[1] LOEWNER S, HEENE S, BAROTH T, et al. Recent advances in melt electro writing for tissue engineering for 3d printing of microporous scaffolds for tissue engineering. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:896719.
[2] VESVORANAN O, ANUP A, HIXON KR. Current concepts and methods in tissue interface scaffold fabrication. Biomimetics (Basel). 2022;7(4):151.
[3] KONG B, LIU R, GUO J, et al. Tailoring micro/nano-fibers for biomedical applications. Bioact Mater. 2023;19:328-347.
[4] XUE J, WU T, DAI Y, et al. Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: methods, materials, and applications. Chem Rev. 2019;119(8):5298-5415.
[5] HUTMACHER DW, DALTON PD. Melt electrospinning. Chem Asian J. 2011;6(1):44-56.
[6] 李好义,贾紫初,刘宇亮,等.高压静电加载形式对聚合物熔体静电直写制备效果的影响[J].纺织学报,2023,44(4):32-37.
[7] MUERZA-CASCANTE ML, HAYLOCK D, HUTMACHER DW, et al. Melt electrospinning and its technologization in tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2015;21(2):187-202.
[8] KIM BS, PARK KE, KIM MH, et al. Effect of nanofiber content on bone regeneration of silk fibroin/poly(ε-caprolactone) nano/microfibrous composite scaffolds. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015;10:485-502.
[9] PARK SH, KIM TG, KIM HC, et al. Development of dual scale scaffolds via direct polymer melt deposition and electrospinning for applications in tissue regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2008;4(5):1198-1207.
[10] WUNNER FM, WILLE ML, NOONAN TG, et al. Melt electrospinning writing of highly ordered large volume scaffold architectures. Adv Mater. 2018;30(20):e1706570.
[11] DAGHRERY A, FERREIRA JA, XU J, et al. Tissue-specific melt electrowritten polymeric scaffolds for coordinated regeneration of soft and hard periodontal tissues. Bioact Mater. 2023;19:268-281.
[12] BUBAKIR M, LI H, BARHOUM A, et al. Advances in melt electrospinning technique.Handbook of Nanofibers,2017.
[13] CHEN Z, LIU Y, HUANG J, et al. Influences of process parameters of near-field direct-writing melt electrospinning on performances of polycaprolactone/nano-hydroxyapatite scaffolds. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(16):3404.
[14] HE XX, ZHENG J, YU GF, et al. Near-field electrospinning: progress and applications. J Phys Chem C. 2017;121(16):8663-8678.
[15] NAZEMI MM, KHODABANDEH A, HADJIZADEH A. Near-field electrospinning: crucial parameters, challenges, and applications. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2022;5(2):394-412.
[16] IBRAHIM YS, HUSSEIN EA, ZAGHO MM, et al. Melt electrospinning designs for nanofiber fabrication for different applications: 10. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(10):2455.
[17] DALTON PD, JOERGENSEN NT, GROLL J, et al. Patterned melt electrospun substrates for tissue engineering. Biomed Mater. 2008;3(3): 034109.
[18] BROWN TD, DALTON PD, HUTMACHER DW. Direct writing by way of melt electrospinning. Adv Mater. 2011;23(47):5651-5657.
[19] BROWN TD, SLOTOSCH A, THIBAUDEAU L, et al. Design and fabrication of tubular scaffolds via direct writing in a melt electrospinning mode. Biointerphases. 2012;7(1-4):13.
[20] FARRUGIA BL, BROWN TD, UPTON Z, et al. Dermal fibroblast infiltration of poly(ε-caprolactone) scaffolds fabricated by melt electrospinning in a direct writing mode. Biofabrication. 2013;5(2):025001.
[21] CASTILHO M, FEYEN D, FLANDES-IPARRAGUIRRE M, et al. Melt electrospinning writing of poly-hydroxymethylglycolide-co-ε-caprolactone-based scaffolds for cardiac tissue engineering. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017;6(18).doi: 10.1002/adhm.201700311.
[22] KADE JC, DALTON PD. Polymers for melt electrowriting. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(1): e2001232.
[23] CIPITRIA A, SKELTON A, DARGAVILLE TR, et al. Design, fabrication and characterization of pcl electrospun scaffolds—a review. J Mater Chem. 2011;21(26):9419-9453.
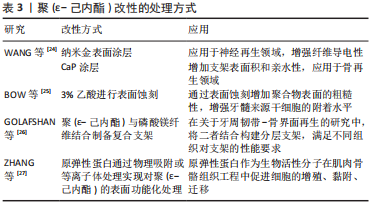
[24] WANG Y, ZHANG Y, ZHANG Z, et al. An injectable high-conductive bimaterial scaffold for neural stimulation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020;195:111210.
[25] BOW AJ, MASI TJ, DHAR MS. Etched 3d-printed polycaprolactone constructs functionalized with reduced graphene oxide for enhanced attachment of dental pulp-derived stem cells. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(12):2146.
[26] GOLAFSHAN N, CASTILHO M, DAGHRERY A, et al. Composite graded melt electrowritten scaffolds for regeneration of the periodontal ligament-to-bone interface. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023;15(10):12735-12749.
[27] ZHANG M, WANG Z, ZHANG A, et al. Development of tropoelastin-functionalized anisotropic pcl scaffolds for musculoskeletal tissue engineering. Regen Biomater. 2023;10:rbac087.
[28] TRACHSEL L, ZENOBI-WONG M, BENETTI EM. The role of poly(2-alkyl-2-oxazoline)s in hydrogels and biofabrication. Biomater Sci. 2021;9(8):2874-2886.
[29] HOCHLEITNER G, HÜMMER JF, LUXENHOFER R, et al. High definition fibrous poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) scaffolds through melt electrospinning writing. Polymer. 2014;55(20): 5017-5023.
[30] GHAVAMINEJAD A, ASHAMMAKHI N, WU XY, et al. Crosslinking strategies for 3d bioprinting of polymeric hydrogels. Small. 2020;16(35):e2002931.
[31] NAHM D, WEIGL F, SCHAEFER N, et al. A versatile biomaterial ink platform for the melt electrowriting of chemically-crosslinked hydrogels. Mater Horiz. 2020;7(3):928-933.
[32] RITZAU-REID KI, SPICER CD, GELMI A, et al. An electroactive oligo-edot platform for neural tissue engineering. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30(42):2003710.
[33] ASRI NAN, MAHAT MM, ZAKARIA A, et al. Fabrication methods of electroactive scaffold-based conducting polymers for tissue engineering application: a review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:876696.
[34] XIAORUI L, FUYIN Z, XUDONG W, et al. Biomaterial inks for extrusion-based 3d bioprinting: property, classification, modification, and selection. Int J Bioprint. 2022; 9(2):649.
[35] DALTON PD, WOODFIELD TBF, MIRONOV V, et al. Advances in hybrid fabrication toward hierarchical tissue constructs. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020;7(11):1902953.
[36] GAO Q, XIE C, WANG P, et al. 3D printed multi-scale scaffolds with ultrafine fibers for providing excellent biocompatibility. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;107: 110269.
[37] JUNGST T, PENNINGS I, SCHMITZ M, et al. Heterotypic scaffold design orchestrates primary cell organization and phenotypes in cocultured small diameter vascular grafts. Adv Funct Mater. 2019;29(43):1905987.
[38] DAGHRERY A, DE SOUZA ARAÚJO IJ, CASTILHO M, et al. Unveiling the potential of melt electrowriting in regenerative dental medicine. Acta Biomater. 2023;156:88-109.
[39] GALARRAGA JH, LOCKE RC, WITHEREL CE, et al. Fabrication of msc-laden composites of hyaluronic acid hydrogels reinforced with mew scaffolds for cartilage repair. Biofabrication. 2021;14(1). doi:10.1088/1758-5090/ac3acb
[40] RYMA M, GENÇ H, NADERNEZHAD A, et al. A print-and-fuse strategy for sacrificial filaments enables biomimetically structured perfusable microvascular networks with functional endothelium inside 3d hydrogels. Adv Mater. 2022;34(28):e2200653.
[41] DE RUIJTER M, HRYNEVICH A, HAIGH JN, et al. Out-of-plane 3d-printed microfibers improve the shear properties of hydrogel composites. Small. 2018;14(8).doi: 10.1002/smll.201702773.
[42] DILOKSUMPAN P, DE RUIJTER M, CASTILHO M, et al. Combining multi-scale 3d printing technologies to engineer reinforced hydrogel-ceramic interfaces. Biofabrication. 2020; 12(2):025014.
[43] AMAGAT J, SU Y, SVEJSØ FH, et al. Self-snapping hydrogel-based electroactive microchannels as nerve guidance conduits. Mater Today Bio. 2022;16:100437.
[44] AFGHAH F, IYISON NB, NADERNEZHAD A, et al. 3D fiber reinforced hydrogel scaffolds by melt electrowriting and gel casting as a hybrid design for wound healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(11):e2102068.
[45] BAS O, DE-JUAN-PARDO EM, MEINERT C, et al. Biofabricated soft network composites for cartilage tissue engineering. Biofabrication. 2017;9(2):025014.
[46] DE RUIJTER M, RIBEIRO A, DOKTER I, et al. Simultaneous micropatterning of fibrous meshes and bioinks for the fabrication of living tissue constructs. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8(7):e1800418.
[47] HRYNEVICH A, ELÇI BŞ, HAIGH JN, et al. Dimension-based design of melt electrowritten scaffolds. Small. 2018;14(22):e1800232.
[48] ZIELIŃSKI PS, GUDETI PKR, RIKMANSPOEL T, et al. 3D printing of bio-instructive materials: toward directing the cell. Bioact Mater. 2023;19:292-327.
[49] WANG F, CAI X, SHEN Y, et al. Cell-scaffold interactions in tissue engineering for oral and craniofacial reconstruction. Bioact Mater. 2023;23:16-44.
[50] PEREZ RA, MESTRES G. Role of pore size and morphology in musculo-skeletal tissue regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;61:922-939.
[51] JENKINS TL, LITTLE D. Synthetic scaffolds for musculoskeletal tissue engineering: cellular responses to fiber parameters. NPJ Regen Med. 2019;4:15.
[52] DEVILLARD CD, MARQUETTE CA. Vascular tissue engineering: challenges and requirements for an ideal large scale blood vessel. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:721843.
[53] PENNINGS I, VAN HAAFTEN EE, JUNGST T, et al. Layer-specific cell differentiation in bi-layered vascular grafts under flow perfusion. Biofabrication. 2019;12(1):015009.
[54] BERTLEIN S, HIKIMOTO D, HOCHLEITNER G, et al. Development of endothelial cell networks in 3d tissues by combination of melt electrospinning writing with cell-accumulation technology. Small. 2018;14(2).doi: 10.1002/smll.201701521.
[55] JANZEN D, BAKIRCI E, WIELAND A, et al. Cortical neurons form a functional neuronal network in a 3d printed reinforced matrix. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(9):e1901630.
[56] HAMMERL A, DIAZ CANO CE, DE-JUAN-PARDO EM, et al. A growth factor-free co-culture system of osteoblasts and peripheral blood mononuclear cells for the evaluation of the osteogenesis potential of melt-electrowritten polycaprolactone scaffolds. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(5):1068.
[57] ZHANG Z, JØRGENSEN ML, WANG Z, et al. 3D anisotropic photocatalytic architectures as bioactive nerve guidance conduits for peripheral neural regeneration. Biomaterials. 2020;253:120108.
[58] PIEN N, KRZYSLAK H, SHASTRY KALLAJE S, et al. Tissue engineering of skeletal muscle, tendons and nerves: a review of manufacturing strategies to meet structural and functional requirements. Appl Mater Today. 2023;31:101737.
[59] FILIPOWSKA J, TOMASZEWSKI KA, NIEDŹWIEDZKI Ł, et al. The role of vasculature in bone development, regeneration and proper systemic functioning. Angiogenesis. 2017;20(3): 291-302.
[60] ZHANG Z, HAO Z, XIAN C, et al. Neuro-bone tissue engineering: multiple potential translational strategies between nerve and bone. Acta Biomater. 2022;153:1-12.
[61] AYTAC Z, DUBEY N, DAGHRERY A, et al. Innovations in craniofacial bone and periodontal tissue engineering - from electrospinning to converged biofabrication. Int Mater Rev. 2022;67(4):347-384.
[62] STAPLES R, IVANOVSKI S, VAQUETTE C. Fibre-guiding biphasic scaffold for perpendicular periodontal ligament attachment. Acta Biomater. 2022;150:221-237.
[63] YAO Y, RAYMOND JE, KAUFFMANN F, et al. Multicompartmental scaffolds for coordinated periodontal tissue engineering. J Dent Res. 2022;101(12):1457-1466.
[64] MONDADORI C, CHANDRAKAR A, LOPA S, et al. Assessing the response of human primary macrophages to defined fibrous architectures fabricated by melt electrowriting. Bioact Mater. 2023;21:209-222.
[65] TYLEK T, BLUM C, HRYNEVICH A, et al. Precisely defined fiber scaffolds with 40 μm porosity induce elongation driven m2-like polarization of human macrophages. Biofabrication. 2020;12(2):025007.
[66] YILDIRIM N, AMANZHANOVA A, KULZHANOVA G, et al. Osteochondral interface: regenerative engineering and challenges. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(3):1205-1223.
[67] GAO H, PAN Q, DONG W, et al. Progress in osteochondral regeneration with engineering strategies. Ann Biomed Eng. 2022;50(10):1232-1242.
[68] HAN Y, LIAN M, SUN B, et al. Preparation of high precision multilayer scaffolds based on melt electro-writing to repair cartilage injury. Theranostics. 2020;10(22):10214-10230.
[69] QIAO Z, LIAN M, HAN Y, et al. Bioinspired stratified electrowritten fiber-reinforced hydrogel constructs with layer-specific induction capacity for functional osteochondral regeneration. Biomaterials. 2021;266:120385. |