中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (30): 4902-4908.doi: 10.12307/2024.632
• 骨与关节综述 bone and joint review • 上一篇 下一篇
机械应力调控Hippo通路影响骨关节炎的发生与发展
杨 攀1,董万涛2,刘静怡1,邱世明1,袁 鹏1
- 1甘肃中医药大学中医临床学院,甘肃省兰州市 730000;2甘肃中医药大学附属医院运动医学科,甘肃省兰州市 730000
-
收稿日期:2023-07-07接受日期:2023-09-18出版日期:2024-10-28发布日期:2023-12-28 -
通讯作者:董万涛,博士,主任医师,甘肃中医药大学附属医院运动医学科,甘肃省兰州市 730000 -
作者简介:杨攀,女,1995年生,河南省驻马店市人,在读硕士,主要从事中医药防治骨伤疾病研究。 -
基金资助:甘肃省科技计划项目任务书-重点研发计划(21YF5FA017),项目负责人:董万涛;甘肃省科技计划项目-创新基地和人才计划项目(20JR10RA341),项目参与人:董万涛;2023年甘肃省研究生“创新之星”项目(2023CXZX-745),项目负责人:杨攀
Mechanical stress affects occurrence and development of osteoarthritis by regulating Hippo pathway
Yang Pan1, Dong Wantao2, Liu Jingyi1, Qiu Shiming1, Yuan Peng1
- 1Clinical College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China; 2Department of Sports Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China
-
Received:2023-07-07Accepted:2023-09-18Online:2024-10-28Published:2023-12-28 -
Contact:Dong Wantao, MD, Chief physician, Department of Sports Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China -
About author:Yang Pan, Master candidate, Clinical College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China -
Supported by:Gansu Provincial Science and Technology Plan Project Task Book - Key Research & Development Plan, No. 21YF5FA017 (to DWT); Gansu Provincial Science and Technology Plan Project - Innovation Base and Talent Plan Project, No. 20JR10RA341 (to DWT); 2023 Gansu Province Graduate Student “Innovation Star” Project, No. 2023CXZX-745 (to YP)
摘要:
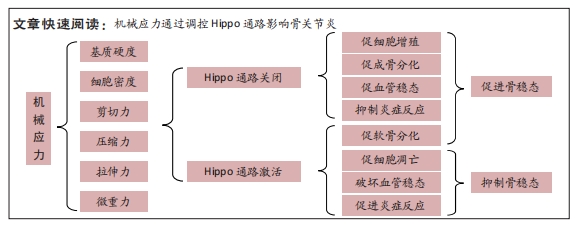
文题释义:
HIPPO通路:是机体生长发育过程中关键的调节因子,具有促进细胞增殖组织器官生长的作用。通过上游因子控制HIPPO通路的激活和关闭,既具有修复损伤的功能又会导致组织器官的异常增生。机械应力:是流体剪切力、拉伸力、压缩力、超重力、微重力、基质硬度及细胞密度等各种物理力的总称。机械应力存在于生命体的方方面面,生理性机械应力可维持机体生长发育,而异常的机械应力则会导致疾病的发生。
背景:骨关节炎是一种常见的由关节软骨退行性改变所导致的关节慢性炎症,越来越多的研究表明机械应力与骨关节炎的发展密切相关。Hippo通路既参与机体组织细胞发育又是机械应力的效应因子,参与调控骨代谢和软骨代谢。
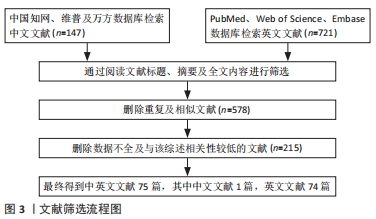
目的:通过调控Hippo通路可能成为干预骨关节炎的新靶点之一,因而此文通过对机械应力调控Hippo通路影响骨关节炎的研究进行综述,以期为骨关节炎的发病机制提供思路并对骨关节炎的治疗方法提供新的理论依据。方法:采用PubMed、Web of Science、Embase、中国知网、维普及万方数据库进行文献检索,检索各数据库建库至2023年有关机械应力对骨关节炎的影响及机械应力、Hippo通路与骨关节炎相关的所有文献,最终纳入75篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:①不同机械应力对骨关节炎的细胞增殖凋亡与分化、骨关节炎症与血管稳态发挥不同的作用;②坚硬细胞外基质、低细胞密度、中等剪切力、中等拉伸力及压缩力通过活化YAP/TAZ可达到细胞增殖、成骨分化、血管稳态及抑制炎症反应的作用;③软细胞外基质、高细胞密度、过度剪切力、过度拉伸力及压缩力通过失活YAP/TAZ进而抑制细胞增殖、促软骨分化、破坏血管稳态及促进炎症反应,促进骨关节炎进程。
https://orcid.org/0009-0002-9763-9929 (杨攀)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
杨 攀, 董万涛, 刘静怡, 邱世明, 袁 鹏. 机械应力调控Hippo通路影响骨关节炎的发生与发展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(30): 4902-4908.
Yang Pan, Dong Wantao, Liu Jingyi, Qiu Shiming, Yuan Peng. Mechanical stress affects occurrence and development of osteoarthritis by regulating Hippo pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(30): 4902-4908.
