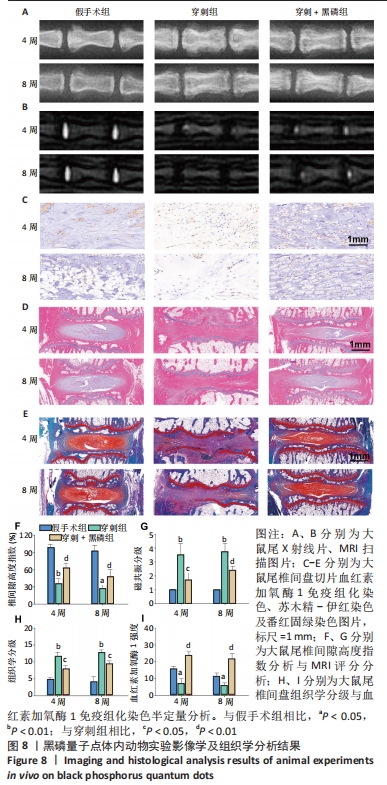
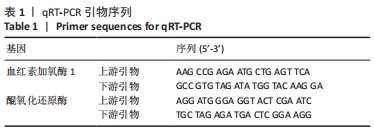
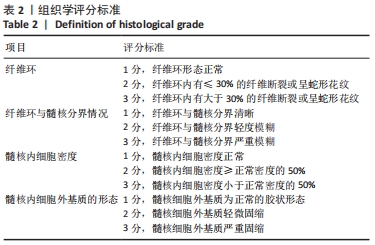
[1] CIEZA A, CAUSEY K, KAMENOV K, et al. Global estimates of the need for rehabilitation based on the Global Burden of Disease study 2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 2021;396(10267):2006-2017.
[2] ADAMS MA, ROUGHLEY PJ. What is intervertebral disc degeneration, and what causes it? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(18):2151-2161.
[3] 解志锋,刘清,刘冰,等.腰椎间盘疲劳损伤的生物力学特性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2021,25(3):339-343.
[4] LE MAITRE CL, FREEMONT AJ, HOYLAND JA. Accelerated cellular senescence in degenerate intervertebral discs: a possible role in the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc degeneration. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(3):R45.
[5] DING F, SHAO ZW, XIONG LM. Cell death in intervertebral disc degeneration. Apoptosis. 2013; 18(7):777-785.
[6] DIMOZI A, MAVROGONATOU E, SKLIROU A, et al. Oxidative stress inhibits the proliferation, induces premature senescence and promotes a catabolic phenotype in human nucleus pulposus intervertebral disc cells. Eur Cell Mater. 2015;30:89-102; discussion 103.
[7] SONG D, GE J, WANG Y, et al. Tea Polyphenol Attenuates Oxidative Stress-Induced Degeneration of Intervertebral Discs by Regulating the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021; 2021:6684147.
[8] LU Y, ZHOU L, HE S, et al. Lycopene alleviates disc degeneration under oxidative stress through the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Mol Cell Probes. 2020;51:101559.
[9] VO N, NIEDERNHOFER LJ, NASTO LA, et al. An overview of underlying causes and animal models for the study of age-related degenerative disorders of the spine and synovial joints. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(6):831-837.
[10] NAVARRO-YEPES J, BURNS M, ANANDHAN A, et al. Oxidative stress, redox signaling, and autophagy: cell death versus survival. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014;21(1):66-85.
[11] FENG C, YANG M, LAN M, et al. ROS: Crucial Intermediators in the Pathogenesis of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:5601593.
[12] MA Q. Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2013;53:401-426.
[13] ESPINOSA-DIEZ C, MIGUEL V, MENNERICH D, et al. Antioxidant responses and cellular adjustments to oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 2015;6:183-197.
[14] MOTOHASHI H, KATSUOKA F, ENGEL JD, et al. Small Maf proteins serve as transcriptional cofactors for keratinocyte differentiation in the Keap1-Nrf2 regulatory pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(17):6379-6384.
[15] ZHANG X, LIANG S, GAO X, et al. Protective Effect of Chitosan Oligosaccharide against Hydrogen Peroxide-Mediated Oxidative Damage and Cell Apoptosis via Activating Nrf2/ARE Signaling Pathway. Neurotox Res. 2021;39(6):1708-1720.
[16] TAO W, SUN W, LIU L, et al. Chitosan Oligosaccharide Attenuates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Induced by High Fat Diet through Reducing Lipid Accumulation, Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in C57BL/6 Mice. Mar Drugs. 2019;17(11):645.
[17] SALOMONE F, GODOS J, ZELBER-SAGI S. Natural antioxidants for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: molecular targets and clinical perspectives. Liver Int. 2016;36(1):5-20.
[18] ZHANG Y, AHMAD KA, KHAN FU, et al. Chitosan oligosaccharides prevent doxorubicin-induced oxidative stress and cardiac apoptosis through activating p38 and JNK MAPK mediated Nrf2/ARE pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 2019;305:54-65.
[19] LI W, KHOR TO, XU C, et al. Activation of Nrf2-antioxidant signaling attenuates NFkappaB-inflammatory response and elicits apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008;76(11):1485-1489.
[20] MA Q, KINNEER K, YE J, et al. Inhibition of nuclear factor kappaB by phenolic antioxidants: interplay between antioxidant signaling and inflammatory cytokine expression. Mol Pharmacol. 2003;64(2):211-219.
[21] ZHANG GZ, LIU MQ, CHEN HW, et al. NF-κB signalling pathways in nucleus pulposus cell function and intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(7):e13057.
[22] FU HD, LI ZB, XIE HH, et al. Different-sized black phosphorus nanosheets with good cytocompatibility and high photothermal performance. Rsc Adv. 2017;7(24):14618-14624.
[23] BRENT JR, GANGULI AK, KUMAR V, et al. On the stability of surfactant-stabilised few-layer black phosphorus in aqueous media. Rsc Adv. 2016;6(90):86955-86958.
[24] HOU J, WANG H, GE Z, et al. Treating Acute Kidney Injury with Antioxidative Black Phosphorus Nanosheets. Nano Lett. 2020;20(2):1447-1454.
[25] CHENG L, CHEN Z, CAI Z, et al. Bioinspired Functional Black Phosphorus Electrospun Fibers Achieving Recruitment and Biomineralization for Staged Bone Regeneration. Small. 2020;16(50):e2005433.
[26] RAUCCI MG, FASOLINO I, CAPORALI M, et al. Exfoliated Black Phosphorus Promotes in Vitro Bone Regeneration and Suppresses Osteosarcoma Progression through Cancer-Related Inflammation Inhibition. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(9):9333-9342.
[27] WANG Z, LIU Z, SU C, et al. Biodegradable Black Phosphorus-based Nanomaterials in Biomedicine: Theranostic Applications. Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(10):1788-1805.
[28] BIAN J, CAI F, CHEN H, et al. Modulation of Local Overactive Inflammation via Injectable Hydrogel Microspheres. Nano Lett. 2021;21(6): 2690-2698.
[29] XU YC, GU Y, CAI F, et al. Metabolism Balance Regulation via Antagonist-Functionalized Injectable Microsphere for Nucleus Pulposus Regeneration. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30(52): 14.
[30] 叶旭文,顾勇,陈亮.负载姜黄素可注射微球延缓椎间盘的退变[J].中国组织工程研究, 2023,27(12):1884-1891.
[31] MASUDA K, AOTA Y, MUEHLEMAN C, et al. A novel rabbit model of mild, reproducible disc degeneration by an anulus needle puncture: correlation between the degree of disc injury and radiological and histological appearances of disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(1):5-14.
[32] CHEN H, LIU Z, WEI B, et al. Redox responsive nanoparticle encapsulating black phosphorus quantum dots for cancer theranostics. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(3):655-665.
[33] GÓMEZ-PÉREZ J, BARNA B, TÓTH IY, et al. Quantitative Tracking of the Oxidation of Black Phosphorus in the Few-Layer Regime. ACS Omega. 2018;3(10):12482-12488.
[34] BELLEZZA I, GIAMBANCO I, MINELLI A, et al. Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in oxidative and reductive stress. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2018;1865(5):721-733.
[35] HAN B, ZHU K, LI FC, et al. A simple disc degeneration model induced by percutaneous needle puncture in the rat tail. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(18):1925-1934.
[36] HUA W, LI S, LUO R, et al. Icariin protects human nucleus pulposus cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced mitochondria-mediated apoptosis by activating nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020;1866(1):165575.
[37] Tang Z, Hu B, Zang F, et al. Nrf2 drives oxidative stress-induced autophagy in nucleus pulposus cells via a Keap1/Nrf2/p62 feedback loop to protect intervertebral disc from degeneration. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(7):510.
[38] HE R, CUI M, LIN H, et al. Melatonin resists oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells. Life Sci. 2018;199:122-130.
