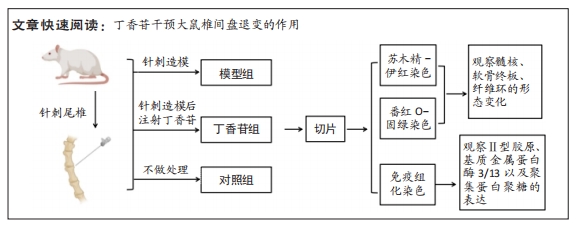
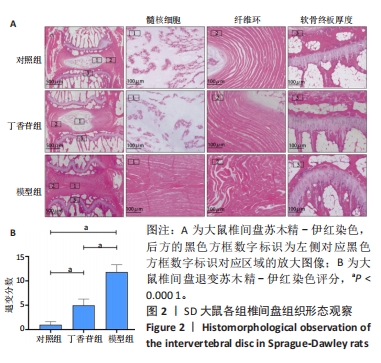
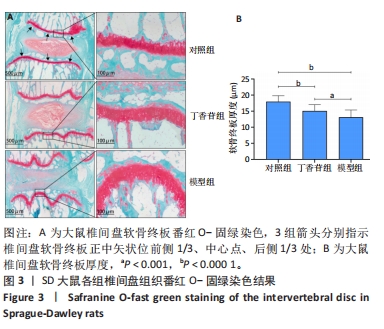
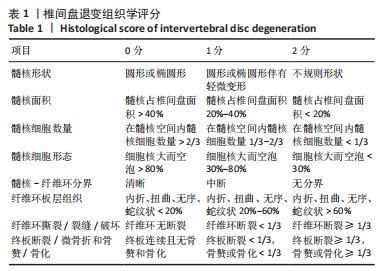
[1] 陈莎,王诗忠,邓德万.大鼠腰椎间盘退变模型的建立及其形态学观察[J].福建中医药,2021,52(9):39-40.
[2] 康小彪,李鹏飞,滕元平,等.淫羊藿苷通过核转录因子KappaB通路减轻大鼠椎间盘退变[J].广州中医药大学学报,2022,39(8):1878-1885.
[3] JENSEN CE, RIIS A, PETERSEN KD, et al. Economic evaluation of an implementation strategy for the management of low back pain in general practice. Pain. 2017;158(5): 891-899.
[4] 方未晶.髓核靶向性纳米给药系统的构建及在椎间盘退变中的应用[D].杭州:浙江大学,2020.
[5] ROH EJ, DARAI A, KYUNG JW, et al. Genetic Therapy for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1579.
[6] 马振,李延坤,翟凯,等.基质金属蛋白酶-1在椎间盘退变中的表达与调节机制的研究进展[J].湖北民族学院学报(医学版),2019,36(1):72-74.
[7] 许大勇,李云朋,魏景梅,等.芸香苷改善大鼠椎间盘退变的机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(14):2139-2145.
[8] 王啸华,何敢声,谢林.氧化应激在椎间盘退变中的作用进展[J].中医正骨,2023, 35(5):44-48.
[9] WANG G, HUANG K, DONG Y, et al. Lycorine Suppresses Endplate-Chondrocyte Degeneration and Prevents Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Inhibiting NF-kappaB Signalling Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;45(3):1252-1269.
[10] 杨青志,毛碧峰.腰椎间盘突出症的治疗进展[J].实用中医内科杂志,2023,37(6): 66-70.
[11] 代守前.丹酚酸B调节氧化应激缓解椎间盘退变的体内体外实验研究[D].苏州:苏州大学,2021.
[12] KEOROCHANA G, JOHNSON JS, TAGHAVI CE, et al. The effect of needle size inducing degeneration in the rat caudal disc: evaluation using radiograph, magnetic resonance imaging, histology, and immunohistochemistry. Spine J. 2010;10(11):1014-1023.
[13] HAN B, ZHU K, LI FC, et al. A simple disc degeneration model induced by percutaneous needle puncture in the rat tail. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(18):1925-1934.