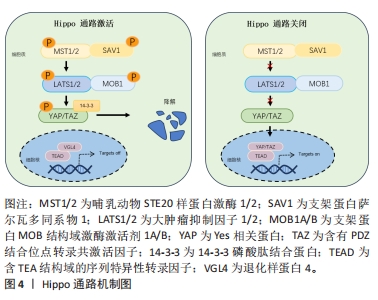
2.1.1 Hippo通路及主要作用 Hippo途径最初是在黑腹果蝇中发现的,它是一种进化上保守的信号级联反应,调节控制细胞增殖和分化、器官大小和组织修复与再生[8]。该通路是主要由哺乳动物STE20样蛋白激酶1/2、支架蛋白萨尔瓦多同系物1、大肿瘤抑制因子1/2和支架蛋白MOB结构域激酶激活剂1A/B组成的激酶级联反应[9],其作用是通过激活转录共激活剂YAP及TAZ的副同源物转录共激活剂的磷酸化依赖性调节发生的[10]。Hippo途径的激活首先由多个上游输入激活并磷酸化哺乳动物STE20样蛋白激酶1/2和大肿瘤抑制因子1/2进而导致YAP/TAZ磷酸化,磷酸化的YAP和TAZ被14-3-3磷酸肽结合蛋白螯合在细胞质中,并分流用于蛋白酶体降解。随后细胞核内含TEA结构域的序列特异性转录因子与退化样蛋白4结合并抑制靶基因表达。当Hippo途径关闭时,哺乳动物STE20样蛋白激酶1/2和大肿瘤抑制因子1/2激酶无活性,YAP和TAZ不被磷酸化并积聚在细胞核中,取代退化样蛋白4并与含TEA结构域的序列特异性转录因子复合促进靶基因的表达而发挥细胞生物学功能[11],见图4。
Hippo通路主要由YAP/TAZ的基因表达发挥作用,研究表明YAP/TAZ具有促进细胞增殖、修复组织损伤、促进器官生长及维持组织稳态的作用[12]。在机体不同状态下YAP/TAZ的这种功能发挥不同作用,在组织器官发育中YAP/TAZ核移位表达促进祖细胞增殖并抑制其分化。随着祖细胞的分化,YAP/TAZ核移位表达减少并可维持其分化后的细胞表型[13]。在正常组织中,YAP/TAZ受到多个负调节剂的调控表达并不显著。而当组织器官受损后,YAP被活化通过促进细胞增殖生长的功能来促进损伤组织的修复和器官再生。组织器官恶化情况下,YAP/TAZ被持续过度激活,则促进组织器官过度生长,造成肿瘤或癌症的发生[14]。在骨骼发育中,成骨细胞祖细胞中的YAP和TAZ抑制成骨细胞谱系分化,但在成熟的成骨细胞和骨细胞中,YAP/TAZ促进骨形成并抑制骨吸收[15]。
2.1.2 Hippo通路对骨关节炎的作用 在骨关节炎中炎性细胞因子作为分解代谢刺激YAP/TAZ的细胞质易位,降低了核YAP/TAZ水平,导致合成代谢基因表达和转录活性降低[16]。YAP/TAZ的核表达可通过拮抗核因子κB信号通路来维持软骨稳态。在骨关节炎中,炎性细胞因子通过TAK1介导的YAP磷酸化和泛素化促进YAP蛋白酶体降解,YAP的敲低可降低蛋白聚糖和Ⅱ型胶原蛋白水平。而YAP的活化可消除IKKα/β活化并抑制IκBα降解,以及p65活化和核易位,而导致核因子κB信号活性的衰减。YAP通过与TAK1和IKKs复合物结合来抑制软骨降解,从而阻止IKKα/β激活和随后的核因子κB易位到细胞核中[17]。机械变化与炎症过程密切相关,炎症刺激通过YAP将刺激转化为细胞和组织机械重塑。YAP/TAZ通过细胞外基质组成的强烈变化来驱动细胞张力和细胞外基质僵硬以响应炎症,从而使骨关节炎呈现更僵硬的微环境。即使炎症停止,僵硬的微环境随着时间的推移仍能保持YAP活性,促进骨关节炎持续恶化[18]。
2.1.3 机械应力对Hippo通路的作用 Hippo信号通路不仅具有调节细胞增殖与凋亡的作用,还是机械刺激对细胞影响的重要介质。YAP/TAZ接收一系列物理线索,包括细胞外基质刚度、细胞密度、流动剪切应力及压缩力等机械力,并将其转化为细胞特异性转录程序[19]。这些机械线索通过细胞与细胞基质间的整合素及Rho/ROCK和局灶性黏附激酶/Src信号级联反应、细胞与细胞间的钙黏蛋白及细胞与环境间的机械敏感离子通道等介导,以控制YAP和TAZ的磷酸化状态和定位[20]。研究表明具有刚性的细胞外基质促进整合素结合,进而构建更多的F-肌动蛋白,肌动肌肽激活产生收缩力使细胞核变平并打开核孔,使YAP易位到细胞核中,核YAP/TAZ活性则促进细胞增殖。相反,在柔软的细胞外基质中YAP被隔离在细胞质中经历降解[21]。在高细胞密度下,大肿瘤抑制因子1/2激酶被激活并在细胞质中重新定位YAP/TAZ,从而导致肌球蛋白-Ⅱ和肌动蛋白应激纤维的损失,这进一步激活大肿瘤抑制因子1/2激酶,保持YAP/TAZ磷酸化并维持其随后的细胞质保留。在低细胞密度下,大肿瘤抑制因子1/2激酶失活,YAP/TAZ被重新激活并穿梭到细胞核中,挽救肌动蛋白应激纤维的形成,这诱导YAP/TAZ重新定位到细胞核中并保持增殖状态[22]。在成骨细胞中整合素αvβ3通过感测流体剪切力在细胞过程中起到机械受体的作用,流体剪切力机械刺激通过成骨细胞谱系细胞中的整合素αvβ3被感知,刺激Src激酶活性和初级力传感器p130Cas及Jun N末端激酶的磷酸化,最终增强YAP/TAZ的核定位并促进其转录功能[23]。研究发现与低压缩力相比,高压缩力下的间充质干细胞明显更大,并且核YAP增加;高压缩力下,大肿瘤抑制因子1/2激酶失活,导致YAP/TAZ核移位增加,促进间充质干细胞体积增加[24]。
2.2 机械应力与骨关节炎
2.2.1 骨关节炎中的异常机械应力 骨关节炎进展中,组织损伤引发的炎症反应可促进软骨细胞外基质降解,进而使得软骨发生生物力学退化[25]。同时软骨细胞和滑膜细胞对这种异常的机械应力产生生化反应,促进分解代谢因子基质金属蛋白酶(matrix metalloproteinase,MMP)和组织抑制剂金属蛋白酶1表达,进而导致软骨变性[26]。软骨损伤导致局部拉伸应力和剪切应力异常增高,诱导软骨细胞表型变化,促进Ⅰ型胶原mRNA表达而抑制Ⅱ型胶原和聚集聚糖的mRNA表达,表现出显著的成纤维细胞形态并伴随细胞凋亡增加[27]。软骨的变化对关节的接触力学有显著影响,有研究表明软骨厚度减少50%会使接触压力增加29%,而厚度增加一倍会使接触压力降低23%。软骨降解导致软骨厚度减少,使局部软骨呈现出异常的高应力状态[28]。
2.2.2 机械应力调控软骨细胞凋亡和关节炎症 伍伟挺等[29]采用细胞体外加力实验系统(Flexcell-5000T Tension System)处理细胞,频率为0.5 Hz拉伸24 h,拉伸应变率大小分别为0%,2%,6%,8%,10%,14%,结果显示拉伸率10%和14%的白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α升高较明显,同时细胞脱落较多,边缘模糊变圆,出现凋亡现象,表明过度的周期性机械应力刺激可引起软骨细胞炎症反应及凋亡。细胞黏附分子整合素是在物理和化学上控制细胞内信号通路的机械感受器,研究发现过度机械应力(峰值电压和频率分别为15 V和2 Hz),激活软骨细胞表面的整合素αVβ3和αVβ5,从而通过局灶性黏附激酶和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶的磷酸化上调白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α、MMP-3和MMP-13的表达来诱导炎症反应[30]。而整合素αVβ3的上调进一步激活下游局灶性黏附激酶-细胞外蛋白激酶信号传导并改变软骨细胞代谢以促进细胞外基质的炎症和降解[31]。除此之外,过度机械应力还可诱发软骨细胞谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4相关性铁死亡[32]。相反,动态负荷设置为(1 N,5 Hz,持续5 min/d)的机械力则能够抑制骨关节炎症和细胞凋亡,骨关节炎诱导内质网应激和抑制自噬来诱导病理性骨骼代谢,结果表明适宜的机械负荷能够抑制内质网压力和促进自噬维持软骨稳态进而减轻骨关节炎症状[33]。转化生长因子β1的升高是机械刺激依赖性的,在中等强度跑步机运动(3.5 m/min,5 min/d,每周4 d,持续5周)疗法下转化生长因子β1通过激活Smad2/3和抑制核因子κB信号传导,对大鼠软骨细胞焦亡产生抑制作用,可阻止骨关节炎进程[34]。
2.2.3 机械应力调控软骨代谢 Gremlin-1为软骨细胞中的机械负荷诱导因子,通过激活核因子κB信号传导,诱导MMP-13和含血小板结合蛋白基序的解聚蛋白样金属蛋白酶5等分解代谢酶产生,抑制基因重组骨形态形成蛋白对Sox9、Ⅱ型胶原α1和聚集聚糖的上调。研究发现在异常循环应变(0.5 Hz,10%循环拉伸应变加载30 min)或静水压力负荷(0.1 Hz的频率施加20 MPa的静水压力30 min)下,Gremlin-1被激活并通过拮抗骨形态发生蛋白下调合成代谢基因促进软骨分解[35]。同样,过度机械应力通过激活Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号传导,可增加骨关节炎相关细胞因子的表达,诱导颞下颌关节软骨的骨关节炎样变[36]。而施加适宜的机械应力可通过抑制丝裂原活化蛋白激酶通路促进软骨祖细胞增殖,抑制基质降解酶基因表达。YAO等[37]通过关节牵引构建适宜的机械应力(压力强度和频率为5 MPa和0.5 Hz),发现骨关节炎软骨组织中P-p38、MMP-13及Ⅹ型胶原蛋白的表达降低,促进了软骨修复。研究发现异常的剪切应力以剂量和时间依赖性方式上调一氧化氮释放,产生炎症反应促进软骨降解,间歇静水压力的干预可抑制一氧化氮释放,从而控制一氧化氮水平升高导致的软骨基质蛋白、聚集聚糖和Ⅱ型胶原蛋白mRNA信号水平降低[38]。
