKE S, STEVENS CV. Recent developments in antibacterial and antifungal chitosan and its derivatives. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;164:268-283.
[14] ISLAM S, ARNOLD L, PADHYE R. Comparison and characterisation of regenerated chitosan from 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride and chitosan from crab shells. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:874316.
[15] ABD EL-HACK ME, EL-SAADONY MT, SHAFI ME, et al. Antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of chitosan and its derivatives and their applications: a review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;164:2726-2744.
[16] WANG W, MENG Q, LI Q, et al. Chitosan derivatives and their application in biomedicine. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(2):487.
[17] HALL CW, MAH TF. Molecular mechanisms of biofilm-based antibiotic resistance and tolerance in pathogenic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2017;41(3):276-301.
[18] MALETTE WG, QUIGLEY HJ, GAINES RD, et al. Chitosan: a new hemostatic. Ann Thorac Surg. 1983;36(1):55-58.
[19] KONG M, CHEN XG, XING K, et al. Antimicrobial properties of chitosan and mode of action: a state of the art review. Int J Food Microbiol. 2010;144(1):51-63.
[20] LU B, WANG T, LI Z, et al. Healing of skin wounds with a chitosan-gelatin sponge loaded with tannins and platelet-rich plasma. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;82:884-891.
[21] 刘海燕,胡阳,武秀萍,等.壳聚糖基多糖材料防治口腔疾病的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(4):631-636.
[22] CHOWDHURY SR, MH BUSRA MF, LOKANATHAN Y, et al. Collagen type I: a versatile biomaterial. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1077:389-414.
[23] FERREIRA AM, GENTILE P, CHIONO V, et al. Collagen for bone tissue regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(9):3191-3200.
[24] RITTIé L. Type I collagen purification from rat tail tendons. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1627:287-308.
[25] NEVE A, CANTATORE FP, MARUOTTI N, et al. Extracellular matrix modulates angiogenesis in physiological and pathological conditions. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:756078.
[26] SONG WK, LIU D, SUN LL, et al. Physicochemical and biocompatibility properties of type I collagen from the skin of nile tilapia (oreochromis niloticus) for biomedical applications. Mar Drugs. 2019;17(3):137.
[27] ZHU Y, LIU W, CHEN S, et al. Collagen type I enhances cell growth and insulin biosynthesis in rat pancreatic cells. J Mol Endocrinol. 2021; 67(3):135-148.
[28] LUO J, MENG Y, ZHENG L, et al. Fabrication and characterization of Chinese giant salamander skin composite collagen sponge as a high-strength rapid hemostatic material. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2018; 29(16):1933-1948.
[29] 谢海霞,沈先荣,葛卫红,等.胶原蛋白-壳聚糖-海藻酸盐复合敷料的促愈合作用. 药物生物技术,2016,23(6):495-502.
[30] GHODBANE SA, DUNN MG. Physical and mechanical properties of cross-linked type I collagen scaffolds derived from bovine, porcine, and ovine tendons. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(11):2685-2692.
[31] ALVEN S, ADERIBIGBE BA. Chitosan and cellulose-based hydrogels for wound management. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(24):9656.
[32] GAUTAM S, CHOU CF, DINDA AK, et al. Surface modification of nanofibrous polycaprolactone/gelatin composite scaffold by collagen type I grafting for skin tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;34:402-409.
[33] CHEN X, ZHANG M, WANG X, et al. Peptide-modified chitosan hydrogels promote skin wound healing by enhancing wound angiogenesis and inhibiting inflammation. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(5):2352-2362.
[34] LI J, WANG H, ZHOU H, et al. Fabrication of highly interconnected poly(ε-caprolactone)/cellulose nanofiber composite foams by microcellular foaming and leaching processes. ACS Omega. 2021;6(35): 22672-22680.
[35] JIANG X, WANG Y, FAN D, et al. A novel human-like collagen hemostatic sponge with uniform morphology, good biodegradability and biocompatibility. J Biomater Appl. 2017;31(8):1099-1107.
[36] MATICA MA, AACHMANN FL, TøNDERVIK A, et al. Chitosan as a wound dressing starting material: antimicrobial properties and mode of action. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(23):5889.
[37] HU Z, ZHANG DY, LU ST, et al. Chitosan-based composite materials for prospective hemostatic applications. Mar Drugs. 2018;16(8):273.
[38] MOUSAVI S, KHOSHFETRAT AB, KHATAMI N, et al. Comparative study of collagen and gelatin in chitosan-based hydrogels for effective wound dressing: physical properties and fibroblastic cell behavior. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;518(4):625-631.
[39] GEDAR TOTUK ÖM, GüZEL ŞE, EKICI H, et al. Effects of Algan Hemostatic Agent on bleeding time in a rat tail hemorrhage model. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2020;26(6):853-858.
[40] YUAN J, HOU Q, CHEN D, et al. Chitosan/LiCl composite scaffolds promote skin regeneration in full-thickness loss. Sci China Life Sci. 2020;63(4):552-562.
[41] ARWEILER NB, NETUSCHIL L. The oral microbiota. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;902:45-60.
[42] WANG X, GUO J, ZHANG Q, et al. Gelatin sponge functionalized with gold/silver clusters for antibacterial application. Nanotechnology. 2020;31(13):134004.
[43] HWANG SJ, HA GH, SEO WY, et al. Human collagen alpha-2 type I stimulates collagen synthesis, wound healing, and elastin production in normal human dermal fibroblasts (HDFs). BMB Rep. 2020;53(10): 539-544.
[44] ZHANG W, ZHAO L, GAO C, et al. Highly resilient, biocompatible, and antibacterial carbon nanotube/hydroxybutyl chitosan sponge dressing for rapid and effective hemostasis. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(47): 9754-9763.
[45] FAN X, LI M, YANG Q, et al. Morphology-controllable cellulose/chitosan sponge for deep wound hemostasis with surfactant and pore-foaming agent. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;118:111408.
[46] GADKARI RR, SUWALKA S, YOGI MR, et al. Green synthesis of chitosan-cinnamaldehyde cross-linked nanoparticles: characterization and antibacterial activity. Carbohydr Polym. 2019;226:115298.
[47] RICO-LLANOS GA, BORREGO-GONZáLEZ S, MONCAYO-DONOSO M, et al. Collagen type I biomaterials as scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Polymers (Basel). 2021;13(4):599.
[48] SEIDI F, KHODADADI YAZDI M, JOUYANDEH M, et al. Chitosan-based blends for biomedical applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;183: 1818-1850.
[49] 汤宋佳.壳聚糖—胶原海绵敷料的制备及其对伤口愈合的作用研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2016.
[50] BARRS RW, JIA J, SILVER SE, et al. Biomaterials for bioprinting microvasculature. Chem Rev. 2020;120(19):10887-10949.
[51] 柯林楠,冯晓明,王春仁.医用敷料研究的现状与进展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(3):521-524.
[52] JAYAKUMAR R, PRABAHARAN M, SUDHEESH KUMAR PT, et al. Biomaterials based on chitin and chitosan in wound dressing applications. Biotechnol Adv. 2011;29(3):322-337.
[53] VARMA S, ORGEL JP, SCHIEBER JD. Nanomechanics of type I collagen. Biophys J. 2016;111(1):50-56.
[54] CHATTOPADHYAY S, RAINES RT. Review collagen-based biomaterials for wound healing. Biopolymers. 2014;101(8):821-833.
[55] SHARIATINIA Z. Carboxymethyl chitosan: properties and biomedical applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;120(Pt B):1406-1419.
[56] SAHANA TG, REKHA PD. Biopolymers: applications in wound healing and skin tissue engineering. Mol Biol Rep. 2018;45(6):2857-2867.
[57] SHI C, ZHU Y, RAN X, et al. Therapeutic potential of chitosan and its derivatives in regenerative medicine. J Surg Res. 2006;133(2):185-192.
[58] ZHANG MX, ZHAO WY, FANG QQ, et al. Effects of chitosan-collagen dressing on wound healing in vitro and in vivo assays. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2021;19:2280800021989698.
[59] LIU L, TANG X, WANG Y, et al. Smart gelation of chitosan solution in the presence of NaHCO3 for injectable drug delivery system. Int J Pharm. 2011;414(1-2):6-15.
[60] GUYOT C, CERRUTI M, LEROUGE S. Injectable, strong and bioadhesive catechol-chitosan hydrogels physically crosslinked using sodium bicarbonate. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;118:111529. |