[14] SUZUKI S, FUJITA N, HOSOGANE N, et al. Excessive reactive oxygen species are therapeutic targets for intervertebral disc degeneration. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:316.
[15] WANG Y, CHENG H, WANG T, et al. Oxidative stress in intervertebral disc degeneration: Molecular mechanisms, pathogenesis and treatment. Cell Prolif. 2023;56(9):e13448.
[16] 王倩,卢子昂,李利和,等.青藤碱可有效抑制白细胞介素1β介导的髓核细胞凋亡[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(2):224-230.
[17] KANG L, LIU S, LI J, et al. The mitochondria-targeted anti-oxidant MitoQ protects against intervertebral disc degeneration by ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction and redox imbalance. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(3):e12779.
[18] YU H, HOU G, CAO J, et al. Mangiferin Alleviates Mitochondrial ROS in Nucleus Pulposus Cells and Protects against Intervertebral Disc Degeneration via Suppression of NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:6632786.
[19] GONG X, ZHANG L, JIANG R, et al. Hepatoprotective effects of syringin on fulminant hepatic failure induced by D-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide in mice. J Appl Toxicol. 2014;34(3):265-271.
[20] ZHANG H, GU H, JIA Q, et al. Syringin protects against colitis by ameliorating inflammation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020;680:108242.
[21] 石雅倩,李鑫,黄思源,等.紫丁香苷调控PI3K/Akt/mTOR诱导乳腺癌细胞凋亡的研究(英文)[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2023:1-16. doi:10.16476/j.pibb.2023.0061
[22] 宋媛媛,周越,孙守兵,等.丁香苷对免疫功能低下小鼠的免疫调节作用[J].中药药理与临床,2013,29(2):44-47.
[23] 石美晶,师幸伟,石珍,等.丁香苷对H/R心肌细胞的保护作用及其机制研究[J].西部医学,2019,31(3):364-369.
[24] 宋媛媛,李媛,张洪泉.丁香苷对大鼠佐剂性关节炎的治疗作用及其机制[J].药学学报,2010,45(8):1006-1011.
[25] 谭俊毅.丁香苷通过FOXO3a/NF-κB途径对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤的神经保护作用[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2021.
[26] ZHANG B, ZHAO Q, LI Y, et al. Moxibustion alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration via activation of the HIF-1alpha/VEGF pathway in a rat model. Am J Transl Res. 2019; 11(9):6221-6231.
[27] 廖瑶,涂婷,曾惜羽,等.瑞芬太尼对椎间盘退变模型大鼠椎间盘的影响及机制[J].重庆医科大学学报,2023,48(7):760-764.
[28] LAI A, GANSAU J, GULLBRAND SE, et al. Development of a standardized histopathology scoring system for intervertebral disc degeneration in rat models: An initiative of the ORS spine section. JOR Spine. 2021;4(2):e1150.
[29] 吴靖平,朱斌,丁磊,等.大鼠椎间盘软骨终板退变与细胞凋亡的形态计量学研究[J].复旦学报(医学版),2010,37(2):140-145.
[30] BASSO M, CAVAGNARO L, ZANIRATO A, et al. What is the clinical evidence on regenerative medicine in intervertebral disc degeneration? Musculoskelet Surg. 2017; 101(2):93-104.
[31] 陈江,肖辉灯,孙旗,等.人椎间盘髓核细胞增殖活性与益肾活血通络方的干预调控[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(8):1200-1206.
[32] ZHANG Y, HE F, CHEN Z, et al. Melatonin modulates IL-1beta-induced extracellular matrix remodeling in human nucleus pulposus cells and attenuates rat intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(22):10499-10512.
[33] XIE T, PAN R, HUANG W, et al. Myricetin alleviates H2O2-induced senescence and apoptosis in rat nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2023;61(2):98-108.
