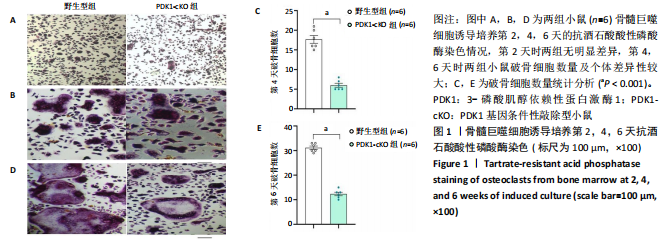
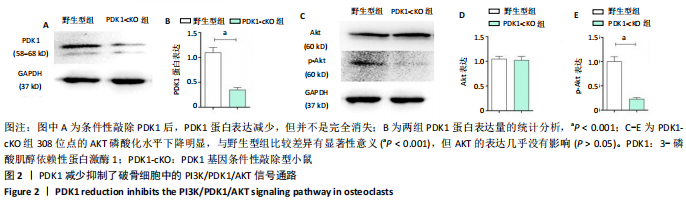
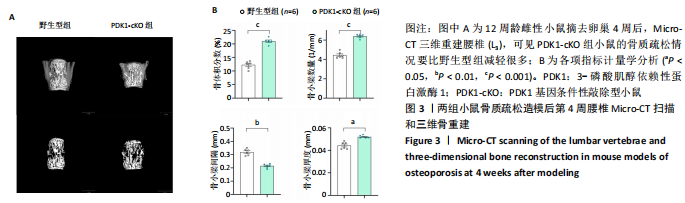
[1] ASPRAY TJ, HILL TR. Osteoporosis and the Ageing Skeleton. Subcell Biochem. 2019;91:453-476.
[2] SZEKANECZ Z, RATERMAN HG, PETHŐ Z, et al. Common mechanisms and holistic care in atherosclerosis and osteoporosis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):15.
[3] HONGO T, KOTAKE K, MURAMATSU H, et al. Loss of bone mineral density following sepsis using Hounsfield units by computed tomography. Acute Med Surg. 2019;6(2):173-179.
[4] MUKHERJEE K, CHATTOPADHYAY N. Pharmacological inhibition of cathepsin K: A promising novel approach for postmenopausal osteoporosis therapy. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016;117:10-19.
[5] ANAGNOSTIS P, SIOLOS P, GKEKAS NK, et al. Association between age at menopause and fracture risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocrine. 2019;63(2):213-224.
[6] KERSCHAN-SCHINDL K. Prevention and rehabilitation of osteoporosis. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2016;166(1-2):22-27.
[7] FÉRON JM, MAUPRIVEZ R. Fracture repair: general aspects and influence of osteoporosis and anti-osteoporosis treatment. Injury. 2016;47 Suppl 1:S10-14.
[8] ABU-AMER Y, DARWECH I, CLOHISY JC. Aseptic loosening of total joint replacements: mechanisms underlying osteolysis and potential therapies. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S6.
[9] LI H, WANG J, SUN Q, et al. Jatrorrhizine Hydrochloride Suppresses RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis and Protects against Wear Particle-Induced Osteolysis. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(11):3698.
[10] YANG XW, WANG XS, CHENG FB, et al. Elevated CCL2/MCP-1 Levels are Related to Disease Severity in Postmenopausal Osteoporotic Patients. Clin Lab. 2016; 62(11):2173-2181.
[11] 周倚墨,张建宁,单中书.补骨脂提取物干预骨质疏松模型大鼠骨密度及骨生物力学的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(2):165-170.
[12] 刘慧,陈慧鸿,廖红兵.破骨细胞衍生的偶联因子鞘氨醇-1-磷酸及血小板衍生生长因子BB对成骨细胞的调节作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2019, 23(23):3739-3745.
[13] LI S, LIU Q, WU D, et al. PKC-δ deficiency in B cells displays osteopenia accompanied with upregulation of RANKL expression and osteoclast-osteoblast uncoupling. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(9):762.
[14] CHEN X, WANG Z, DUAN N, et al. Osteoblast-osteoclast interactions. Connect Tissue Res. 2018;59(2):99-107.
[15] KIKUTA J, ISHII M. Bone Imaging: Osteoclast and Osteoblast Dynamics. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1763:1-9.
