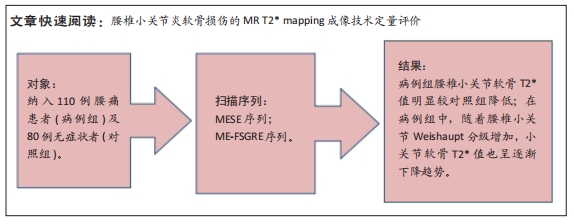
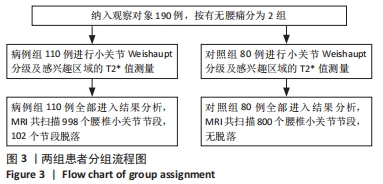
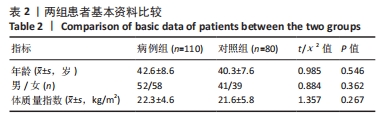
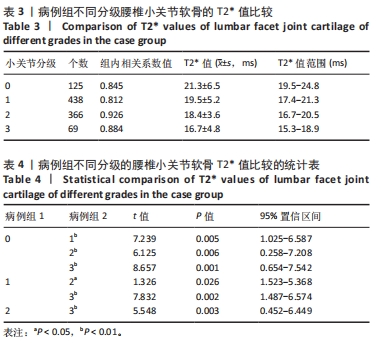
[1] HAUSER RA, MATIAS D, WOZNICA D, et al. Lumbar instability as an etiology of low back pain and its treatment by prolotherapy: A review. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2022;35(4):701-712.
[2] PAN CC, SIMON P, ESPINOZA ORÍAS AA, et al. Lumbar facet joint subchondral bone density in low back pain and asymptomatic subjects. Skeletal Radiol. 2020; 49(4):571-576.
[3] CHEN YS, LIU B, GU F, et al. Radiofrequency Denervation on Lumbar Facet Joint Pain in the Elderly: A Randomized Controlled Prospective Trial. Pain Physician. 2022;25(8):569-576.
[4] ZHAO H, LI H, LIANG S, et al. T2 mapping for knee cartilage degeneration in young patients with mild symptoms. BMC Med Imaging. 2022;22(1):72.
[5] BANJAR M, HORIUCHI S, GEDEON DN, et al. Review of Quantitative Knee Articular Cartilage MR Imaging. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2022;21(1):29-40.
[6] SHOJI T, SAKA H, INOUE T, et al. Preoperative T2 mapping MRI of articular cartilage values predicts postoperative osteoarthritis progression following rotational acetabular osteotomy. Bone Joint J. 2021;103-B(9):1472-1478.
[7] TSAI PH, WONG CC, CHAN WP. Radial T2* mapping reveals early meniscal abnormalities in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Eur Radiol. 2022;32(8):5642-5649.
[8] VERSCHUEREN J, EIJGENRAAM SM, KLEIN S, et al. T(2) mapping of healthy knee cartilage: multicenter multivendor reproducibility. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2021;11(4):1247-1255.
[9] 罗慕晴, 李宏伟, 张堃, 等. 3.0T MRI 3种扫描序列对腰椎小关节软骨成像的对比研究[J].磁共振成像,2022,13(8):65-70.
[10] HARADA K, TAKAHASHI K, IKUTA F, et al. Efficacy of a Deep Thermal Therapy System for Osteoarthritis of the Knee. J Nippon Med Sch. 2021;88(4):335-341.
[11] TAO H, HU Y, LU R, et al.Impact of Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability with Lateral Collateral Ligament Injuries on Biochemical Alterations in the Cartilage of the Subtalar and Midtarsal Joints Based on MRI T2 Mapping. Korean J Radiol. 2021;22(3):384-394.
[12] NISHINO K, HASHIMOTO Y, NISHIDA Y, et al. Magnetic Resonance Imaging T2 Relaxation Times of Articular Cartilage Before and After Arthroscopic Surgery for Discoid Lateral Meniscus. Arthroscopy. 2021;37(2):647-654.
[13] Leskinen HPP, Hänninen NE, Nissi MJ. T(2)orientation anisotropy mapping of articular cartilage using qMRI. Phys Med Biol. 2023;68(8). doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/acc169.
[14] Özcan-Ekşi EE, Börekci A, EKŞI MŞ. Facet Joint Orientation/Tropism Could Be Associated with Fatty Infiltration in the Lumbar Paraspinal Muscles. World Neurosurg. 2023;173:e606-e615.
[15] Raudner M, Schreiner MM, Hilbert T, et al. Clinical implementation of accelerated T(2) mapping: Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging as a biomarker for annular tear and lumbar disc herniation. Eur Radiol. 2021;31(6): 3590-3599.
[16] Chalian M, Li X, Guermazi A, et al. The QIBA Profile for MRI-based Compositional Imaging of Knee Cartilage. Radiology. 2021;301(2):423-432.
[17] Hu Y, Zhang Y, Li Q, et al. Magnetic Resonance Imaging T2* Mapping of the Talar Dome and Subtalar Joint Cartilage 3 Years After Anterior Talofibular Ligament Repair or Reconstruction in Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability. Am J Sports Med. 2021;49(3):737-746.