2.2.4 机械应力改变软骨结构 异常的血液流变力在骨关节炎恶化中起关键作用,有学者通过大规模膝骨关节炎患者队列研究发现,血液循环、脉压和心脏功能等血流动力学指数与骨关节炎病理学关系密切,血流动力学应激增加软骨下骨密度并促进杆状小梁到板状小梁的转换[39]。在骨关节炎高应力区域异常剪切应力(0.658 Pa)加强了αV整合素和RGD之间的键,提高了αV整合素-RGD键的细胞刚度、张力耐受性和收缩力,进而增加了软骨细胞硬度导致软骨变形[40]。而脉冲电磁场和全身振动干预可有效缓解骨关节炎小鼠软骨变性,保留软骨下小梁骨微结构[41]。异常机械应力还可诱导骨赘的增生,VENNE等[42]发现大鼠股骨内侧髁骨膜在接受单次撞击负荷30 N(24 MPa)9周后,产生了软骨组织刺软骨,呈现出高级矿化的迹象。水凝胶系统可以将来自关节接触点的应力分布在关节中更宽的表面积上,从而减轻组织内高应力状态。HOLYOAK等[43]通过PEG-4MAL水凝胶系统制作“机械枕头”治疗负荷诱导的骨关节炎模型小鼠,发现水凝胶系统在响应高水平的循环压缩时保持其机械性能,保护膝关节免受软骨降解-抑制骨赘形成并缓解骨关节炎的进展。
2.3 通过机械应力调控Hippo通路对骨关节炎的治疗
2.3.1 机械应力调控Hippo通路影响细胞增殖与凋亡
(1)细胞增殖:YAP的失活会触发细胞周期停滞,研究发现YAP失活通过下调Skp0诱导细胞周期退出,导致p21/p27积累[44]。而机械应力干预可以调控细胞增殖或细胞周期停滞,YANG等[45]将大鼠软骨细胞以0.5 Hz的频率暴露于循环拉伸应变,发现相较于1 000 με应变,3 000 με应变下施加应变1 h在生理范围内诱导YAP激活程度最大。YAP介导机械菌株诱导的细胞周期进程,通过RhoA和大鼠生长板软骨细胞中的细胞骨架动力学上调了细胞周期相关基因增殖细胞核蛋白和cyclin D1的表达水平。KLINCUMHOM等[46]分别以0.23 Hz的频率1.5 g/cm2的间歇性压缩力和1.5 g/cm2的连续压缩力作用于细胞,发现相较于连续压缩力,用循环压缩力处理的人牙周膜细胞中YAP的核易位增加,YAP的活性增强,细胞增殖相关标志物(包括LIN28a、LIN28b、OCT4、REX1、SOX2和KI67)的mRNA表达水平显著上调。YAO等[47]探究机械应力调控Hippo通路促进软骨祖细胞的增殖和软骨修复的研究中,将间歇静水压设置为振幅和频率为5 MPa,0.5 Hz,4 h/d。结果显示应用间歇静水压后,YAP在细胞核的表达增加,阳性率达到46%,伴随Sox-9、聚集聚糖、Ⅱ型胶原α1、结缔组织生长因子和细胞周期蛋白的增殖和软骨分化,这表明YAP活化促进软骨祖细胞增殖,并且通过Hippo-YAP信号传导静水压可以促进软骨修复和软骨细胞增殖。
(2)细胞凋亡:研究发现在生理渗透压(400 mOsm)刺激下软骨细胞YAP/TAZ核易位增加,合成代谢基因表达和转录活性升高,而YAP低表达时软骨细胞蛋白聚糖染色和Ⅱ型胶原蛋白水平降低,表明骨关节炎软骨细胞中核YAP的降低抑制合成代谢活性并促进软骨损失[48]。在退行性椎间盘微环境的压缩力下,YAP被磷酸化,促进细胞凋亡。缺氧诱导因子1α在缺氧条件下可促进YAP的去磷酸化和活化,保护骨髓间充质干细胞免受压缩诱导的细胞凋亡[49]。而循环机械应力可促进缺氧诱导因子1α和YAP蛋白的表达,其中4 000 με应变下的循环力学应力对缺氧诱导因子1α和YAP上调的促进作用最为显著。YAP的上调显著促进了缺氧诱导因子1α的稳定和表达,进而缓解大鼠软骨细胞分解代谢应激诱导的细胞凋亡[50]。KONG等[51]研究YAP1在间歇性循环机械张力诱导终板软骨细胞衰老和变性的机制中发现Flexcell FX-5000TM应变加载系统设置为5.8 Hz 正弦应变,伸长率分别为12%,16% 和 3%下,间歇性循环机械张力的增加导致细胞形状从椭圆形逐渐变为长纺锤形,其中16%组的细胞密度最为稀疏且细胞增殖最少,张力刺激后终板软骨中Ⅱ型胶原α1、Sox-9、YAP1和结缔组织生长因子的表达降低,p53和p21的表达增加。说明间歇性循环机械张力通过失活YAP促进终板软骨细胞衰老和变性过程,过表达YAP1可以挽救间歇性循环牵张力诱导的终板软骨细胞衰老和变性。
(3)骨稳态:Piezo1是骨稳态中必不可少的机械传感器,对机械负荷高度敏感。YAP是Piezo1通道的下游效应器,研究表明失重或废弃引起的骨延迟愈合中Piezo1通道激活可通过骨膜干细胞中的YAP-β-连环蛋白信号通路刺激骨形态发生蛋白2和血管内皮生长因子表达以促进骨稳态恢复[52]。WANG等[53]模拟中等强度作用对细胞施加强度为1%、频率为0.5 Hz、时间为4 h的压缩力,结果显示中等压缩力刺激piezo1激活,促进YAP核表达升高,Ⅱ型胶原α1、Ⅸ型胶原α2等骨基质蛋白的表达升高同时抑制破骨细胞活性进而维持骨稳态。
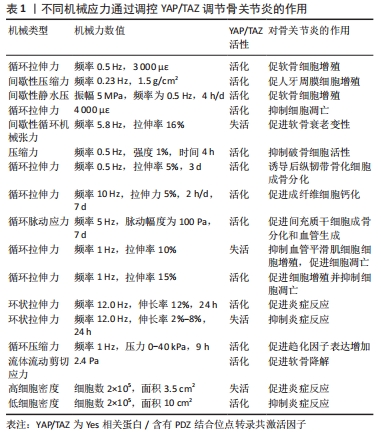
2.3.2 机械应力调控Hippo调节成骨和成软骨分化 骨稳态是通过成骨细胞的骨形成和破骨细胞骨吸收的平衡来维持的。其中骨髓间充质干细胞、成骨细胞参与骨形成的重建,破骨细胞则通过骨吸收作用形成骨凹陷,血管内皮细胞通过与成骨细胞偶联耦合刺激骨形成作用,各种细胞在骨代谢过程中扮演着不同角色,而YAP在其中发挥重要调控作用[54],见图5及表1。外机械力在促进成骨方面也起着关键作用,如基质硬度、压缩应力、拉伸应力、流体剪切应力等。研究发现细胞外基质刚度上调激活YAP活性,导致YAP/TAZ易位到细胞核中,诱导间充质干细胞分化为成骨细胞[55]。对于流体剪切应力有研究发现血流动力学超负荷导致Piezo1 活化促进了钙依赖性YAP的活化,YAP调节GLS1介导的谷氨分解,可通过RUNX2启动子增强成骨分化[56]。研究表明,YAP是介导循环拉伸刺激诱导成骨分化的重要调节因子[57]。刺激通过细胞骨架重塑激活了YAP信号通路,高表达的YAP与RUNX2相互作用,在成骨过程中增强其转录活性。对后纵韧带组织原代细胞进行单轴正弦循环拉伸(5%,0.5 Hz,3 d),比较静态组和实验组中相关转录因子、Ⅰ型胶原、骨蛋白、骨钙素和碱性磷酸酶的表达,结果显示,循环拉伸刺激增加了后纵韧带骨化组成骨基因和成骨蛋白的表达,当后纵韧带骨化细胞被拉伸时,YAP表现出明显的核易位,Wnt/β-catenin通路被激活,诱导后纵韧带组织原代细胞成骨分化[58]。成纤维细胞在10 Hz下暴露于5%的循环拉伸应力,1次/d,每次施用2 h,7 d后发现循环拉应力可促进成纤维细胞碱性磷酸酶和RUNX2的表达,促进成纤维细胞钙化[59]。此外,生物材料诱导的间充质干细胞成骨分化,可通过改变材料的刚度、黏弹性和形貌,形成不同强度的机械刺激传递信号介导成骨分化。ZHONG等[60]使用集成微流控灌注装置研究流体流动刺激在调节YAP表达对间充质干细胞和原代软骨细胞的分化的影响,结果发现YAP表达受间充质干细胞和软骨细胞中液流刺激水平的调节,强刺激程度可增强YAP的表达,最终导致间充质干细胞的成骨增加和脂肪生成减少及软骨细胞的去分化。YIN等[61]利用3D打印技术研制了一种具有微孔通道结构的生物材料,通过f-肌动蛋白重塑和YAP激活的机械转导,实现了微孔通道为间充质干细胞的增殖和分化提供了不需要生长因子的引导结构。
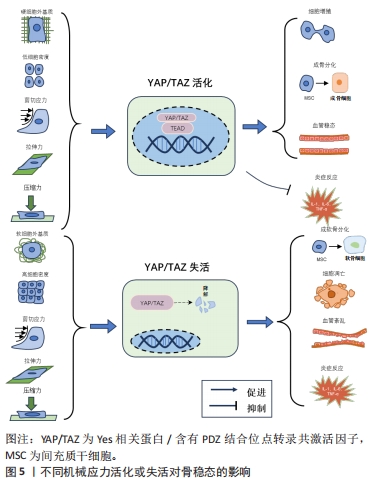
机械应力降低YAP/TAZ表达可促进间充质干细胞成软骨分化,细胞外基质刚度下调导致YAP核表达减少并促进细胞质YAP的积累,在此过程中伴随着Ⅱ型胶原、Sox9和聚集聚糖的显著增加,表明YAP失活有利于间充质干细胞向软骨细胞分化[62]。通过定制低中高3种交联密度细胞微凝胶的机械性能控制其机械微环境,发现骨髓间充质干细胞在Gel-HA(L)中显示出分化为透明软骨的明显趋势,在Gel-HA(M)和Gel-HA(H)中分化为纤维软骨。表明机械微环境可通过Hippo通路、整合素/YAP/TAZ通路进一步调节骨髓间充质干细胞分化为透明软骨或是纤维软骨[63]。
