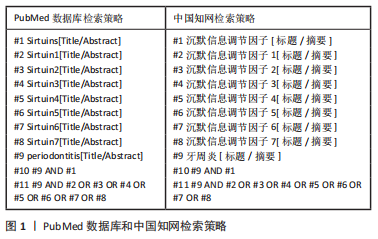
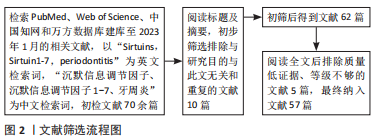
[1] HAJISHENGALLIS G. Immunomicrobial pathogenesis of periodontitis: keystones, pathobionts, and host response. Trends Immunol. 2014;35(1):3-11.
[2] SANZ M, MARCO DEL CASTILLO A, JEPSEN S, et al. Periodontitis and cardiovascular diseases: Consensus report. J Clin Periodontol. 2020;47(3):268-288.
[3] SALHI L, RENERS M. Update on the Bidirectional Link Between Diabetes and Periodontitis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1373:231-240.
[4] KANEKO C, KOBAYASHI T, ITO S, et al. Association among periodontitis severity, anti-agalactosyl immunoglobulin G titer, and the disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis. J Periodontal Res. 2021;56(4):702-709.
[5] SADRAMELI M, BATHINI P, ALBERI L. Linking mechanisms of periodontitis to Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Opin Neurol. 2020;33(2):230-238.
[6] BOBETSIS YA, GRAZIANI F, GÜRSOY M, et al. Periodontal disease and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Periodontol 2000. 2020;83(1):154-174.
[7] 王兴.第四次全国口腔健康流行病学调查报告[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2018
[8] BONKOWSKI MS, SINCLAIR DA. Slowing ageing by design: the rise of NAD+ and sirtuin-activating compounds. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016;17(11):679-690.
[9] PALOMER X, ROMÁN-AZCONA MS, PIZARRO-DELGADO J, et al. SIRT3-mediated inhibition of FOS through histone H3 deacetylation prevents cardiac fibrosis and inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(1):14.
[10] LUNAR SILVA I, CASCALES E. Molecular Strategies Underlying Porphyromonas gingivalis Virulence. J Mol Biol. 2021;433(7):166836.
[11] WADDINGTON RJ, MOSELEY R, EMBERY G. Reactive oxygen species: a potential role in the pathogenesis of periodontal diseases. Oral Dis. 2000; 6(3):138-151.
[12] SCZEPANIK FSC, GROSSI ML, CASATI M, et al. Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease of oxidative stress: We should treat it that way. Periodontol 2000. 2020;84(1):45-68.
[13] SINGH CK, CHHABRA G, NDIAYE MA, et al. The Role of Sirtuins in Antioxidant and Redox Signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018;28(8):643-661.
[14] PARK S, SHIN J, BAE J, et al. SIRT1 Alleviates LPS-Induced IL-1β Production by Suppressing NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and ROS Production in Trophoblasts. Cells. 2020;9(3):728.
[15] YE Q, XU H, LIU S, et al. Apoptotic extracellular vesicles alleviate Pg-LPS induced inflammatory responses of macrophages via AMPK/SIRT1/NF-κB pathway and inhibit osteoclast formation. J Periodontol. 2022;93(11): 1738-1751.
[16] 丁旭. Sirt3诱导的自噬在大鼠牙周炎相关肾损伤中的作用研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2022.
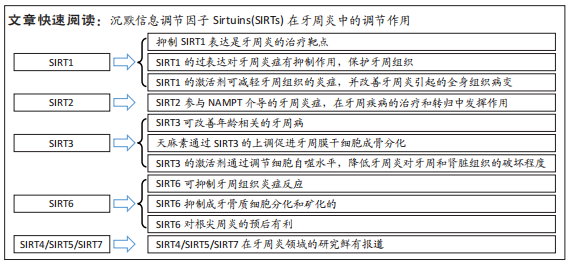
[17] 周丰,陈野,陈晨,等.沉默信息调节因子1调控牙周炎发生发展的机制[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2021,48(3):341-346.
[18] CARIBÉ PMV, VILLAR CC, ROMITO GA, et al. Prospective, case-controlled study evaluating serum concentration of sirtuin-1 and mannose-binding lectin in patients with and without periodontal and coronary artery disease. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2020;11:2040622320919621.
[19] CARIBÉ PMV, VILLAR CC, ROMITO GA, et al. Influence of the treatment of periodontal disease in serum concentration of sirtuin 1 and mannose-binding lectin. J Periodontol. 2020;91(7):900-905.
[20] TAMAKI N, CRISTINA ORIHUELA-CAMPOS R, INAGAKI Y, et al. Resveratrol improves oxidative stress and prevents the progression of periodontitis via the activation of the Sirt1/AMPK and the Nrf2/antioxidant defense pathways in a rat periodontitis model. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014;75:222-229.
[21] CORRÊA MG, ABSY S, TENENBAUM H, et al. Resveratrol attenuates oxidative stress during experimental periodontitis in rats exposed to cigarette smoke inhalation. J Periodontal Res. 2019;54(3):225-232.
[22] CIRANO FR, MOLEZ AM, RIBEIRO FV, et al. Resveratrol and insulin association reduced alveolar bone loss and produced an antioxidant effect in diabetic rats. J Periodontol. 2021;92(5):748-759.
[23] LI X, LIU XC, DING X, et al. Resveratrol protects renal damages induced by periodontitis via preventing mitochondrial dysfunction in rats [published online ahead of print, 2022 Feb 10]. Oral Dis. 2022;10.1111/odi.14148.
[24] 李鑫,丁旭,刘笑梦,等.沉默信息调节因子1对慢性牙周炎模型大鼠肾损伤的影响[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2022,48(5):1200-1208.
[25] PARK YD, KIM YS, JUNG YM, et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide regulates interleukin (IL)-17 and IL-23 expression via SIRT1 modulation in human periodontal ligament cells. Cytokine. 2012; 60(1):284-293.
[26] PARK GJ, KIM YS, KANG KL, et al. Effects of sirtuin 1 activation on nicotine and lipopolysaccharide-induced cytotoxicity and inflammatory cytokine production in human gingival fibroblasts. J Periodontal Res. 2013;48(4): 483-492.
[27] LI K, LV G, PAN L. Sirt1 alleviates LPS induced inflammation of periodontal ligament fibroblasts via downregulation of TLR4. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018; 119:249-254.
[28] INTINI G, KATSURAGI Y, KIRKWOOD KL, et al. Alveolar bone loss: mechanisms, potential therapeutic targets, and interventions. Adv Dent Res. 2014;26(1):38-46.
[29] LACEY DL, TIMMS E, TAN HL, et al. Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell. 1998;93(2):165-176.
[30] WANG H, BLOOM O, ZHANG M, et al. HMG-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice. Science. 1999;285(5425):248-251.
[31] TANIGUCHI N, KAWAHARA K, YONE K, et al. High mobility group box chromosomal protein 1 plays a role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis as a novel cytokine. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(4):971-981.
[32] MORIMOTO Y, KAWAHARA KI, TANCHAROEN S, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulates gingival epithelial cells to release high mobility-group box 1. J Periodontal Res. 2008;43(1):76-83.
[33] YAMASHIRO K, IDEGUCHI H, AOYAGI H, et al. High Mobility Group Box 1 Expression in Oral Inflammation and Regeneration. Front Immunol. 2020; 11:1461.
[34] KIM YS, LEE YM, PARK JS, et al. SIRT1 modulates high-mobility group box 1-induced osteoclastogenic cytokines in human periodontal ligament cells. J Cell Biochem. 2010;111(5):1310-1320.
[35] 王亚敏,张瑞敏.基质金属蛋白酶作为牙周炎调节因子的研究进展[J].口腔医学,2019,39(3):271-274.
[36] QU L, YU Y, QIU L, et al. Sirtuin 1 regulates matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression induced by Porphyromonas endodontalis lipopolysaccharide via targeting nuclear factor-κB in osteoblasts. J Oral Microbiol. 2017;9(1):1317578.
[37] RIAHI RAD Z, RIAHI RAD Z, GOUDARZI H, et al. MicroRNAs in the interaction between host-bacterial pathogens: A new perspective. J Cell Physiol. 2021; 236(9):6249-6270.
[38] Zheng M, Guo J. NICOTINAMIDE-INDUCED SILENCING OF SIRT1 BY MIR-22-3P INCREASES periodontal ligament stem cell proliferation and differentiation. Cell Biol Int. 2020;44(3):764-772.
[39] ZHENG Y, DONG C, YANG J, et al. Exosomal microRNA-155-5p from PDLSCs regulated Th17/Treg balance by targeting sirtuin-1 in chronic periodontitis. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(11):20662-20674.
[40] LEE YM, SHIN SI, SHIN KS, et al. The role of sirtuin 1 in osteoblastic differentiation in human periodontal ligament cells. J Periodontal Res. 2011;46(6):712-721.
[41] XU Y, WANG X, LIU W, et al. Thrombin-activated platelet-rich plasma enhances osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells by activating SIRT1-mediated autophagy. Eur J Med Res. 2021;26(1):105.