[39] KIM KW, CHUNG HN, HA KY, et al. Senescence mechanisms of nucleus pulposus chondrocytes in human intervertebral discs. Spine J. 2009;9(8):658-666.
[40] FINKEL T. Signal transduction by reactive oxygen species. J Cell Biol. 2011;194(1):7-15.
[41] THURAKKAL S, ZHANG X. Recent Advances in Chemical Functionalization of 2D Black Phosphorous Nanosheets. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020;7(2):1902359.
[42] WANG H, YANG X, SHAO W, et al. Ultrathin Black Phosphorus Nanosheets for Efficient Singlet Oxygen Generation. J Am Chem Soc. 2015;137(35):11376-11382.
[43] DING F, SHAO ZW, YANG SH, et al. Role of mitochondrial pathway in compression-induced apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells. Apoptosis. 2012;17(6):579-590.
[44] NASTO LA, ROBINSON AR, NGO K, et al. Mitochondrial-derived reactive oxygen species (ROS) play a causal role in aging-related intervertebral disc degeneration. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(7):1150-1157.
[45] BUENDIA I, MICHALSKA P, NAVARRO E, et al. Nrf2-ARE pathway: An emerging target against oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 2016;157: 84-104.
[46] WANG P, ZHANG S, LIU W, et al. Selenium Attenuates TBHP-Induced Apoptosis of Nucleus Pulposus Cells by Suppressing Mitochondrial Fission through Activating Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:7531788.
[47] LI Y, CHEN L, GAO Y, et al. Oxidative Stress and Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Pathophysiology, Signaling Pathway, and Therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:1984742.
[48] FENG C, ZHANG Y, YANG M, et al. Oxygen-Sensing Nox4 Generates Genotoxic ROS to Induce Premature Senescence of Nucleus Pulposus Cells through MAPK and NF-κB Pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:7426458.
[49] 杨林,石军,郭中华,等.基于高分子材料的椎间盘组织工程:研究重点和热点[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(16):2589-2596.
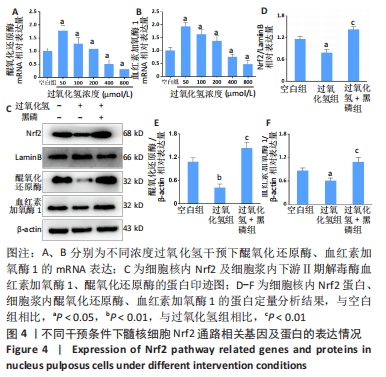
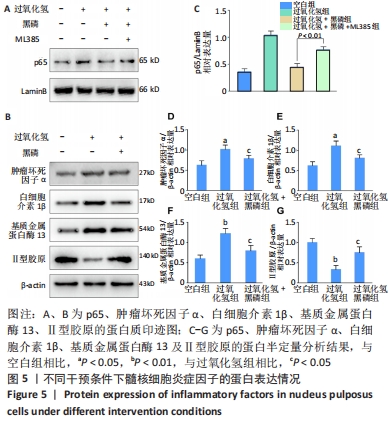
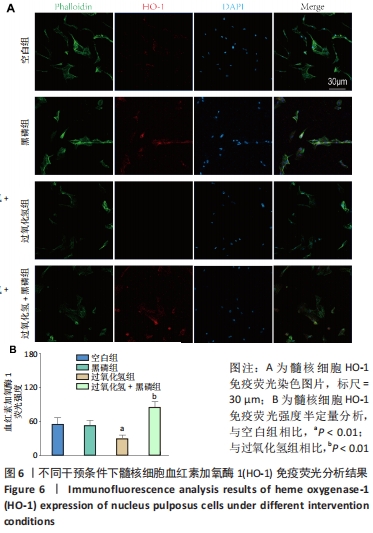
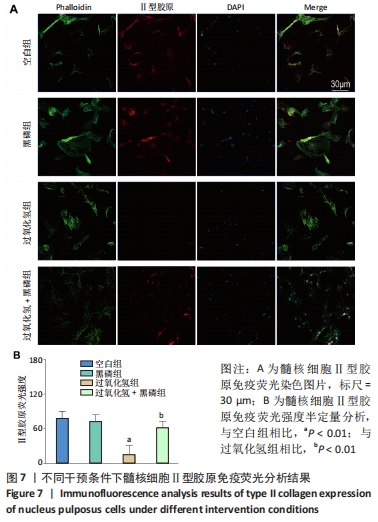
|