2.3.3 机械应力调控Hippo通路调节血管稳态 血管生成与骨骼发育期间以及骨重塑期间的成骨密切相关。血管不仅为骨组织提供必要的营养、氧气、生长因子和激素,还通过产生刺激骨髓中骨祖细胞增殖和分化的因子来调节骨骼形成。血管形成与成骨耦合可受机械力的调控而发生,DZAMUKOVA等[64]探究机械力对青少年骨骼生长影响的研究中发现青春期末期的体质量增加激活机械感受器PIEZO1离子通道,介导成骨细胞中激酶FAM20C的产生增加,进而刺激牙本质基质蛋白1以爆发样方式从成骨细胞分泌到细胞外基质当中,阻止血管内皮生长因子受体2的磷酸化来抑制血管内皮生长因子信号传导,因而使H型血管转变为静止的L型脉管系统以限制骨生长活性。YAP作为机械应力的下游因子,在此过程中承担“桥梁”的作用,LI等[65]研究循环脉动应力促进大鼠间充质干细胞的成骨和血管生成的能力,设置脉动幅度为100 Pa,频率为5 Hz,干预7 d,结果发现与对照组相比,循环脉动应力促进YAP1的表达和核易位,还促进了血管生成基因如血管内皮生长因子A和成纤维细胞生长因子2的表达水平;同时循环脉动应力组中RUNX2、OSTERIX、碱性磷酸酶和骨形态发生蛋白7等成骨基因的表达水平也高于对照组,进一步研究发现循环脉动应力通过F-actin传递,促进YAP1的核易位,进而减少β-Catenin的降解,促进其核易位。β-Catenin的核易位促进了间充质干细胞的成骨分化和血管生成能力,从而促进了组织工程板的骨和血管的形成。在血管疾病状态下,内皮细胞可以受到不同的机械刺激,从而影响控制血管生成的途径。NAKAJIMA等[66]在培养的人内皮细胞中发现,高层流剪切应力刺激可诱导YAP的核输入及其转录活性;血流通过调控丝状肌动蛋白和血管运动蛋白诱导YAP核易位,维持血管稳态,而低层流剪切应力刺激中Yap1失活则表现出血管稳定性缺陷,表明Yap1在血管中起着至关重要的作用。血管平滑肌细胞是血管壁的基质细胞,持续暴露于机械信号中。研究发现将FX-5000T张力系统产生的循环拉伸中,分别设置伸长率为10%,15%和20%的拉伸力,频率为1 Hz(60个循环/min),持续时间为24 h[67];结果显示10%和20%的拉伸力提高了血管平滑肌细胞的凋亡率,并下调了血管平滑肌细胞的增殖,而15%的拉伸力相反,可降低细胞凋亡率并上调血管平滑肌细胞的增殖。进一步研究发现10%的拉伸力下Rho-ROCK通路受到抑制导致大肿瘤抑制因子1/2水平降低,导致YAP磷酸化的增加降低了ccnd1蛋白水平,导致血管平滑肌细胞增殖减少和细胞凋亡增加,然而,15%的拉伸力降低了YAP磷酸化并促进其进入核,从而促进细胞增殖并抑制细胞凋亡。以上说明YAP在不同强度的拉伸力下对血管平滑肌细胞的增殖和凋亡有不同的调节,适当强度的机械拉伸可以通过激活YAP促进血管平滑肌细胞的增殖并抑制细胞凋亡,而低于或高于生理拉伸力的刺激会导致相反的结果。
2.3.4 机械应力调控Hippo通路调节炎症反应 骨关节炎主要表现为软骨细胞和细胞外基质的破坏,导致功能障碍,其中炎症因子起主要作用[68]。促炎细胞因子通过激活分解代谢酶如MMPs和含血小板结合蛋白基序的解聚蛋白样金属蛋白酶,导致软骨和其他关节内结构损伤。白细胞介素1β通过与其受体白细胞介素1受体Ⅰ结合,激活核因子κB和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路,提高含血小板结合蛋白基序的解聚蛋白样金属蛋白酶和MMP的表达,导致蛋白聚糖降解和胶原蛋白破坏的分解代谢反应。此外,白细胞介素1β通过Sox-9抑制Ⅱ型胶原蛋白的合成,并通过增加环氧合酶2、前列腺素2和一氧化氮的合成来抑制蛋白多糖的合成。此外,骨关节炎中趋化因子如CXCL8、CCL2和CCL5等以及细胞因子白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α的高表达,使得它们分别吸引炎症细胞并引起滑膜炎症,导致更加剧烈的炎症反应,促进骨关节炎恶化[69]。机械应力抑制YAP/TAZ活化可减轻炎症反应,研究发现高幅度(15%-20%)环状拉伸应变增强了促炎细胞因子的表达,而低幅度(2%-8%)环状拉伸应变显著抑制肿瘤坏死因子α处理的人牙周膜间充质干细胞中白细胞介素6、血管细胞黏附分子1和细胞间黏附分子1的基因表达,提示环状拉伸应变具有抗炎作用[70]。深入研究发现应用低幅度(2%-8%)环状拉伸应变可减少YAP活化,而减少YAP活化可降低肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的白细胞介素6、血管细胞黏附分子1和细胞间黏附分子1基因表达;说明在炎症环境下,低幅度(2%-8%)的环状拉伸应力通过抑制YAP活化可以减轻炎症反应。有研究将3D MLO-Y4培养物在37 ℃和5%CO2的湿化气氛中以1 Hz的正弦波形循环压缩0-40 kPa,持续9 h。发现3D机械加载通过上调YAP/TAZ的核移位导致包括M-csf、Cxcl1、Cxcl2、Cxcl3、Cxcl9和Cxcl10机械敏感基因和趋化因子亚群的表达增加;而将YAP/TAZ敲低能够缓解其水平的增加,说明上述3D骨细胞压缩培养模型可以通过活化YAP/TAZ促进炎症反应[71]。在WEI等[72]研究预防伴有咬合创伤加重牙周炎的实验中同样发现,活化去磷酸化的YAP伴随炎症因子表达增加。在伴有咬合创伤的牙周炎小鼠模型中,YAP转移到细胞核中,导致Jun N末端激酶相关的促炎途径上调;XAV939的应用抑制了YAP蛋白去磷酸化,降低了Jun N末端激酶促炎途径因子在体内外的表达,说明抑制YAP活化可减轻炎症反应。FENG等[73]利用Flexcell装置对ATDC5软骨细胞施加2.4 Pa的流体流动剪切应力,刺激Piezo1在骨关节炎软骨细胞中过表达,进而促进YAP的核易位并上调了MMP-13和含血小板结合蛋白基序的解聚蛋白样金属蛋白酶5的表达,导致软骨降解。
然而部分研究机械应力调控Hippo通路调节炎症反应的实验结果却呈现出相反的趋势,WANG等[74]开展了阿司匹林治疗减轻小鼠内侧半月板不稳定模型中软骨变性的实验,结果显示其作用机制是阿司匹林通过过表达YAP减轻肿瘤坏死因子α对氧化应激的促进作用,而沉默YAP则部分逆转了阿司匹林对氧化应激的减轻作用,抑制了骨髓间充质干细胞的软骨生成,表明YAP在氧化应激过程中起着负调节作用。另外,ZHANG等[75]将相同数量的细胞(约2×105)分别镀在10,6和3.5 cm的板上,分别作为低、中、高细胞密度组,发现低细胞密度时YAP活化,YAP抑制许多核因子κB的选择性靶基因,抑制炎症反应;高细胞密度时YAP灭活,核因子κB的靶基因表达增多,炎症反应增强。

| [1] YUNUS MHM, NORDIN A, KAMAL H. Pathophysiological Perspective of Osteoarthritis. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020;56(11):614. [2] MANDL LA. Osteoarthritis year in review 2018: clinical. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(3):359-364. [3] PANCIERA T, AZZOLIN L, CORDENONSI M, et al. Mechanobiology of YAP and TAZ in physiology and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017;18(12):758-770. [4] CAI X, WANG KC, MENG Z. Mechanoregulation of YAP and TAZ in Cellular Homeostasis and Disease Progression. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:673599. [5] ZARKA M, HAŸ E, COHEN-SOLAL M. YAP/TAZ in Bone and Cartilage Biology. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;9:788773. [6] DENG Y, LU J, LI W, et al. Reciprocal inhibition of YAP/TAZ and NF-κB regulates osteoarthritic cartilage degradation. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):4564. [7] QI H, ZHANG Y, XU L, et al. Loss of RAP2A Aggravates Cartilage Degradation in TMJOA via YAP Signaling. J Dent Res. 2023;102(3):302-312. [8] MA S, MENG Z, CHEN R, et al.The Hippo Pathway: Biology and Pathophysiology. Annu Rev Biochem. 2019;88:577-604. [9] YU FX, GUAN KL. The Hippo pathway: regulators and regulations. Genes Dev. 2013;27(4):355-71. [10] ROSELLÓ-DÍEZ A, JOYNER AL. Regulation of Long Bone Growth in Vertebrates; It Is Time to Catch Up. Endocr Rev. 2015;36(6):646-680. [11] JOHNSON R, HALDER G. The two faces of Hippo: targeting the Hippo pathway for regenerative medicine and cancer treatment. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014;13(1):63-79. [12] DEY A, VARELAS X, GUAN KL. Targeting the Hippo pathway in cancer, fibrosis, wound healing and regenerative medicine. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020; 19(7):480-494. [13] POCATERRA A, ROMANI P, DUPONT S. YAP/TAZ functions and their regulation at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2020;133(2):jcs230425. [14] CAO X, WANG C, LIU J, et al. Regulation and functions of the Hippo pathway in stemness and differentiation. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2020;52(7):736-748. [15] XIONG J, ALMEIDA M, O’BRIEN CA. The YAP/TAZ transcriptional co-activators have opposing effects at different stages of osteoblast differentiation. Bone. 2018;112:1-9. [16] GONG Y, LI SJ, LIU R, et al. Inhibition of YAP with siRNA prevents cartilage degradation and ameliorates osteoarthritis development. J Mol Med (Berl). 2019;97(1):103-114. [17] CHEN L, JIN X, MA J, et al. YAP at the progression of inflammation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;11:1204033. [18] CAIRE R, AUDOUX E, COURBON G, et al. YAP/TAZ: Key Players for Rheumatoid Arthritis Severity by Driving Fibroblast Like Synoviocytes Phenotype and Fibro-Inflammatory Response. Front Immunol. 2021;12:791907. [19] LI Y, WANG J, ZHONG W. Regulation and mechanism of YAP/TAZ in the mechanical microenvironment of stem cells (Review). Mol Med Rep. 2021; 24(1):506. [20] KEGELMAN CD, COLLINS JM, NIJSURE MP, et al. Gone Caving: Roles of the Transcriptional Regulators YAP and TAZ in Skeletal Development. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020;18(5):526-540. [21] CHENG B, LI M, WAN W, et al. Predicting YAP/TAZ nuclear translocation in response to ECM mechanosensing. Biophys J. 2023;122(1):43-53. [22] PAVEL M, RENNA M, PARK SJ, et al. Contact inhibition controls cell survival and proliferation via YAP/TAZ-autophagy axis. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):2961. [23] KANEKO K, ITO M, NAOE Y, et al.Integrin αv in the mechanical response of osteoblast lineage cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;447(2):352-357. [24] DICERBO M, BENMASSAOUD MM, VEGA SL. Porous Scaffold-Hydrogel Composites Spatially Regulate 3D Cellular Mechanosensing. Front Med Technol. 2022;4:884314. [25] KOSONEN JP, ESKELINEN ASA, OROZCO GA, et al. Injury-related cell death and proteoglycan loss in articular cartilage: Numerical model combining necrosis, reactive oxygen species, and inflammatory cytokines. PLoS Comput Biol. 2023;19(1):e1010337. [26] TAKAHATA K, ARAKAWA K, ENOMOTO S, et al. Joint instability causes catabolic enzyme production in chondrocytes prior to synovial cells in novel non-invasive ACL ruptured mouse model. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2023;31(5):576-587. [27] ESKELINEN ASA, TANSKA P, FLOREA C, et al.Mechanobiological model for simulation of injured cartilage degradation via pro-inflammatory cytokines and mechanical stimulus. PLoS Comput Biol. 2020;16(6):e1007998. [28] KHAJEHSAEID H, ABDOLLAHPOUR Z. Progressive deformation-induced degradation of knee articular cartilage and osteoarthritis. J Biomech. 2020; 111:109995. [29] 伍伟挺,黎润光,曹生鲁,等.过度周期性机械应力刺激可引起软骨细胞炎症反应及凋亡[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(29):4608-4613. [30] HIROSE N, OKAMOTO Y, YANOSHITA M, et al. Protective effects of cilengitide on inflammation in chondrocytes under excessive mechanical stress. Cell Biol Int. 2020;44(4):966-974. [31] SONG F, MAO X, DAI J, et al. Integrin αVβ3 Signaling in the Progression of Osteoarthritis Induced by Excessive Mechanical Stress. Inflammation. 2023;46(2):739-751. [32] WANG S, LI W, ZHANG P, et al. Mechanical overloading induces GPX4-regulated chondrocyte ferroptosis in osteoarthritis via Piezo1 channel facilitated calcium influx. J Adv Res. 2022;41:63-75. [33] ZHENG W, LI X, LIU D, et al.Mechanical loading mitigates osteoarthritis symptoms by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy. FASEB J. 2019;33(3):4077-4088. [34] WANG Y, JIN Z, JIA S, et al. Mechanical stress protects against chondrocyte pyroptosis through TGF-β1-mediated activation of Smad2/3 and inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway in an osteoarthritis model. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;159:114216. [35] CHANG SH, MORI D, KOBAYASHI H, et al. Excessive mechanical loading promotes osteoarthritis through the gremlin-1-NF-κB pathway. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1442. [36] CAI S, ZOU Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Mechanical stress reduces secreted frizzled-related protein expression and promotes temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Bone. 2022;161:116445. [37] YAO W, DAI H, GUI J. Mechanical stress promotes cartilage repair in inflammatory environment. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2019; 48(5):517-525. [38] LEE MS, TRINDADE MC, IKENOUE T, et al. Intermittent hydrostatic pressure inhibits shear stress-induced nitric oxide release in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes in vitro. J Rheumatol. 2003;30(2):326-328. [39] NI R, GUO XE, YAN C, et al.Hemodynamic stress shapes subchondral bone in osteoarthritis: An emerging hypothesis. J Orthop Translat. 2021;32:85-90. [40] ZHEN G, GUO Q, LI Y, et al. Mechanical stress determines the configuration of TGFβ activation in articular cartilage. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):1706. [41] YE W, GUO H, YANG X, et al. Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Versus Whole Body Vibration on Cartilage and Subchondral Trabecular Bone in Mice With Knee Osteoarthritis. Bioelectromagnetics. 2020;41(4):298-307. [42] VENNE G, TSE MY, PANG SC, et al. Mechanically-induced osteophyte in the rat knee. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(6):853-864. [43] HOLYOAK DT, WHEELER TA, VAN DER MEULEN MCH, et al. Injectable mechanical pillows for attenuation of load-induced post-traumatic osteoarthritis. Regen Biomater. 2019;6(4):211-219. [44] JANG W, KIM T, KOO JS, et al. Mechanical cue-induced YAP instructs Skp2-dependent cell cycle exit and oncogenic signaling. EMBO J. 2017; 36(17):2510-2528. [45] YANG K, WU Y, CHENG P, et al. YAP and ERK mediated mechanical strain-induced cell cycle progression through RhoA and cytoskeletal dynamics in rat growth plate chondrocytes. J Orthop Res. 2016;34(7):1121-1129. [46] KLINCUMHOM N, LORTHONGPANICH C, THUMANU K, et al. Intermittent compressive force regulates human periodontal ligament cell behavior via yes-associated protein. Heliyon. 2022;8(10):e10845. [47] YAO W, MA A, ZHANG Z, et al.Intermittent Hydrostatic Pressure Promotes Cartilage Repair in an Inflammatory Environment through Hippo-YAP Signaling In Vitro and In Vivo. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022:3215461. [48] CUI Y, MIAO MZ, WANG M, et al.Yes-associated protein nuclear translocation promotes anabolic activity in human articular chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2023:S1063-4584(23)00760-4. [49] WANG Z, CUI M, QU Y, et al.Hypoxia Protects Rat Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Against Compression-Induced Apoptosis in the Degenerative Disc Microenvironment Through Activation of the HIF-1α/YAP Signaling Pathway. Stem Cells Dev. 2020;29(20):1309-1319. [50] JING X, YANG X, ZHANG W, et al. Mechanical loading induces HIF-1α expression in chondrocytes via YAP. Biotechnol Lett. 2020;42(9):1645-1654. [51] KONG L, XIE YS, MA XD, et al. Mechanism of YAP1 in the senescence and degeneration of endplate chondrocytes induced by intermittent cyclic mechanical tension. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):229. [52] LIU Y, TIAN H, HU Y, et al. Mechanosensitive Piezo1 is crucial for periosteal stem cell-mediated fracture healing. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18(10):3961-3980. [53] WANG L, YOU X, LOTINUN S, et al.Mechanical sensing protein PIEZO1 regulates bone homeostasis via osteoblast-osteoclast crosstalk. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):282. [54] WEI Q, HOLLE A, LI J, et al. BMP-2 Signaling and Mechanotransduction Synergize to Drive Osteogenic Differentiation via YAP/TAZ. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020;7(15):1902931. [55] YAPKLINCUMHOM N, LORTHONGPANICH C, THUMANU K, et al. Intermittent compressive force regulates human periodontal ligament cell behavior via yes-associated protein. Heliyon. 2022;8(10):e10845. [56] ZHONG G, SU S, LI J, et al. Activation of Piezo1 promotes osteogenic differentiation of aortic valve interstitial cell through YAP-dependent glutaminolysis. Sci Adv. 2023;9(22):eadg0478. [57] YANG Y, WANG BK, CHANG ML, et al. Cyclic Stretch Enhances Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Periodontal Ligament Cells via YAP Activation. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:2174824. [58] ZHU Z, TANG T, HE Z, et al. Uniaxial cyclic stretch enhances osteogenic differentiation of OPLL-derived primary cells via YAP-Wnt/β-catenin axis. Eur Cell Mater. 2023;45:31-45. [59] PENG Y, QU R, FENG Y, et al.Regulation of the integrin αVβ3- actin filaments axis in early osteogenesis of human fibroblasts under cyclic tensile stress. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):523. [60] ZHONG W, TIAN K, ZHENG X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell and chondrocyte fates in a multishear microdevice are regulated by Yes-associated protein. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(14):2083-2093. [61] YIN S, ZHANG W, TANG Y, et al. Preservation of alveolar ridge height through mechanical memory: A novel dental implant design. Bioact Mater. 2020;6(1):75-83. [62] LI Y, XIAO C, LI R, et al. Role of Yes-associated protein (YAP) in regulation of mesenchymal stem cell tenogenic differentiation. J Mol Histol. 2022; 53(2):273-283. [63] FENG Q, GAO H, WEN H, et al. Engineering the cellular mechanical microenvironment to regulate stem cell chondrogenesis: Insights from a microgel model. Acta Biomater. 2020;113:393-406. [64] DZAMUKOVA M, BRUNNER TM, MIOTLA-ZAREBSKA J, et al. Mechanical forces couple bone matrix mineralization with inhibition of angiogenesis to limit adolescent bone growth. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):3059. [65] LI L, LI H, HE Y, et al. Cyclic pulsation stress promotes bone formation of tissue engineered laminae through the F-actin/YAP-1/β-Catenin signaling axis. NPJ Regen Med. 2021;6(1):51. [66] NAKAJIMA H, YAMAMOTO K, AGARWALA S, et al. Flow-Dependent Endothelial YAP Regulation Contributes to Vessel Maintenance. Dev Cell. 2017;40(6):523-536.e6. [67] WANG X, LIANG X, ZHOU L, et al. Yes-associated protein reacts differently in vascular smooth muscle cells under different intensities of mechanical stretch. Aging (Albany NY). 2022;14(1):286-296. [68] ZHU J, RUAN G, CEN H, et al. Association of serum levels of inflammatory markers and adipokines with joint symptoms and structures in participants with knee osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2022;61(3):1044-1052. [69] MOLNAR V, MATIŠIĆ V, KODVANJ I, et al. Cytokines and Chemokines Involved in Osteoarthritis Pathogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(17):9208. [70] ZHAO Z, BEHM C, TIAN Z, et al. Cyclic tensile strain-induced yes-associated protein activity modulates the response of human periodontal ligament mesenchymal stromal cells to tumor necrosis factor-α. Arch Oral Biol. 2022;143:105527. [71] ZARKA M, ETIENNE F, BOURMAUD M, et al. Mechanical loading activates the YAP/TAZ pathway and chemokine expression in the MLO-Y4 osteocyte-like cell line. Lab Invest. 2021;101(12):1597-1604. [72] WEI W, XUE L, TAN L, et al. Inhibition of yes-associated protein dephosphorylation prevents aggravated periodontitis with occlusal trauma. J Periodontol. 2021;92(7):1036-1048. [73] FENG X, LI S, WANG S, et al. Piezo1 mediates the degradation of cartilage extracellular matrix in malocclusion-induced TMJOA. Oral Dis. 2023. doi: 10.1111/odi.14615. [74] WANG X, LIAO H, LIU Y, et al. Aspirin reverses inflammatory suppression of chondrogenesis by stabilizing YAP. Cell Prolif. 2023;56(4):e13380. [75] ZHANG Q, HAN X, CHEN J, et al. Yes-associated protein (YAP) and transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif (TAZ) mediate cell density-dependent proinflammatory responses. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(47): 18071-18085. |
