中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (21): 3438-3444.doi: 10.12307/2024.068
• 植入物相关大数据分析 Implant related big data analysis • 上一篇
椎间盘退变相关焦亡基因的综合分析
谢 越1,2,翟伟峰2,郭 际2,贾永伟2
- 1上海中医药大学,上海市 200120;2 上海中医药大学附属光华医院,上海市 201203
Integrative analyses of pyroptosis-related genes associated with intervertebral disc degeneration
Xie Yue1, 2, Zhai Weifeng2, Guo Ji2, Jia Yongwei2
- 1Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200120, China; 2Guanghua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China
摘要:
文题释义:
椎间盘退变:是一种退行性疾病,常伴有炎症,是导致椎间盘源性腰痛的重要原因之一。在年龄增长过程中,椎间盘内的髓核组织水分逐渐减少,椎间盘失去正常的弹性和张力,在外界因素(如损伤,劳累等)的作用下,纤维环结构破坏,髓核组织结构发生异常改变。细胞焦亡:又称细胞炎性坏死,是一种细胞程序性死亡方式。依赖于炎性半胱天冬酶(主要是Caspase-1,4,5,11),并伴有大量促炎症因子的释放,表现为细胞不断胀大直至细胞膜破裂,导致细胞内容物的释放进而激活强烈的炎症反应。
背景:椎间盘退变早期诊断和治疗尤为重要,髓核细胞焦亡在早期椎间盘退变过程中发挥着重要作用,但髓核细胞焦亡相关分子在早期椎间盘退变中发挥的作用及相关分子标志物仍不明确。
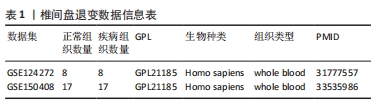
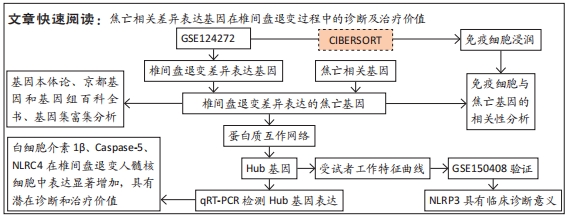
目的:探讨焦亡相关差异表达基因在椎间盘退变过程中的诊断及治疗价值。方法:整合GEO数据库椎间盘退变的公开数据集进行差异分析,与之前报道的33个焦亡基因取交集;使用基因本体论、京都基因和基因组百科全书对椎间盘退变焦亡相关基因进行通路富集分析,并使用基因集富集分析对椎间盘退变数据集进行富集分析;构建椎间盘退变样本中的免疫细胞谱,并将差异表达的细胞焦亡相关基因与免疫细胞进行相关性分析;构建蛋白质互作网络,筛选Hub基因以鉴定蛋白质相互作用网络中与椎间盘退变相关的关键基因;整合数据集绘制差异表达焦亡基因的受试者工作特征曲线,计算曲线下面积,探索目标基因的临床诊断价值;qRT-PCR验证正常人髓核细胞与椎间盘退变人髓核细胞之间焦亡相关基因的表达差异。
