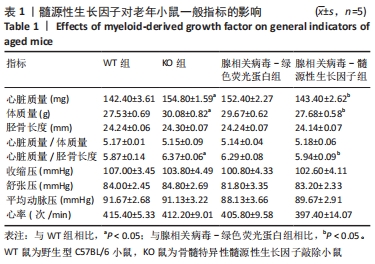
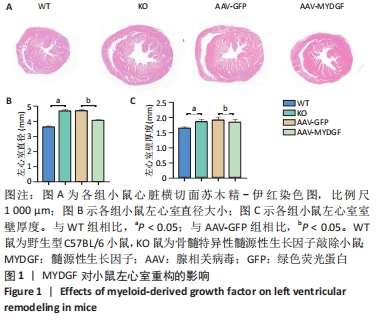
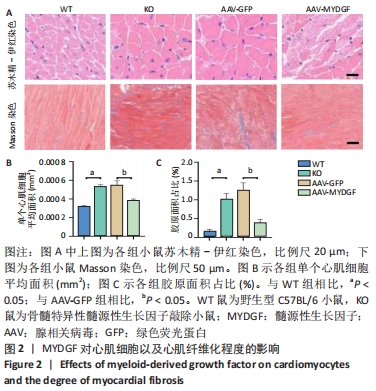
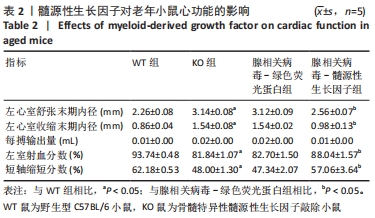
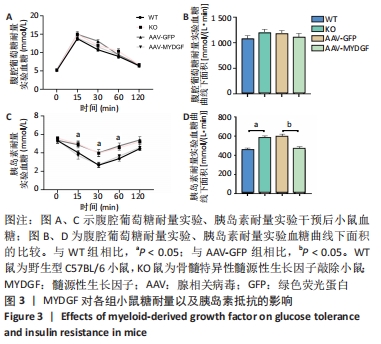
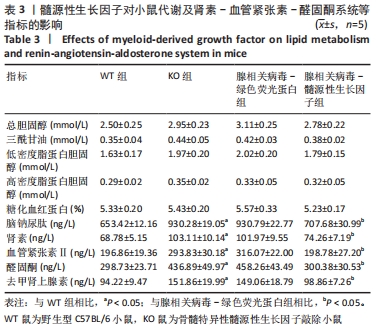
[1] ROTH GA, FOROUZANFAR MH, MORAN AE, et al. Demographic and epidemiologic drivers of global cardiovascular mortality. New Eng J Med. 2015;372(14):1333-1341.
[2] OBAS V, VASAN R. The aging heart. Clin Sci. 2018;132(13):1367-1382.
[3] 李嘉欣,钱欣,赵俊捷,等.衰老对心脏结构和功能的影响与机制的研究[J].心脏杂志,2020,32(2):88-90+103.
[4] STEENMAN M, LANDE G. Cardiac aging and heart disease in humans. Biophys Rev. 2017;9(2):131.
[5] LOFFREDO F, STEINHAUSER M, JAY S, et al. Growth differentiation factor 11 is a circulating factor that reverses age-related cardiac hypertrophy. Cell. 2013;153(4):828-839.
[6] 胡盛寿, 杨跃进, 郑哲,等.《中国心血管病报告2018》概要[J]. 中国循环杂志,2019,34(3):209-220.
[7] 陶丽婵, 贾方. 运动训练对心脏衰老的保护机制[J]. 上海大学学报:自然科学版,2017,23(6):828-834.
[8] NO MH, HEO JW, YOO SZ, et al. Effects of aging and exercise training on mitochondrial function and apoptosis in the rat heart. Eur J Physiol. 2020; 472(2):179-193.
[9] 宋亚男,王烙佩,郑杰,等. 竹节参总皂苷通过调节TGF-β1/Smad3通路改善衰老大鼠心肌纤维化的作用研究[J]. 中国中药杂志,2018,43(22): 155-160.
[10] 庞溢媛,秦雪梅,杜冠华,等. 基于衰老假说的黄芩黄酮药理作用及机制研究进展[J]. 中草药,2019,50(13):3207-3216.
[11] CHANG WT, FISCH S, DANGWAL S, et al. Angiotensin II blockers improve cardiac coronary flow under hemodynamic pressure overload. Hypertens Res. 2021;44(7):803-812.
[12] MA Y, YUAN J, HU J, et al. ACE inhibitor suppresses cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction by regulating dendritic cells and AT2 receptor-mediated mechanism in mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;114:108660.
[13] YIN H, LI P, HU F, et al. IL-33 attenuates cardiac remodeling following myocardial infarction via inhibition of the p38 MAPK and NF-κB pathways. Mol Med Rep. 2014;9(5):1834-1838.
[14] KORF-KLINGEBIEL M, REBOLL MR, KLEDE S, et al. Myeloid-derived growth factor (C19orf10) mediates cardiac repair following myocardial infarction. Nat Med. 2015;21(2):140-149.
[15] WANG Y, LI Y, FENG J, et al. Mydgf promotes Cardiomyocyte proliferation and Neonatal Heart regeneration. Theranostics. 2020;10(20):9100-9112.