| [1] | 马 驰, 王 宁, 陈 拥, 魏志晗, 刘逢纪, 朴成哲. 3D打印个体化截骨导板结合定制钢板在开放楔形胫骨高位截骨中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1863-1869. |
| [2] | 余 帅, 刘家伟, 朱 彬, 潘 檀, 李兴龙, 孙广峰, 于海洋, 丁 亚, 王宏亮. 小分子药物治疗骨关节炎的热点问题及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [3] | 赵济宇, 王少伟. 叉头框转录因子O1信号通路与骨代谢[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [4] | 孙韫頔, 程露露, 万海丽, 常 赢, 熊雯娟, 夏 渊. 神经肌肉训练对膝骨关节炎患者疼痛和功能影响的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1945-1952. |
| [5] | 邓柯淇, 李光第, GOSWAMI ASHUTOSH, 刘星余, 何孝勇. 基于生物信息学对骨关节炎铁超载关键基因的筛选与验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1972-1980. |
| [6] | 尹 路, 蒋川锋, 陈俊杰, 易 明, 王子赫, 石厚银, 汪国友, 沈骅睿. 沙苑子苷A对关节软骨细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [7] | 王佩光, 张小文, 麦美斯, 黎璐茜, 黄 浩. 广义估计方程评估浮针法联合穴位埋线治疗不同分期膝骨关节炎的疗效[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1565-1571. |
| [8] | 王秋月, 靳 攀, 蒲 锐. 运动干预与细胞焦亡在骨关节炎中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [9] | 陈跃平, 陈 锋, 彭清林, 陈荟伊, 董盼锋. 三七治疗骨关节炎机制:基于UHPLC-QE-MS、网络药理学及分子动力学模拟[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1751-1760. |
| [10] | 杨治航, 孙祖延, 黄文良, 万 喻, 陈仕达, 邓 江. 神经生长因子促进兔骨髓间充质干细胞软骨分化并抑制肥大分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [11] | 钱 琨, 李子卿, 孙 水. 内质网应激与常见退行性骨骼疾病的发生与发展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1285-1295. |
| [12] | 马浩宇, 乔鸿超, 郝茜茜, 史冬博. 不同运动强度与骨关节炎发病风险的效应分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1305-1311. |
| [13] | 贺光辉, 原 杰, 柯燕琴, 丘小婷, 张晓玲. Hemin调控小鼠软骨细胞氧化应激的线粒体途径[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [14] | 何 波, 陈 文, 马岁录, 何志军, 宋 渊, 李金鹏, 刘 涛, 魏晓涛, 王威威, 谢 婧. 皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤的发病机制及治疗进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1230-1238. |
| [15] | 徐田杰, 樊佳欣, 郭小玲, 贾 祥, 赵兴旺, 刘凯楠, 王 茜. 二甲双胍抑制PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路保护骨关节炎模型大鼠关节软骨[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(5): 1003-1012. |
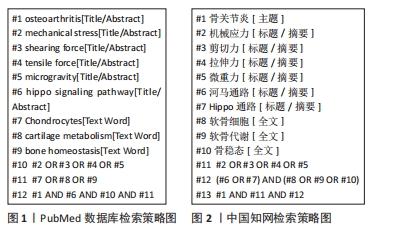
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者于2023年5月进行文献检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 各数据库建库时间至2023 年。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed、Web of Science、Embase、中国知网、维普及万方数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“骨关节炎,机械应力,河马通路,软骨细胞,软骨代谢,骨稳态”,英文检索词为“osteoarthritis,mechanical stress,hippo pathway,Chondrocytes,cartilage metabolism,bone homeostasis”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著,综述,述评,实验报告,基础或临床研究等。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 未进行手工检索。
1.1.7 检索策略 见图1,2。
1.2 纳入排除标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①机械应力调控Hippo干预骨关节炎的相关研究;②采用随机对照试验、临床前研究和动物实验等科学设计,具有较高的可靠性和可信度的文献;③对同一研究领域内选择发表年份较新的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①研究内容重复及相似的文献;②资料及数据不全的文献;③与该综述相关性较低的文献。
1.3 质量评估 初步共得到868篇相关文献,经资料收集者互相评估纳入文献的有效性和适用性,通过阅读文题和摘要进行初步筛选;排除中英文文献重复性研究,以及内容不相关的文献,最终共纳入中英文文献75篇进行综述,其中中文文献1篇,来源于中国知网;英文文献74篇,来源于 PubMed、Web of Science、Embase数据库。文献检索流程见图3。
机械应力刺激常采用拉伸、压缩、剪切力学等,其调控效应具有频率、时间、强度依赖性。不同机械类型和刺激强度、频率对Hippo通路的调控不同,异常的机械应力通常强度较大或较小、频率较快或较慢及较持久和较短暂,而生理性机械应力通常处于两者之间。对于间充质干细胞,强刺激导致YAP核移位增加刺激间充质干细胞增殖并向成骨分化,弱刺激则导致YAP失活诱导其向软骨分化。对于软骨细胞来说,适宜的刺激活化YAP则导致软骨细胞增殖,促进软骨修复,强刺激则灭活YAP导致软骨细胞变性。因此对不同的组织,相同的机械应力也会产生不同的作用。生理性机械应力与病理性机械应力对骨关节炎具有相反的影响,但对产生生理和病理性刺激的机械应力阈值还未有一致结论,所以探究生理病理机械应力刺激的界限和阈值可以作为今后的研究方向,以期为临床定制治疗性机械刺激提供理论依据。另外,随着组织工程的发展和生物材料研究,生物力学对疾病的影响受到广泛关注,众多研究已表明异常机械应力与骨关节炎的发生发展密切相关,因此应用生物材料调整机械应力可能在治疗骨关节炎方面具有疗效,但目前相关研究较少,还需更多研究结果进行验证。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
HIPPO通路:是机体生长发育过程中关键的调节因子,具有促进细胞增殖组织器官生长的作用。通过上游因子控制HIPPO通路的激活和关闭,既具有修复损伤的功能又会导致组织器官的异常增生。机械应力:是流体剪切力、拉伸力、压缩力、超重力、微重力、基质硬度及细胞密度等各种物理力的总称。机械应力存在于生命体的方方面面,生理性机械应力可维持机体生长发育,而异常的机械应力则会导致疾病的发生。
(2)由于机械应力的类型、刺激的强度、频率、持续时间不同,对骨关节炎的影响不同,至今还未有统一的阈值界限能够区分机械刺激对骨关节炎的正向和反向作用。还需进一步实验研究来确定。另外研究尚存在一些不足,对机械应力的探索仍旧停留在实验室阶段,具体如何作用于临床还需进一步的后续研究。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||