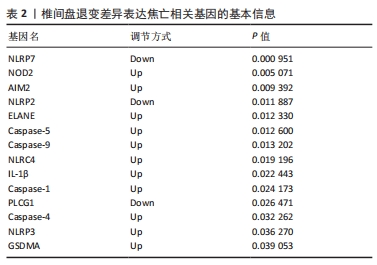
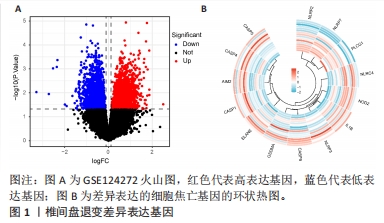
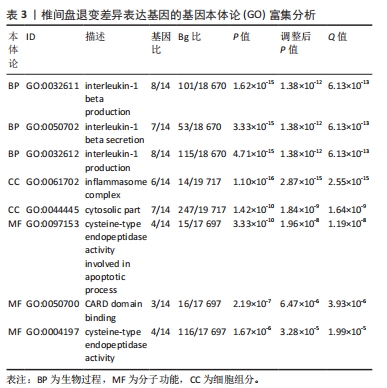
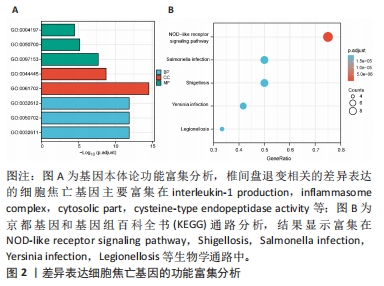
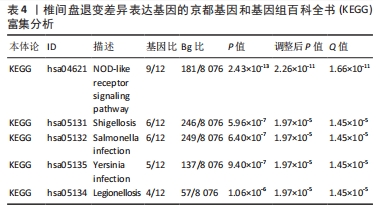
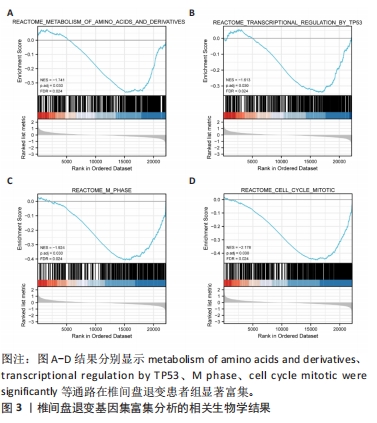
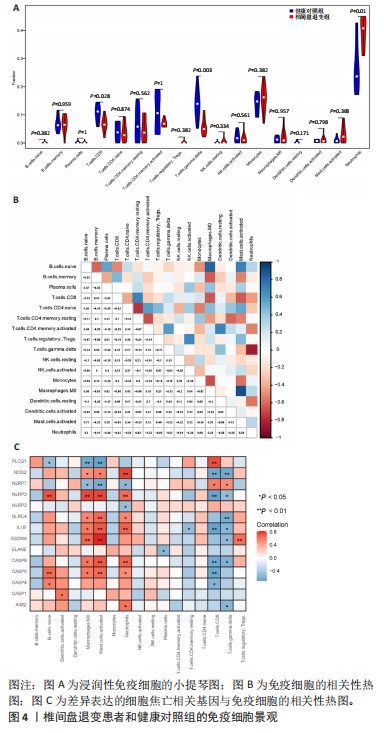
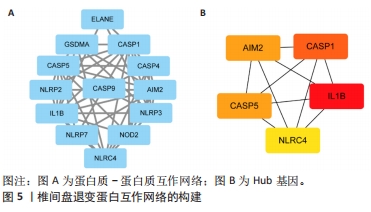
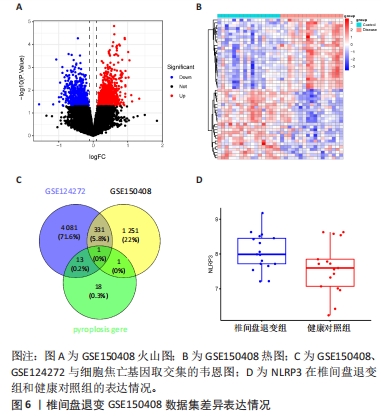
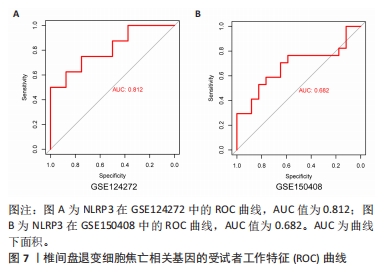
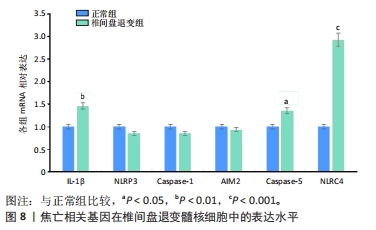
结果与结论:①获得4 426个与椎间盘退变相关的差异表达基因,交集后获得14个差异表达的焦亡相关基因;②基因本体论、京都基因和基因组百科全书分析揭示了重要的富集途径,主要与炎症、细胞周期、感染和NOD样受体通路相关;基因集富集分析显示氨基酸代谢、P53转录调节等通路在椎间盘退变患者中显著富集;免疫浸润分析提示椎间盘退变的发生发展与免疫细胞密切相关;③共筛选出5个Hub基因,分别为IL-1β、Caspase-1、AIM2、Caspase-5、NLRC4;④椎间盘退变关键生物标志物的获取及鉴定:将GEO两个数据集与焦亡基因取交集后发现NLRP3具有显著表达差异,受试者工作特征曲线显示NLRP3具有临床诊断意义;⑤qRT-PCR显示IL-1β、Caspase-5和NLRC4等Hub基因在椎间盘退变的髓核细胞中表达显著增加(P < 0.05),Caspase-1、AIM2以及NLRP3表达无差异(P > 0.05);⑥提示细胞焦亡在椎间盘退变发生发展过程中发挥重要作用,其中焦亡相关基因NLRP3、IL1-β、Caspase-5、NLRC4具有早期诊断和治疗价值。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2746-082X (谢越)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: