中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (10): 1592-1598.doi: 10.12307/2024.313
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
羟基磷灰石/聚合物骨修复材料的特性及问题
齐军强,王浩田,肖 冰,刘 佳,刘一飞,许国华
- 海军军医大学第二附属医院骨科脊柱微创中心,上海市 200001
-
收稿日期:2022-12-19接受日期:2023-05-19出版日期:2024-04-08发布日期:2023-08-21 -
通讯作者:许国华,主任医师,教授,博士生导师,海军军医大学第二附属医院骨科脊柱微创中心,上海市 200001 -
作者简介:齐军强,男,1995年生,甘肃省平凉市人,汉族,海军军医大学第二附属医院在读硕士,主要从事脊柱外科、生物材料与骨组织工程研究。 王浩田,男,1987年生,山东省青岛市人,汉族,海军军医大学第二附属医院在读硕士,主要从事脊柱外科与骨组织工程研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(81972076),项目负责人:许国华
Characteristics and problems of hydroxyapatite/polymer bone repair material
Qi Junqiang, Wang Haotian, Xiao Bing, Liu Jia, Liu Yifei, Xu Guohua
- Spinal Minimally Invasive Center, Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Naval Medical University, Shanghai 200001, China
-
Received:2022-12-19Accepted:2023-05-19Online:2024-04-08Published:2023-08-21 -
Contact:Xu Guohua, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Spinal Minimally Invasive Center, Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Naval Medical University, Shanghai 200001, China -
About author:Qi Junqiang, Master candidate, Spinal Minimally Invasive Center, Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Naval Medical University, Shanghai 200001, China Wang Haotian, Master candidate, Spinal Minimally Invasive Center, Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Naval Medical University, Shanghai 200001, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81972076 (to XGH)
摘要:
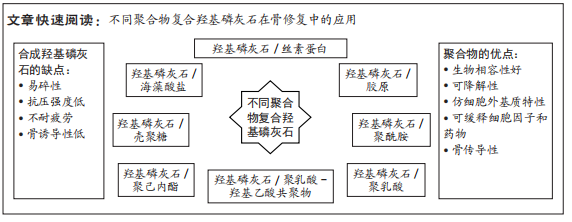