[34] VO N, NIEDERNHOFER LJ, NASTO LA, et al. An overview of underlying causes and animal models for the study of age-related degenerative disorders of the spine and synovial joints. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(6):831-837.
[35] KIM KW, CHUNG HN, HA KY, et al. Senescence mechanisms of nucleus pulposus chondrocytes in human intervertebral discs. Spine J. 2009;9(8):658-666.
[36] FINKEL T. Signal transduction by reactive oxygen species. J Cell Biol. 2011;194(1):7-15.
[37] 刘祺,杨舟,朱青安.氧化应激与椎间盘退变的研究进展[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2020,38(3):363-366.
[38] JOHNSON ZI, SHAPIRO IM, RISBUD MV. Extracellular osmolarity regulates matrix homeostasis in the intervertebral disc and articular cartilage: evolving role of TonEBP. Matrix Biol. 2014;40:10-16.
[39] 陶红平,张觅,游长江,等.IL-13抑制剂在损伤大鼠尾椎间盘退变中的作用研究[J].生物技术进展,2021,11(3):369-377.
[40] ZHOU T, LIN H, CHENG Z, et al. Mechanism of microRNA-146a-mediated IL-6/STAT3 signaling in lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(2):1131-1135.
[41] HSU HT, YUE CT, TENG MS, et al. Immuohistochemical score of matrix metalloproteinase-1 may indicate the severity of symptomatic cervical and lumbar disc degeneration. Spine J. 2020;20(1):124-137.
[42] 赵继荣,杨正汉,马俊飞,等.中医药干预基质金属蛋白酶表达治疗椎间盘退变研究进展[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2023,29(5):272-282.
[43] 李陆虎.腰椎间盘突出症中医证型与退变椎间盘组织中MMP-2、MMP-13相关性研究[D].咸阳:陕西中医药大学,2017.
[44] 李熙阳.HOTAIR与COLⅡ、MMP3在椎间盘退变中的表达及相关性研究[D].衡阳:南华大学,2020.
[45] WANG Q, SUN CT. Characteristics and correlation analysis of spino-pelvic sagittal parameters in elderly patients with lumbar degenerative disease. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):127.
[46] LI W, ZHOU P, YAN B, et al. Disc regeneration by injectable fucoidan-methacrylated dextran hydrogels through mechanical transduction and macrophage immunomodulation. J Tissue Eng. 2023;14:1778670354.
[47] LIU J, ZHANG Z, GUO Q, et al. Syringin prevents bone loss in ovariectomized mice via TRAF6 mediated inhibition of NF-kappaB and stimulation of PI3K/AKT. Phytomedicine. 2018;42:43-50.
[48] SUN S, ZHANG Y, XU W, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction is involved in the cellular activity inhibition by eleutheroside B in SMMC-7721 and HeLa cells. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2022;41:774860050.
[49] DENG Z, REN C, TANG C, et al. Syringin alleviates hepatic fibrosis by enhancing autophagic flux and attenuating ER stress-TRIB3/SMAD3 in diabetic mice. Tissue Cell. 2023;83:102159.
[50] 罗力文,简秀英,周跃.GATA4调控NF-κB信号通路促进椎间盘髓核细胞发生炎症和衰老[J].免疫学杂志,2021,37(7):553-559.
[51] 李敬超.红景天苷通过Nrf2/ARE信号通路缓解椎间盘退变的研究[D].天津:天津医科大学,2020.
[52] 刘志超,张帆,祝永刚,等.身痛逐瘀汤方对椎间盘退变中PI3K/AKT通路影响的研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2018,26(10):14-19.
[53] 罗明秀,马海江,张甜,等.TGF-β对C-28/I2人软骨细胞聚集蛋白聚糖硫酸化修饰的影响[J].宁夏医学杂志,2021,43(6):481-484.
[54] 姚思琦,黎文正,汪虹.转化生长因子β/Smad信号通路与瘢痕疙瘩的靶向治疗[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(16):2619-2624. |