[1] HUANG EE, ZHANG N, GANIO EA, et al. Differential dynamics of bone graft transplantation and mesenchymal stem cell therapy during bone defect healing in a murine critical size defect. J Orthop Translat. 2022;36(8):64-74.
[2] SCHEMITSCH EH. Size Matters: defining critical in bone defect size. J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31(10):S20-S22.
[3] 罗卓荆,毕龙.中国骨缺损修复的成就与展望[J].空军军医大学学报,2022,43(4):263-267.
[4] KASHIRINA A, YAO YT, LIU YJ, et al. Biopolymers as bone substitutes: a review. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(10):3961-3983.
[5] 苑博,王智巍,唐一钒,等.3D打印技术构建不同比例聚己内酯-磷酸三钙支架及其体外诱导成骨性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(6):821-826.
[6] VAN VOSS MRH, VESUNA F, BOL GM, et al. Targeting mitochondrial translation by inhibiting DDX3: a novel radiosensitization strategy for cancer treatment. Oncogene. 2018;37(1):63-74.
[7] ALMUBARAK S, NETHERCOTT H, FREEBERG M, et al. Tissue engineering strategies for promoting vascularized bone regeneration. Bone. 2016;83(2):197-209.
[8] 栾春娟,侯海燕,王贤文.国际科技政策研究热点与前沿的可视化分析[J].科学学研究,2009,27(2):240-243.
[9] 陈悦,陈超美,刘则渊,等.CiteSpace知识图谱的方法论功能[J].科学学研究,2015, 33(2):242-253.
[10] 汪德根,陈田,王金莲,等.1980-2009年国内外旅游研究比较[J].地理学报,2011, 66(4):535-548.
[11] 于良楠,柯尊清.中国文化安全研究的热点主题与前沿——基于CiteSpace软件的可视化分析[J].中国文化产业评论,2021,30(1):130-146
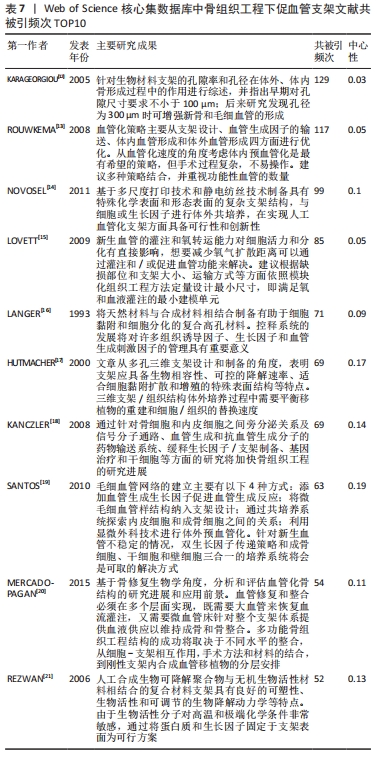
[12] KARAGEORGIOU V, KAPLAN D. Porosity of 3D biomaterial scaffolds and osteogenesis. Biomaterials. 2005;26(27):5474-5491.
[13] ROUWKEMA J, RIVRON NC, VAN BLITTERSWIJK CA. Vascularization in tissue engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 2008;26(8):434-441.
[14] NOVOSEL EC, KLEINHANS C, KLUGER PJ. Vascularization is the key challenge in tissue engineering. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011;63(4):300-311.
[15] LOVETT M, LEE K, EDWARDS A, et al. Vascularization strategies for tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2009;15(3):353-370.
[16] LANGER R, VACANTI JP. Tissue engineering. Science. 1993;260(5110):920-926.
[17] HUTMACHER DW. Scaffolds in tissue engineering bone and cartilage. Biomaterials. 2000,21(24):2529-2543.
[18] KANCZLER JM, OREFFO RO. Osteogenesis and angiogenesis: the potential for engineering bone. Eur Cell Mater. 2008;15(2):100-114.
[19] SANTOS MI, REIS RL.Vascularization in bone tissue engineering: physiology,current strategies,major hurdles and future challenges. Macromol Biosci. 2010;10(1):12-27.