文题释义:
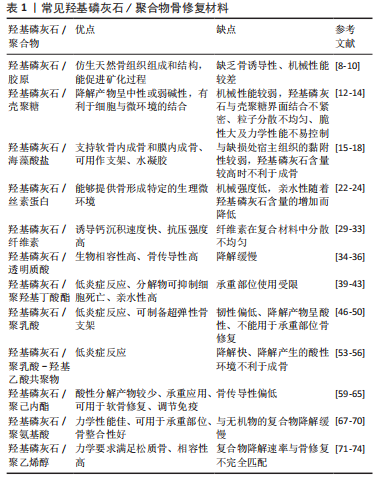
羟基磷灰石:是人体骨组织的主要无机质成分,其钙/磷比为1.67,与自然骨组织相似,可与人体骨组织通过羟基键合,且有一定的降解性,可释放钙、磷离子刺激或诱导骨组织生成,促进骨缺损局部修复,具有良好的生物相容性,但其脆性高、降解速度慢及骨诱导性、成血管活性等较弱,限制了其在临床上的单独使用。聚合物:包括天然聚合物和人工合成聚合物,在结构上与细胞外基质类似,具有良好的生物相容性、可调控的降解性、细胞因子和药物缓释性、骨传导性,常与其他材料复合制备新材料用于细胞因子和药物的缓释、骨组织缺损的修复等。
背景:羟基磷灰石是骨组织的主要无机成分,聚合物可仿生细胞外基质的结构和功能,两者的复合材料得到了广泛研究。
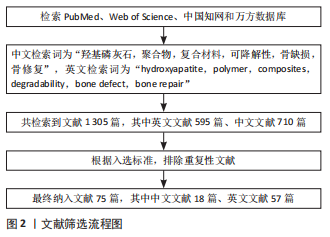
目的:总结羟基磷灰石复合聚合物材料用于骨组织修复的研究现状。方法:检索2010年1月至2023年4月PubMed、Web of Science、中国知网及万方数据库收录的相关文献,中文检索词为“羟基磷灰石,聚合物,复合材料,可降解性,骨缺损,骨修复”,英文检索词:“hydroxyapatite,polymer,composites,degradability,bone defect,bone repair”,最终纳入75篇文献进行综述分析。
结果与结论:常与羟基磷灰石复合用于骨组织修复的聚合物包括天然聚合物(胶原、壳聚糖、海藻酸盐、丝素蛋白、纤维素、透明质酸、聚羟基丁酸酯等)和合成聚合物(聚乳酸、聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物、聚已内酯、聚氨基酸、聚乙烯醇等)。羟基磷灰石/聚合物复合材料较纯羟基磷灰石的机械性能、骨诱导性得到了提高,羟基磷灰石与聚合物复合可制成多孔支架、水凝胶、涂层等用于骨修复。羟基磷灰石/聚合物复合材料因其仿生细胞外基质结构和功能可缓释负载的药物和细胞因子,加速骨重建。基于骨缺损原因的多样性以及骨修复为多种生物因子和蛋白共同参与的复杂连续过程,机械性能与骨组织匹配、降解过程与骨修复同步、高效成骨成血管的修复材料有待进一步研究。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1492-9289(齐军强)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
齐军强, 王浩田, 肖 冰, 刘 佳, 刘一飞, 许国华. 羟基磷灰石/聚合物骨修复材料的特性及问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(10): 1592-1598.
Qi Junqiang, Wang Haotian, Xiao Bing, Liu Jia, Liu Yifei, Xu Guohua. Characteristics and problems of hydroxyapatite/polymer bone repair material[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(10): 1592-1598.
2.1.1 羟基磷灰石/胶原 胶原作为一种具有特殊三螺旋结构的肽,主要由甘氨酸和脯氨酸组成,是天然骨的主要有机成分,在骨修复中起重要作用[7]。模仿天然骨组成和结构的羟基磷灰石/胶原复合材料,是骨组织工程生物材料研究热点之一。
羟基磷灰石与胶原复合可提高材料的生物活性,常以支架的形式用于骨修复。骨诱导性是指植入材料或提取物诱导间充质干细胞分化为骨源细胞、成骨细胞,继而形成骨组织的性能;骨传导性指植入物为新生骨长入提供支架支撑和引导的性能。OU等[8]探究了不同比例羟基磷灰石/胶原复合支架的成骨诱导活性,发现羟基磷灰石/胶原质量比为7∶3的复合支架具有较强的促骨形成能力,能够募集成骨细胞附着并进入支架内,促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。李冬梅等[9]的研究发现,纳米羟基磷灰石/胶原复合材料可促进猪下颌骨缺损的修复,对材料促骨修复机制的进一步研究发现,复合材料可促进血管内皮生长因子的表达,继而促进骨缺损处的血管生成,加速骨组织再生。骨骼中的微量元素如锰、铁等有助于身体的生长和发育,缺乏锰、铁可减弱成骨细胞的活动,导致成骨延迟,引起骨变形、生长抑制、运动协调性减弱,甚至骨吸收。YU等[10]将铁和锰掺入羟基磷灰石/胶原层状支架,支架的骨诱导活性得到了增强,在体外成骨实验中,负载铁/锰的支架可显著促进成骨细胞的黏附和增殖,促进骨涎蛋白、牙本质基质蛋白的表达和碱性磷酸酶的活性,增加骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨特异性基因表达,并且与不加载铁/锰的支架相比体内骨再生能力明显增强。羟基磷灰石/胶原支架还可作为药物、生长因子和其他大分子的有效持续输送载体。LEE等[11]开发了一种羟基磷灰石/胶原支架,与骨形态发生蛋白2和负载阿伦膦酸钠的聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物微球相结合,用于顺序释放骨重建的药物,骨形态发生蛋白2通过激活成骨细胞促进成骨,而阿伦膦酸钠抑制破骨细胞介导的骨吸收,骨形态发生蛋白2和阿伦膦酸钠从支架中的顺序释放在体内外都对骨再生有协同作用,证实序贯给药的羟基磷灰石/胶原复合支架是一种很有前景的骨修复材料。
2.1.2 羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖 壳聚糖是N-乙酰-d-葡糖胺和d-葡糖胺的线性氨基多糖共聚物,降解产物主要呈中性或弱碱性,有利于细胞生长。壳聚糖类似细胞外基质,具有促进细胞增殖和组织发育的能力。独特的理化性能和生物特性使壳聚糖在组织工程和再生医学领域得到广泛应用[12]。
卢育南等[13]将柚皮苷-壳聚糖/羟基磷灰石复合支架植入大鼠颅骨缺损处,研究发现柚皮苷-壳聚糖/羟基磷灰石复合支架可为骨缺损修复提供载体,并促进骨形态发生蛋白2和血管内皮生长因子的表达,诱导骨组织和毛细血管的生成,加速骨修复过程。移植物的植入常伴随着致炎因子的增加,这些细胞因子不利于骨形成。LI等[14]制备了纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖/白藜芦醇复合微球,该材料可局部缓释白藜芦醇,下调炎症标志物(肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和诱导型一氧化氮合酶)的表达而增强抗炎反应,体内、外实验表明,复合微球能促进骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖和成骨分化,并能促进骨质疏松条件下的软骨形成和骨重建。理想的骨科植入物需具有抗菌和成骨特性。纳米银粒子优异的抗菌性在植入物相关感染治疗中引起了学者的兴趣,然而,银的剂量依赖性细胞毒性及其对植入物的负面影响,限制了纳米银粒子涂层的进一步应用。