[18] Acosta JI, Mandell JC, Ermann J, et al. Grading Systems of Lumbar Facet Joint Inflammatory Changes on Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Scoping Review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2023;48(9):636-644.
[19] Yoon J, Efendy J, Redmond MJ. Septic arthritis of the lumbar facet joint. Case and literature review. J Clin Neurosci. 2020;71:299-303.
[20] Guermazi A, Roemer F, Burstein D, et al. Why radiography should no longer be considered a surrogate outcome measure for longitudinal assessment of cartilage in knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(6):247.
[21] Wang YX, Griffifith JF, Ahuja AT, et al. Non-invasive MRI assessment of the articular cartilage in clinical studies and experimental settings. World J Radiol. 2010;2(1):44-54.
[22] Crema MD, Roemer FW, Marra MD, et al. Articular cartilage in the knee: current MR imaging techniques and applications in clinical practice and research. Radiographics. 2011;31(1):37-61.
[23] Krause FG, Klammer G, Benneker LM, et al. Biochemical T2* MR quantification of ankle arthrosis in pes cavovarus. J Orthop Res. 2010;28(12): 1562-1568.
[24] Oneto J, Ellermann J, LaPrade R. Longitudinal evaluation of cartilage repair tissue after microfracture using T2-mapping: a case report with arthroscopic and MRI correlation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18(11):1545-1550.
[25] Su X, Zhang Y, Gao Q, et al. Preliminary study on the assessment of early cartilage degeneration by quantitative ultrashort echo time magnetic resonance imaging in vivo. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2022;12(7):3803-3812.
[26] Thaha R, Jogi SP, Rajan S, et al. A semi-automatic framework based upon quantitative analysis of MR-images for classification of femur cartilage into asymptomatic, early OA, and advanced-OA groups. J Orthop Res. 2022;40(4):779-790.
[27] Chen J, Qin Z, Zeng X, et al.Applicative value of T2 mapping in evaluating lumbosacral nerve root injury induced by lumbosacral disc herniation. Acta Radiol. 2023;64(4):1526-1532.
[28] Komaki S, Nakagawa S, Arai Y, et al. Cartilage degeneration of patellofemoral joint occurs in open wedge high tibial osteotomy, rather than in hybrid closed wedge high tibial osteotomy, during the early postoperative period: A qualitative analysis using MRI T(2) mapping. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2023; 31(1):10225536221151132.
[29] Abdollah V, Parent EC, Su A, et al. The effects of axial loading on the morphometric and T(2) characteristics of lumbar discs in relation to disc degeneration. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2021;83:105291.
[30] Liu ZZ, Wen HQ, Zhu YQ, et al. Short-Term Effect of Lumbar Traction on Intervertebral Discs in Patients with Low Back Pain: Correlation between the T2 Value and ODI/VAS Score. Cartilage. 2021;13(1_suppl):414S-423S.
[31] Ashmeik W, Baal JD, Foreman SC, et al. Investigating the Association of Metabolic Biomarkers With Knee Cartilage Composition and Structural Abnormalities Using MRI: A Pilot Study. Cartilage. 2021;13 (1_suppl):630S-638S.
[32] Guimaraes JB, Schwaiger BJ, Gersing AS, et al. Meniscal ramp lesions: frequency, natural history, and the effect on knee cartilage over 2 years in subjects with anterior cruciate ligament tears. Skeletal Radiol. 2021;50(3):551-558.
[33] 曹观美,赵斌. 轴位MR T2* mapping对腰椎小关节和椎间盘的定量研究[J].医学影像学杂志,2014,24(11):1993-1997.
[34] Gersing AS, Schwaiger BJ, Nevitt MC, et al. Anterior cruciate ligament abnormalities are associated with accelerated progression of knee joint degeneration in knees with and without structural knee joint abnormalities: 96-month data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021; 29(7):995-1005.
[35] Liao TC, Jergas H, Tibrewala R, et al. Longitudinal analysis of the contribution of 3D patella and trochlear bone shape on patellofemoral joint osteoarthritic features. J Orthop Res. 2021;39(3):506-515.
[36] Wang DY, Meng XY, Gong X, et al. Meniscal allograft transplantation in discoid meniscus patients achieves good clinical outcomes and superior chondroprotection compared to meniscectomy in the long term. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023;31(7):2877-2887.
[37] 文王强, 徐浩翔, 张泽佩, 等. 腰椎小关节退变的相关因素及生物力学特点[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(24):3883-3889.
[38] Wilson RL, Emery NC, Pierce DM, et al. Spatial Gradients of Quantitative MRI as Biomarkers for Early Detection of Osteoarthritis: Data From Human Explants and the Osteoarthritis Initiative. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2023;58(1):189-197.
[39] Iwata S, Eguchi Y, Takaoka H, et al. MRI T2-mapping of lumbar facet joints is effective for quantitative evaluation of lumbar instability in patients with degenerative lumbar disorders. Eur Spine J. 2022;31(6):1479-1486.
|