[20] MERCADO-PAGÁN ÁE, STAHL AM, SHANJANI Y, et al. Vascularization in bone tissue engineering constructs. Ann Biomed Eng. 2015;43(3):718-729.
[21] REZWAN K, CHEN QZ, BLAKER JJ, et al. Biodegradable and bioactive porous polymer/inorganic composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2006;27(18): 3413-3431.
[22] WU C, ZHOU Y, XU M, et al. Copper-containing mesoporous bioactive glass scaffolds with multifunctional properties of angiogenesis capacity, osteostimulation and antibacterial activity. Biomaterials. 2013;34(2):422-433.
[23] SPILLER KL, NASSIRI S, WITHEREL CE, et al. Sequential delivery of immunomodulatory cytokines to facilitate the M1-to-M2 transition of macrophages and enhance vascularization of bone scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2015;37(1):194-207.
[24] TANG D, TARE RS, YANG LY, et al. Biofabrication of bone tissue: approaches, challenges and translation for bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2016;83(3):363-382.
[25] DE WITTE TM, FRATILA-APACHITEI LE, ZADPOOR AA, et al. Bone tissue engineering via growth factor delivery: from scaffolds to complex matrices. Regen Biomate. 2018; 5(4):197-211.
[26] ABBASI N, HAMLET S, LOVE RM, et al. Porous scaffolds for bone regeneration. J Sci Adv Mater Dev. 2020;5(1):1-9.
[27] WU C, CHANG J. Multifunctional mesoporous bioactive glasses for effective delivery of therapeutic ions and drug/growth factors. J Control Release. 2014;193(11):282-295.
[28] XU HHK, WANG P, WANG L, et al. Calcium phosphate cements for bone engineering and their biological properties. Bone Res. 2017;5(1):1-19.
[29] KARGOZAR S, BAINO F, HAMZEHLOU S, et al. Bioactive glasses: sprouting angiogenesis in tissue engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 2018;36(4):430-444.
[30] DIOMEDE F, MARCONI GD, FONTICOLI L, et al. Functional relationship between osteogenesis and angiogenesis in tissue regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(9):32-42.
[31] WU L, GU Y, LIU L, et al. Hierarchical micro/nanofibrous membranes of sustained releasing VEGF for periosteal regeneration. Biomaterials. 2019;227(1):119555.
[32] 董佳乐,魏远好,张洪武.基于知识图谱的骨缺损治疗可视化分析[J].国组织工程研究,2022,26(18):2906-2913.
[33] HSU EL, STOCK SR. Growth factors,carrier materials, and bone repair. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2020;262:121-56.
[34] BOSE S, ROY M, BANDYOPADHYAY A. Recent advances in bone tissue engineering scaffolds. Trends Biotechnol. 2012;30(10):546-554.
[35] CHEN YC, LIN RZ, QI H, et al. Functional human vascular network generated in photocrosslinkable gelatin methacrylate hydrogels. Adv Funct Mater. 2012;22(10):2027-2039.
[36] ZHU H, MONAVARI M, ZHENG K, et al. 3D bioprinting of multifunctional dynamic nanocomposite bioinks incorporating cu-doped mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles for bone tissue engineering. Small. 2022;18(12):2104996.
[37] TWOHIG C, HELSINGA M, MANSOORIFAR A, et al. A dual-ink 3D printing strategy to engineer pre-vascularized bone scaffolds in-vitro. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;123(3):111976.
[38] MANZINI BM, MACHADO LMR, NORITOMI PY, et al. Advances in Bone tissue engineering: a fundamental review. J Biosci. 2021;46(1):1-18.
[39] DALY AC, PITACCO P, NULTY J, et al. 3D printed microchannel networks to direct vascularisation during endochondral bone repair. Biomaterials. 2018;162(1):34-46.
[40] FITZPATRICK V, MARTIN-MOLDES Z, DECK A, et al. Functionalized 3D-printed silk-hydroxyapatite scaffolds for enhanced bone regeneration with innervation and vascularization. Biomaterials. 2021;276(9):120995.
[41] 贺丹.骨髓间充质干细胞在RGD改良壳聚糖基可注射纳米复合凝胶中的血管化研究[D].成都:西南交通大学,2019.
[42] 孙安,毕翔宇,韩祥祯,等.联合应用血管内皮生长因子及血小板衍生生长因子BB干预骨髓间充质干细胞的血管化及增殖能力[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(1):1-6.
[43] 周琦琪,韩祥祯,张文静,等.碱性成纤维细胞生长因子诱导大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞膜片成骨及成血管分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(1):1-5.
[44] 晏金超.3D打印挤出沉积制备金属阳离子掺杂HA骨支架研究[D].南昌:南昌大学, 2020.
[45] ZHOU X, QIAN Y, CHEN L, et al. Flowerbed-inspired biomimetic scaffold with rapid internal tissue infiltration and vascularization capacity for bone repair. ACS Nano. 2023; 17(5):5140-5156.
[46] CHENG WX, LIU YZ, MENG XB, et al. PLGA/β-TCP composite scaffold incorporating cucurbitacin B promotes bone regeneration by inducing angiogenesis. J Orthop Transl. 2021;31(11):41-51.
[47] XU H, WANG C, LIU C, et al. Cotransplantation of mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells for treating steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021;10(5):781-796.
[48] WINKLER S, MUTSCHALL H, BIGGEMANN J, et al. Human umbilical vein endothelial cell support bone formation of adipose-derived stem cell-loaded and 3D-printed osteogenic matrices in the arteriovenous loop model. Tissue Engineering Part A. 2021;27(5-6):413-423.
[49] ZHANG Y, XIE Y, HAO Z, et al. Umbilical mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome-encapsulated hydrogels accelerate bone repair by enhancing angiogenesis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(16):18472-18487.
[50] PIARD C, LUTHCKE R, KAMALITDINOV T, et al. Sustained delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor from mesoporous calcium‐deficient hydroxyapatite microparticles promotes in vitro angiogenesis and osteogenesis. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2021;109(7):1080-1087.
[51] BAYER EA, JORDAN J, ROY A, et al. Programmed platelet-derived growth factor-BB and bone morphogenetic protein-2 delivery from a hybrid calcium phosphate/alginate scaffold. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017;23(23-24):1382-1393.
[52] NOVAIS A, LESIEUR J, SADOINE J, et al. Priming dental pulp stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth with fibroblast growth factor-2 enhances mineralization within tissue-engineered constructs implanted in craniofacial bone defects. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(8):844-857.
[53] LEE J, HUH SJ, SEOK JM, et al. Surface engineering of 3D-printed scaffolds with minerals and a pro-angiogenic factor for vascularized bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2022; 140(3):730-744.
[54] WEI X, ZHOU W, TANG Z, et al. Magnesium surface-activated 3D printed porous PEEK scaffolds for in vivo osseointegration by promoting angiogenesis and osteogenesis. Bioact Mater. 2023;20(5):16-28.
[55] HOEMANN CD, GONZÁLEZ JR, GUZMÁN-MORALES J, et al. Chitosan coatings with distinct innate immune bioactivities differentially stimulate angiogenesis, osteogenesis and chondrogenesis in poly-caprolactone scaffolds with controlled interconnecting pore size. Bioact Mater. 2022;10(9):430-442.
[56] LI T, PENG M, YANG Z, et al. 3D-printed IFN-gamma-loading calcium silicate-beta-tricalcium phosphate scaffold sequentially activates M1 and M2 polarization of macrophages to promote vascularization of tissue engineering bone. Acta Biomater. 2018;71(3):96-107.
[57] CHEN S, WANG H, LIU D, et al. Early osteoimmunomodulation by mucin hydrogels augments the healing and revascularization of rat critical-size calvarial bone defects. Bioactive Materials. 2023;25(2):176-188.
[58] BISWAS L, CHEN J, DE ANGELIS J, et al. Lymphatic vessels in bone support regeneration after injury. Cell. 2023;186(2):382-397.
|