[16] FLORENCIO-SILVA R, SASSO GR, SASSO-CERRI E, et al. Biology of Bone Tissue: Structure, Function, and Factors That Influence Bone Cells. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:421746.
[17] 高云兵,岑忠喜,黄建华,等.BX-912对脂多糖诱导小鼠颅骨骨溶解症状的影响[J].实用医学杂志,2019,35(10):1540-1544.
[18] BAI Y, ZHANG Q, ZHOU Q, et al. Effects of inhibiting PDK‑1 expression in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on osteoblast differentiation in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2021;23(2):118.
[19] ONO T, NAKASHIMA T. Recent advances in osteoclast biology. Histochem Cell Biol. 2018;149(4):325-341.
[20] XIAO D, ZHOU Q, GAO Y, et al. PDK1 is important lipid kinase for RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and function via the regulation of the Akt-GSK3β-NFATc1 signaling cascade. J Cell Biochem. 2020;121(11): 4542-4557.
[21] 方玲,张琪,魏恩韬,等.基于PI3K/Akt信号通路的中医药改善胰岛素抵抗的研究进展[J].中国医药导报,2018,15(23):26-29.
[22] DIBBLE CC, CANTLEY LC. Regulation of mTORC1 by PI3K signaling. Trends Cell Biol. 2015;25(9):545-555.
[23] GAGLIARDI PA, PULIAFITO A, PRIMO L. PDK1: At the crossroad of cancer signaling pathways. Semin Cancer Biol. 2018;48:27-35.
[24] KALBASI ANARAKI P, PATECKI M, TKACHUK S, et al. Urokinase receptor mediates osteoclastogenesis via M-CSF release from osteoblasts and the c-Fms/PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway in osteoclasts. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(2):379-388.
[25] GALLUZZI L, PIETROCOLA F, LEVINE B,et al. Metabolic control of autophagy. Cell. 2014;159(6):1263-1276.
[26] SAXTON RA, SABATINI DM. mTOR Signaling in Growth, Metabolism, and Disease. Cell. 2017;169(2):361-371.
[27] DAI Q, HAN Y, XIE F, et al. A RANKL-based Osteoclast Culture Assay of Mouse Bone Marrow to Investigate the Role of mTORC1 in Osteoclast Formation. J Vis Exp. 2018;(133):56468.
[28] LI M, LUO R, YANG W, et al. miR-363-3p is activated by MYB and regulates osteoporosis pathogenesis via PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2019;55(5):376-386.
[29] HU J, MAO Z, HE S, et al. Icariin protects against glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis, increases the expression of the bone enhancer DEC1 and modulates the PI3K/Akt/GSK3β/β-catenin integrated signaling pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 2017;136:109-121.
[30] KONG Y, NIE ZK, LI F, et al. MiR-320a was highly expressed in postmenopausal osteoporosis and acts as a negative regulator in MC3T3E1 cells by reducing MAP9 and inhibiting PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Exp Mol Pathol. 2019;110:104282.
[31] SAPIR-KOREN R, LIVSHITS G. Postmenopausal osteoporosis in rheumatoid arthritis: The estrogen deficiency-immune mechanisms link. Bone. 2017;103:102-115.
[32] VÄÄNÄNEN HK, HÄRKÖNEN PL. Estrogen and bone metabolism. Maturitas. 1996; 23 Suppl:S65-69.
[33] LI L, WANG Z. Ovarian Aging and Osteoporosis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1086:199-215.
[34] MIYAMOTO T. Mechanism Underlying Post-menopausal Osteoporosis: HIF1alpha is Required for Osteoclast Activation by Estrogen Deficiency. Keio J Med. 2015; 64(3):44-47.
[35] KOMM BS, MORGENSTERN D, YAMAMOTO LA, et al. The safety and tolerability profile of therapies for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2015;8(6):769-784.
[36] LI W, ZHU HM, XU HD, et al. CRNDE impacts the proliferation of osteoclast by estrogen deficiency in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(18):5815-5821.
[37] CHOI MH, LEE K, KIM MY, et al. Pisidium coreanum Inhibits Multinucleated Osteoclast Formation and Prevents Estrogen-Deficient Osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(23):6076.
(责任编辑:MZH,ZN,SX) |