XIE等[15]制备了一种聚多巴胺、壳聚糖、羟基磷灰石和纳米银粒子杂化涂层,涂层对金黄色葡萄球菌、表皮葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌的抑菌率分别为91.7%,89.5%和92.0%,并可显著促进MC3T3-E1细胞的成骨分化,促进体内骨-植入物的整合。治疗性金属离子由于具有特殊生物学特性可用于骨组织工程。GRITSCH等[16]将铜和锶分别负载于壳聚糖和羟基磷灰石中制得复合支架,铜经壳聚糖迅速释放,使其能够快速阻止可能的细菌定植,而锶被均匀缓慢释放,以支持更长时间的骨再生过程,体外磷酸钙沉积和成骨细胞共培养实验证实,该复合支架具有良好的生物活性和细胞相容性。
2.1.3 羟基磷灰石/海藻酸盐 海藻酸盐是由两种糖醛酸组成的线性共聚物,在低pH值条件下可凝胶化,可与金属离子或有机分子交联,用于制造具有更强机械性能、化学稳定性、改善细胞相容性和理想形态的凝胶。海藻酸盐已被广泛用于制造生物医学支架、药物输送的胶囊、微球和水凝胶[17]。
MAHMOUD等[18]通过在生物羟基磷灰石支架表面涂覆海藻酸盐制备复合支架,用3%海藻酸盐涂覆的复合支架既能支持软骨内成骨又能支持膜内成骨,支架植入大鼠股骨缺损处6 个月后缺损区基本完全再生,大部分被成熟的板层骨填充,且新骨钙/磷原子比为1.64,接近正常骨,证明该材料有很好的促成骨性。水凝胶的一个主要缺点是其与缺损处宿主组织的黏附性较弱,这限制了其再生性能。BARROS等[19]研究了纳米羟基磷灰石含量(30%-70%)对海藻酸盐水凝胶生物活性的影响,发现纳米羟基磷灰石含量为30%的水凝胶可促进成骨细胞的增殖和成骨转录因子的表达,促进胶原沉积、骨小梁形成和基质矿化;而较高浓度(50%和70%)的水凝胶则会降低成骨细胞的活性。HASANI-SADRABADI等[20]以多巴胺修饰的海藻酸盐为原料,以羟基磷灰石微粒作为牙周间充质干细胞的聚集体,设计出了光交联型骨传导黏附性水凝胶,该水凝胶埋植小鼠皮下7 d未见淋巴细胞或巨噬细胞浸润的迹象;利用成熟大鼠种植体周围炎模型分析细胞-水凝胶构建物的有效性和功能性,结果证实了该水凝胶可注射到缺损处、快速光聚合、与周围组织粘连以及促进骨组织再生和修复的能力。
2.1.4 羟基磷灰石/丝素蛋白 丝素蛋白结构类似于Ⅰ型胶原,具有非凡的细胞相容性、可控的降解性、最小的免疫原性和易加工性[21-22]。多孔丝素蛋白支架能有效地建立起细胞黏附、增殖和分化的微环境,然而其成骨能力偏低,需对其进行修饰和功能化,例如将纳米颗粒加入聚合物基质中,以增强成骨潜力并诱导骨组织再生[23]。
研究发现,当羟基磷灰石的含量从0增加到30%时,丝素蛋白/羟基磷灰石的力学性能变化不大;当羟基磷灰石的含量大于30%时,随着羟基磷灰石含量的增加,丝素蛋白/羟基磷灰石的亲水性下降;而羟基磷灰石含量为30%的丝素蛋白/羟基磷灰石亲水性最高,对骨髓间充质干细胞具有较高的细胞黏附能力,相比纯丝素蛋白可观察到更多的钙沉积[24]。这意味着丝素蛋白/羟基磷灰石复合材料的力学性能决定于丝素蛋白,成骨能力与羟基磷灰石密切相关。李智等[25]利用石蜡微球沥滤技术制得丝素蛋白/羟基磷灰石支架,支架的弹性模量达(54.93±5.44) kPa,支架具有连接互通的仿生大孔结构,有利于脂肪间充质干细胞的黏附、增殖和分泌细胞外基质,具有良好的细胞相容性。SONG等[26]设计了一种负载不同浓度槲皮素的丝素蛋白/羟基磷灰石支架用于促进成骨,支架具有较大的孔径、不规则的多孔结构和良好的机械强度,槲皮素/丝素蛋白/羟基磷灰石支架与骨髓间充质干细胞体外共培养发现支架具有良好的细胞相容性,可促进细胞成骨分化,显著上调成骨基因表达;与丝素蛋白/羟基磷灰石纯支架和高含量槲皮素的支架相比,低含量槲皮素的支架植入骨缺损处与周围组织结合良好,术后6 周骨体积恢复约80%,是一种可提供仿生骨微环境、促进细胞生长、成骨分化和增殖的有效载体。KO等[27]开发了一种由两段羟基磷灰石颗粒功能化的电纺丝素蛋白纳米纤维支架,体外促进细胞成骨分化和体内修复骨缺损的能力测试显示,该支架可显著促进间充质干细胞的成骨分化,并在临界大小颅骨缺损模型中促进矿化骨的形成。
2.1.5 羟基磷灰石/纤维素 纤维素是由D-吡喃式葡萄糖基通过β-1,4-D-糖苷键连接而成的聚合物,是自然界储量最多的天然高分子,它是植物细胞壁的主要成分,同时也可以由特定的被囊动物、藻类、真菌和细菌合成[28]。纤维素因来源广泛、可再生、无毒性、可生物降解、生物相容性好等特性被广泛应用于医用材料中。
杨蕾[29]结合原位钙离子活化仿生矿化法和生物原位矿化法,将羟基磷灰石沉积在细菌纤维素上制得复合材料,与普通矿化纤维素相比,复合材料在模拟体液中的矿化速度明显提高,且拉伸强度和杨氏模量分别提高了49.2%和63.8%,可显著促进骨细胞生长,具有良好的细胞相容性。付冉冉[30]合成纳米羟基磷灰石/细菌纤维素复合材料,复合材料与成骨细胞MC3T3-E1共培养结果显示,材料可促进细胞的生长,无细胞毒性,生物相容性良好。HE等[31]通过原位法、冷等静压技术和冷冻干燥技术制得胶原-羟基磷灰石-微纤化纤维素支架,支架呈三维多孔结构,羟基磷灰石沉积在胶原和微纤化纤维素上,通过调节纤维素的含量可调节支架的抗压强度和降解性;与纯羟基磷灰石支架相比,复合支架的抗压强度提高到了20-40 MPa,接近天然骨的抗压强度,具有良好的生物相容性,细胞生长率> 70%,溶血率≤5%。AO等[32]采用静电纺丝技术将棉纤维素和纳米羟基磷灰石制备成纳米纤维支架,支架的平均直径随着纳米羟基磷灰石含量的增加而增加,支架的直径分布在天然细胞外基质纤维的范围内(50-500 nm);纳米纤维支架表现出非凡的机械性能,拉伸强度和弹性模量分别高达70.6 MPa和3.12 GPa;细胞培养实验表明,复合支架对人牙囊细胞具有良好的细胞相容性,可促进细胞的黏附和增殖,提示其作为骨组织工程支架材料的巨大潜力。DAUGELA等[33]通过从乙酰化衍生物中再生纤维素、机械固定羟基磷灰石颗粒,再经冷冻干燥制备含有羟基磷灰石的纤维素支架,纤维素/纳米羟基磷灰石支架呈现高度连通的多孔结构,平均孔径为(490±94) μm;与一种市售同种异体骨对比,纤维素/纳米羟基磷灰石支架可更好地促进成骨细胞黏附、增殖和成骨基因(矮小相关转录因子2、碱性磷酸酶和骨形态发生蛋白2)的表达,对兔颅骨缺损的修复能力亦比市售同种异体骨更强。
2.1.6 羟基磷灰石/透明质酸 透明质酸是一种天然多糖,由线性葡萄糖胺聚糖组成,其中N-乙酰-D-葡萄糖胺和D-葡萄糖酸的重复单位通过交替β-1,3-糖苷键和β-1,4-糖苷键连接。透明质酸是细胞外基质的重要组成部分,广泛分布于人体的各种组织中,具有良好的亲水性,可吸附细胞,增强细胞的迁移、黏附、增殖、分化,诱导骨组织再生。
南晓茹[34]通过冷冻干燥法制得不同透明质酸比例(质量分数分别为0%,1.5%,2.5%,5.0%,7.5%)的丝素蛋白/纳米羟基磷灰石/透明质酸多孔复合支架,当透明质酸含量为5.0%时,支架的吸水性和力学性能最高;支架与细胞共培养发现,大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞在透明质酸含量为5.0%的复合支架上增殖最快;体外成骨诱导分化实验发现,各组支架的碱性磷酸酶活性随时间的增加而增强,而透明质酸含量为5.0%的复合支架在各测定时间点的碱性磷酸酶活性和钙盐沉积量均高于其他组支架。郭倩楠[35]通过冷冻干燥和化学交联法合成明胶-透明质酸-纳米羟基磷灰石多孔支架,支架的平均孔径为80.50 μm,平均孔隙率达96.23%,可为细胞的黏附、延展、增殖和分化提供良好的支撑和空间;支架植入大鼠下颌骨缺损处第4,6,8 周时,复合支架的新生骨面积均大于纳米羟基磷灰石组和空白组,且复合支架组在早期可见大量的成骨细胞和骨细胞,骨修复速度快于对照组和空白组。KACZMAREK等[36]将壳聚糖和胶原等比例混合并添加不同比例的透明质酸和羟基磷灰石,采用冷冻干燥法制成复合支架,与人骨肉瘤细胞体外培养发现,质量分数2%透明质酸和质量分数80%羟基磷灰石、质量分数5%透明质酸和质量分数50%或80%羟基磷灰石的复合支架具有良好的生物相容性,可促进细胞的黏附和增殖,支架植入实验兔皮下的研究发现,不含羟基磷灰石的对照支架和添加质量分数50%羟基磷灰石的支架在6 个月后发生降解,然而含80%羟基磷灰石的支架仍存在于植入部位,证实在支架中加入羟基磷灰石会减缓植入物的生物降解过程,并产生一种为周围组织提供更稳定性的支架。
2.1.7 羟基磷灰石/聚羟基丁酸酯 聚羟基丁酸酯是聚羟基脂肪酸(一种可生物降解和生物相容的基于微生物的聚合物)家族中最常见的成员,除了具有优异的生物相容性和可降解性,还可促进体内骨再生。同时,作为聚羟基丁酸酯分解产物的3-羟基丁酸是人体血液的正常成分,可以抑制细胞的死亡,也使聚羟基丁酸酯植入机体后表现出延迟的炎症反应[37-38]。
聚羟基丁酸酯虽具有良好的生物相容性、降解性,但其脆性大、亲水性低。管东华等[39]制得加入不同质量百分比(0%,10%,20%,30%)纳米羟基磷灰石的电纺纳米羟基磷灰石/聚羟基丁酸酯纤维支架,材料表征发现,纳米羟基磷灰石含量越大,其在复合纤维支架表面的分布越多且趋于均匀, 当纳米羟基磷灰石含量为30%时,其已基本布满聚羟基丁酸酯表面, 支架的粗糙度也增加,随着纳米羟基磷灰石含量的增大,复合支架表面的接触角逐渐降低,亲水性逐渐提高。宋越[40]利用静电纺丝技术制得聚羟基丁酸酯支架和纳米羟基磷灰石/聚羟基丁酸酯支架,成骨细胞MG-63可在支架上呈长梭形或球状生长,纳米羟基磷灰石/聚羟基丁酸酯支架表面和内部可见更多的细胞黏附,且复合支架表面由于纳米羟基磷灰石的附着可显著促进成骨细胞的分化,促进碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素的表达,促进骨髓间充质干细胞的定向分化。SADAT-SHOJAI等[41]发现与纯聚羟基丁酸酯相比,含纳米羟基磷灰石的聚羟基丁酸酯复合材料,由于表面粗糙的纳米羟基磷灰石可显著增加MC3T3-E1细胞在材料上的黏附、增殖,并促进细胞分化。SENATOV等[42]通过烧结得到聚羟基丁酸酯/羟基磷灰石多孔复合支架,与纯聚羟基丁酸酯相比,聚羟基丁酸酯/ 20%羟基磷灰石可更好地诱导小鼠多能间充质基质细胞增殖,且植入大鼠胫骨缺损处30 d后可更好地与周围骨组织整合,促进血管生成和新骨形成,有望用于非承重部位的骨缺损修复。CHEN等[43]先通过静电纺丝制得纳米羟基磷灰石/聚羟基丁酸酯的薄层,再层压该复合薄层获得用于细胞接种和骨组织工程的支架,研究表明层压支架具有优异的细胞负载能力,骨髓间充质干细胞在纳米羟基磷灰石/聚羟基丁酸酯支架上表现出比聚羟基丁酸酯支架更好的黏附、增殖和成骨表型;将骨髓间充质干细胞接种到纳米羟基磷灰石/聚羟基丁酸酯支架上,并植入小鼠背部皮下,2 个月后见支架被一层软组织包裹,表面可见血管,组织学观察显示整个支架中都形成了类骨组织,并可在移植物中观察到血管向内生长,纳米羟基磷灰石/聚羟基丁酸酯组形成的胶原、平均血管密度均显著多于聚羟基丁酸酯组。
