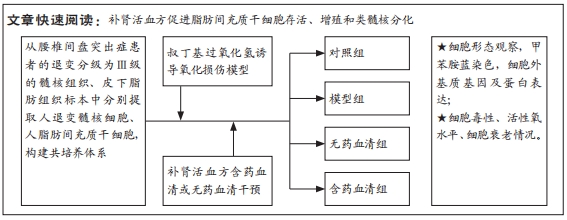
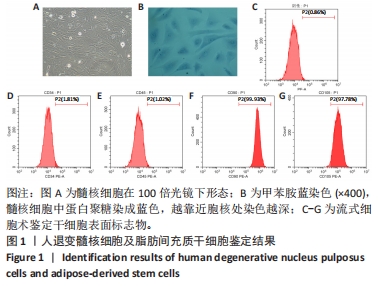
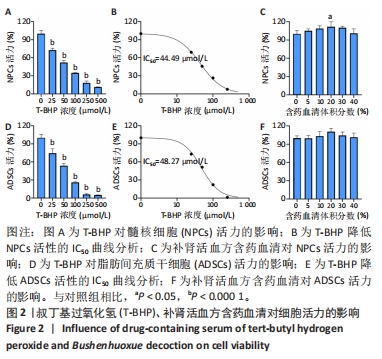
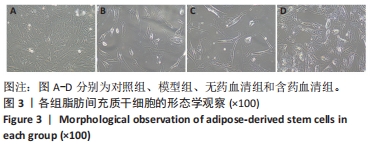
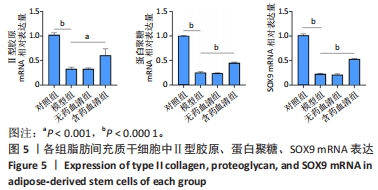
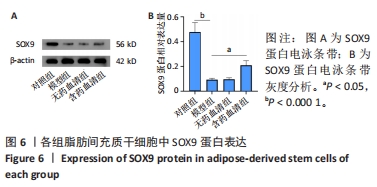
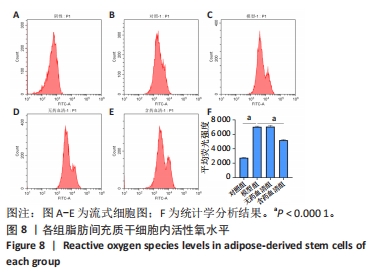
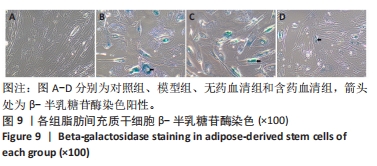
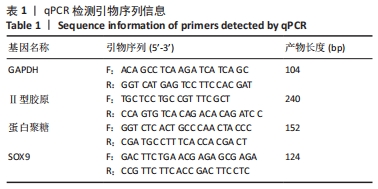
[1] GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392(10159):1789-1858.
[2] SONG Y, LU S, GENG W, et al. Mitochondrial quality control in intervertebral disc degeneration. Exp Mol Med. 2021;53(7):1124-1133.
[3] MA H, XIE C, CHEN Z, et al. MFG-E8 alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration by suppressing pyroptosis and extracellular matrix degradation in nucleus pulposus cells via Nrf2/TXNIP/NLRP3 axis. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8(1):209.
[4] KAMALI A, ZIADLOU R, LANG G, et al. Small molecule-based treatment approaches for intervertebral disc degeneration: Current options and future directions. Theranostics. 2021;11(1):27-47.
[5] COSTĂCHESCU B, NICULESCU AG, TELEANU RI, et al. Recent Advances in Managing Spinal Intervertebral Discs Degeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(12):6460.
[6] WANG J, XIA D, LIN Y, et al. Oxidative stress-induced circKIF18A downregulation impairs MCM7-mediated anti-senescence in intervertebral disc degeneration. Exp Mol Med. 2022;54(3):285-297.
[7] SONG D, GE J, WANG Y, et al. Tea Polyphenol Attenuates Oxidative Stress-Induced Degeneration of Intervertebral Discs by Regulating the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:6684147.
[8] ZHAO Y, QIU C, WANG W, et al. Cortistatin protects against intervertebral disc degeneration through targeting mitochondrial ROS-dependent NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Theranostics. 2020;10(15):7015-7033.
[9] 李才,许盼盼,胡捷,等.褪黑素调控Nrf2/ARE信号通路延缓髓核间充质干细胞退变的实验研究[J].中华全科医学,2022,20(11):1831-1835.
[10] ALPÍZAR-AGUIRRE A, GONZÁLEZ-CARBONELL RA, ORTIZ-PRADO A, et al. Biomechanics of the bone-screw interface in transpedicular spinal instrumentation. Acta Ortop Mex. 2022;36(3):172-178.
[11] CHU G, ZHANG W, HAN F, et al. The role of microenvironment in stem cell-based regeneration of intervertebral disc. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:968862.
[12] BURROW KL, HOYLAND JA, RICHARDSON SM. Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Exhibit Enhanced Proliferative Capacity and Retain Multipotency Longer than Donor-Matched Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells during Expansion In Vitro. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:2541275.
[13] 张永辉,李玲慧.人退变髓核细胞诱导脂肪间充质干细胞向类髓核细胞分化的实验研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(7):644-649.