[16] WANG L, LI Y, GUO B, et al. Myeloid-Derived Growth Factor Promotes Intestinal Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Production in Male Mice With Type 2 Diabetes. Endocrinology. 2020;161(2):bqaa003.
[17] 孟碧莹, 向光大, 丁燕,等. 髓源性生长因子改善载脂蛋白E基因敲除小鼠动脉粥样硬化作用的研究[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志,2020,12(8):624-630.
[18] KOLIAKI C, LIATIS S, KOKKINOS A. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: revisiting an old relationship. Metabolism. 2019;92:98-107.
[19] 王清霞, 张光明. 肥胖与心血管疾病研究进展[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志, 2020,29(20):2277-2280.
[20] 杨宗璐,柯亭羽.糖尿病并发心血管疾病的研究进展[J].中国老年保健医学,2021,19(1):92-94,98.
[21] 尹庆磊,谢运,沈艳,等. 烟酰胺核苷酸转氢酶基因突变对C57BL/6小鼠糖代谢稳态的影响[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志,2017,33(8):673-679.
[22] 赵田,汤雅迪,赵一楠,等. 肥胖及限食对胰岛素分泌调节异常的影响[J]. 中国比较医学杂志,2019,29(10):3-10.
[23] 张晓圆,郭成成,玉应香,等. 高脂饲料诱导肥胖胰岛素抵抗大鼠模型的建立[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版),2020,52(3):557-563.
[24] 赵剑华,胡春阳,陈林庆. 大鼠左心室肥厚模型研究概况[J]. 医学信息, 2006,19(11):2055-2057.
[25] 祝旭东,李菁媛,苏敬阳,等. 异丙肾上腺素诱导小鼠心肌肥厚模型的方法优化[J]. 解剖科学进展,2018,24(3):53-55.
[26] SUTTON MG, SHARPE N. Left Ventricular Remodeling After Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology and Therapy. Circulation. 2000;101(25):2981-2988.
[27] 杨晓利,瞿惠燕,戎靖枫,等.心肌纤维化发病机制的研究进展[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2020,18(14):2255-2258.
[28] TRIAL J, CIESLIK KA. Changes in cardiac resident fibroblast physiology and phenotype in aging. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018;315(4):H745-H755.
[29] 主有峰,韦建瑞. B型钠尿肽的临床意义及研究进展[J]. 国际医药卫生导报,2010,16(5):631-635.
[30] 陶以嘉,李春庆,金伟东,等. 血浆B型利钠肽(BNP)在心功能不全中的诊断和治疗效果中的应用[J]. 中国微循环,2005,9(6):433-435.
[31] MESQUITA T, RUI ZM, COUTO GD, et al. Mechanisms of atrial fibrillation in aged rats with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction-ScienceDirect. Heart Rhythm. 2020;17(6):1025-1033.
[32] YY A, KN A, MDA B, et al. Alteration of Cardiac Performance and Serum B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Level in Healthy Aging. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019; 74(14):1789-1800.
[33] OTANI K, HIGA Y, KITANO T, et al. Prediction of cardiac events using fully automated GLS and BNP titers in patients with known or suspected heart failure. PLoS ONE. 2020;15(6):e0234294.
[34] WARNER HR, HODES RJ, POCINKI K. What Does Cell Death Have To Do with Aging? J Am Geriatr Soc. 1997;45(9):1140-1146.
[35] 杨丹,樊迪,杨政,等. STAT3与心血管疾病的研究进展[J]. 中华心血管病杂志,2020,48(7):616-620.
[36] CUSPIDI C, RESCALDANI M, SALA C, et al. Left-ventricular hypertrophy and obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of echocardiographic studies. J Hypertens. 2014;32(1):16-25.
[37] 曾惠娴, 孙嘉. 脂肪肾素-血管紧张素-醛固酮系统与肥胖及其相关疾病[J]. 国际内分泌代谢杂志,2013,33(5):329-331.
[38] AMES MK, ATKINS CE, PITT B. Erratum for The renin‐angiotensin‐aldosterone system and its suppression. J Vet Intern Med. 2019;33(5):2551.
[39] Kaye D. Sympathetic neuronal regulation of the heart in aging and heart failure. Cardiovasc Res. 2005;66(2):256-264.
[40] FINCK BN. The role of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha pathway in pathological remodeling of the diabetic heart. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2004;7(4):391-396.
[41] UNGER RH. Diseases of liporegulation: new perspective on obesity and related disorders. Faseb J. 2001;15(2):312-321.
[42] FANG ZY, PRINS JB, MARWICK TH. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: evidence, mechanisms, and therapeutic implications. Endocr Rev. 2004;25(4):543-567.
[43] 宋璐璐,萧建中.交感神经激活与2型糖尿病及心血管损害[J].国际内分泌代谢杂志,2010,30(2):73-75.
[44] 段菊花,谢志泉.代谢综合征交感神经系统兴奋性增高的机制[J].临床心血管病杂志,2008,24(8):562-564.
[45] YUAN Z, TSOU YH, ZHANG XQ, et al. Injectable Citrate-Based Hydrogel as an Angiogenic Biomaterial Improves Cardiac Repair after Myocardial Infarction. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(42):38429-38439.
|