[42] AUDRITO V, MESSANA VG, DEAGLIO S. NAMPT and NAPRT: Two Metabolic Enzymes With Key Roles in Inflammation. Front Oncol. 2020;10:358.
[43] PARK KH, KIM DK, HUH YH, et al. NAMPT enzyme activity regulates catabolic gene expression in gingival fibroblasts during periodontitis. Exp Mol Med. 2017;49(8):e368.
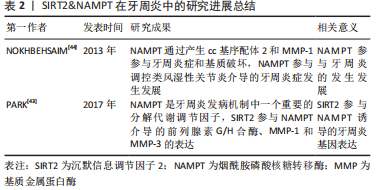
[44] NOKHBEHSAIM M, EICK S, NOGUEIRA AV, et al. Stimulation of MMP-1 and CCL2 by NAMPT in PDL cells. Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:437123.
[45] DAI SH, CHEN T, LI X, et al. Sirt3 confers protection against neuronal ischemia by inducing autophagy: Involvement of the AMPK-mTOR pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017;108:345-353.
[46] YU W, GAO B, LI N, et al. Sirt3 deficiency exacerbates diabetic cardiac dysfunction: Role of Foxo3A-Parkin-mediated mitophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017;1863(8):1973-1983.
[47] PI H, XU S, REITER RJ, et al. SIRT3-SOD2-mROS-dependent autophagy in cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity and salvage by melatonin. Autophagy. 2015;11(7):1037-1051.
[48] GREABU M, GIAMPIERI F, IMRE MM, et al. Autophagy, One of the Main Steps in Periodontitis Pathogenesis and Evolution. Molecules. 2020;25(18):4338.
[49] HE S, ZHOU Q, LUO B, et al. Chloroquine and 3-Methyladenine Attenuates Periodontal Inflammation and Bone Loss in Experimental Periodontitis. Inflammation. 2020;43(1):220-230.
[50] DING X, HOU Y, LIU X, et al. The role of Sirt3-induced autophagy in renal structural damage caused by periodontitis in rats. J Periodontal Res. 2023; 58(1):97-108.
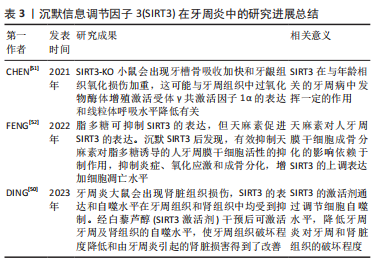
[51] CHEN J, ZHANG Y, GAO J, et al. Sirtuin 3 deficiency exacerbates age-related periodontal disease. J Periodontal Res. 2021;56(6):1163-1173.
[52] FENG Q. Gastrodin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and oxidative stress, and promotes the osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells through enhancing sirtuin3 expression. Exp Ther Med. 2022;23(4):296.
[53] LI C, XIAO F, WEN Y, et al. Krüppel-like factor 5 -mediated Sirtuin6 promotes osteogenic differentiation and inhibits inflammatory injury of lipopolysaccharide-induced periodontal membrane stem cells by inhibiting nuclear factor kappa-B pathway. Bioengineered. 2022;13(3):6966-6977.
[54] LI B, XIN Z, GAO S, et al. SIRT6-regulated macrophage efferocytosis epigenetically controls inflammation resolution of diabetic periodontitis. Theranostics. 2023;13(1):231-249.
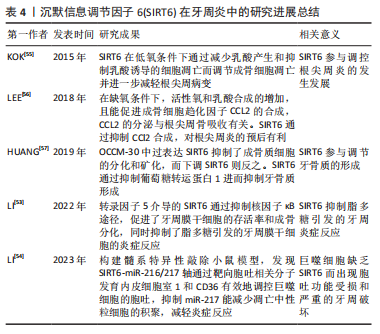
[55] KOK SH, HOU KL, HONG CY, et al. Sirtuin 6 Modulates Hypoxia-induced Apoptosis in Osteoblasts via Inhibition of Glycolysis: Implication for Pathogenesis of Periapical Lesions. J Endod. 2015;41(10):1631-1637.
[56] LEE YL, LIN SK, HOU KL, et al. Sirtuin 6 attenuates periapical lesion propagation by modulating hypoxia-induced chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 production in osteoblasts. Int Endod J. 2018;51 Suppl 2:e74-e86.
[57] HUANG L, SUN H, SONG F, et al. SIRT6 overexpression inhibits cementogenesis by suppressing glucose transporter 1. J Cell Physiol. 2019; 234(4):4005-4014. |