[14] SUN J, YANG F, WANG L, et al. Delivery of coenzyme Q10 loaded micelle targets mitochondrial ROS and enhances efficiency of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in intervertebral disc degeneration. Bioact Mater. 2022;23:247-260.
[15] 陈炜成,董达胜,黄竞威,等.补肾健脾法联合顺势牵引对脾肾两虚型腰椎间盘突出症患者的临床疗效[J].中成药,2023,45(4):1146-1149.
[16] 程明,吴杨玲,刘羽,等.腰痹逐瘀止痛汤结合调脊通督针法治疗气滞血瘀型腰椎间盘突出症临床疗效及安全性观察[J].中华中医药学刊, 2021,39(11):236-239.
[17] 朱立国,展嘉文,冯敏山,等.补肾活血方治疗椎间盘源性腰痛的临床观察[J].世界中医药,2017,12(3):554-557.
[18] YANG S, LI L, ZHU L, et al. Bu-Shen-Huo-Xue-Fang modulates nucleus pulposus cell proliferation and extracellular matrix remodeling in intervertebral disk degeneration through miR-483 regulation of Wnt pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(12):19318-19329.
[19] 胡俊翔,包文娟,胡佳,等.揿针联合中药对气滞血瘀型腰椎间盘突出症患者的临床疗效观察[J/OL].中华中医药学刊:1-11[2023-08-10]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1546.R. 20230605.1709.014.html
[20] 赵旭涛,俞仲翔.石氏温经强腰方结合中药熏蒸治疗腰椎间盘突出症(寒湿痹阻型)临床效果研究[J/OL].辽宁中医杂志:1-9[2023-08-10]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1128.R.20230607. 1534.058.html
[21] 李凯明,朱立国,李玲慧,等.补肾活血方对兔退变椎间盘模型经典Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2020,35(12):6001-6005.
[22] LIU L, HE J, LIU C, et al. Cartilage intermediate layer protein affects the progression of intervertebral disc degeneration by regulating the extracellular microenvironment (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2021;47(2):475-484.
[23] ZHANG Y, YANG B, WANG J, et al. Cell Senescence: A Nonnegligible Cell State under Survival Stress in Pathology of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:9503562.
[24] SONG H, PARK KH. Regulation and function of SOX9 during cartilage development and regeneration. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020;67(Pt 1):12-23.
[25] FUGLERUD BM, DRISSLER S, LOTTO J, et al. SOX9 reprograms endothelial cells by altering the chromatin landscape. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(15):8547-8565.
[26] CHENG CC, UCHIYAMA Y, HIYAMA A, et al. PI3K/AKT regulates aggrecan gene expression by modulating Sox9 expression and activity in nucleus pulposus cells of the intervertebral disc. J Cell Physiol. 2009;221(3):668-676.
[27] ZHANG P, GAO G, ZHOU Z, et al. microRNA-130b downregulation potentiates chondrogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by targeting SOX9. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2021;54(4):e10345.
[28] KHALID S, EKRAM S, RAMZAN F, et al. Co-regulation of Sox9 and TGFβ1 transcription factors in mesenchymal stem cells regenerated the intervertebral disc degeneration. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:1127303.
[29] HUA W, LI S, LUO R, et al. Icariin protects human nucleus pulposus cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced mitochondria-mediated apoptosis by activating nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020;1866(1):165575.
[30] WANG Y, CHENG H, WANG T, et al. Oxidative stress in intervertebral disc degeneration: Molecular mechanisms, pathogenesis and treatment. Cell Prolif. 2023:e13448.
[31] XU J, SHAO T, LOU J, et al. Aging, cell senescence, the pathogenesis and targeted therapies of intervertebral disc degeneration. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1172920.
[32] CHEN HW, ZHOU JW, ZHANG GZ, et al. Emerging role and therapeutic implication of mTOR signalling in intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Prolif. 2023;56(1):e13338.
[33] SEOL D, COLEMAN MC, MARTIN JA, et al. Targeting oxidative stress with amobarbital to prevent intervertebral disc degeneration: Part I. in vitro and ex vivo studies. Spine J. 2021;21(6):1021-1030.
[34] FORRESTER SJ, KIKUCHI DS, HERNANDES MS, et al. Reactive Oxygen Species in Metabolic and Inflammatory Signaling. Circ Res. 2018;122(6):877-902.
[35] ZHANG C, GULLBRAND SE, SCHAER TP, et al. Combined Hydrogel and Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Moderate-Severity Disc Degeneration in Goats. Tissue Eng Part A. 2021;27(1-2):117-128.
[36] NORIEGA DC, ARDURA F, HERNÁNDEZ-RAMAJO R, et al. Treatment of Degenerative Disc Disease With Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Long-term Follow-up Results. Transplantation. 2021;105(2):e25-e27.
[37] 王宇翔,徐海栋,赵建宁.细胞移植治疗椎间盘退变的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2021,29(11):1009-1012.
[38] MOHAMED-AHMED S, FRISTAD I, LIE SA, et al. Adipose-derived and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: a donor-matched comparison. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):168.
[39] XIAO L, XU SJ, LIU C, et al. Sod2 and catalase improve pathological conditions of intervertebral disc degeneration by modifying human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Life Sci. 2021;267:118929.
[40] ZHANG W, SUN T, LI Y, et al. Application of stem cells in the repair of intervertebral disc degeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):70.
|