2.2 羟基磷灰石/合成聚合物 合成聚合物具有良好的生物相容性,其中部分聚合物具有可控降解性,但生物活性、骨传导性较低,与羟基磷灰石联合则可改善其表面性能用于骨组织再生[4,44]。
2.2.1 羟基磷灰石/聚乳酸 聚乳酸因具有优异的生物相容性、可调节的降解率、独特的药代动力学和药理学功效,其在药物输送、缝合、植入和组织工程方面的生物医学应用已被广泛探索,但聚乳酸的低韧性和有限的生物活性限制了其在组织工程骨领域的应用[45]。羟基磷灰石的加入可提高其机械性能和成骨活性,已得到较深入的研究。
ZIMINA等[46]制得孔径为300-400 μm、孔隙率为79%的多孔聚乳酸/羟基磷灰石支架,间充质干细胞在其表面的黏附数量是纯聚乳酸样品的3.2 倍;小鼠皮下植入实验证实与纯聚乳酸相比,含羟基磷灰石支架在植入2 周后未见明显的炎症反应。刘冬等[47]通过3D打印制得羟基磷灰石/聚乳酸网状复合物,并植入兔颅骨缺损处评估材料修复骨缺损的可行性,研究发现3 个月时新生骨组织已完全填充缺损处,与周围正常骨组织连接自然,边界难以分辨;组织切片染色可见致密且连接良好的骨小梁和骨细胞穿行于材料中,同时可见骨单位和骨髓腔,成骨细胞活跃且排列有序,说明该材料可促进骨细胞迁移、诱导骨组织生成,具有良好的骨修复能力。ZHANG等[48]通过3D打印制得羟基磷灰石-聚乳酸复合支架,以骨膜包裹并负载骨髓间充质干细胞和血管蒂的复合支架作为实验组,骨膜包裹的载骨髓间充质干细胞复合支架为对照组,植入兔胫骨缺损模型,结果显示实验组新生骨中血管的数量和体积均显著高于对照组。3D打印的羟基磷灰石-聚乳酸复合支架联合血管蒂为血管化组织工程骨提供了实验支持,有望用于修复大面积骨缺损。HUANG等[49]将90%羟基磷灰石和10%聚乳酸打印的超弹性骨支架植入大鼠临界尺寸颅骨缺损,在8 周和12 周时发现矿化骨体积与总组织体积的比例分别为自体骨组骨体积/总组织体积的74.2%和64.5%;组织学分析显示,在8 周时支架周围有纤维组织形成,12 周时有新骨形成。YE等[50]利用聚多巴胺涂层将骨形态发生蛋白2负载于纳米羟基磷灰石/聚乳酸/明胶支架上,骨形态发生蛋白2可持续释放21? d,测定支架与骨髓间充质干细胞共培养的细胞活力、碱性磷酸酶活性、基因表达,并评估支架在大鼠颅骨缺损处的骨形成能力,结果表明支架具有良好的生物相容性和骨诱导性。
2.2.2 羟基磷灰石/聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物 聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物是一种线性共聚物,由不同比例的乳酸和羟基乙酸组成,通过调整两者比例可以调节共聚物的降解率,然而由于其骨传导性低使用受到限制,因此聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物通常与生物陶瓷等材料结合使用[51-52]。
王德欣等[53]发现将适量羟基磷灰石加入聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物中可提高支架的抗压强度,羟基磷灰石含量为10%的羟基磷灰石/聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物支架拉伸强度可达(1.67±0.37) MPa,压缩模量为(4.17±1.62) MPa,支架表面的纳米微结构可以促进骨髓间充质干细胞的黏附;将可促进成骨的淫羊藿苷负载于复合支架上,可促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化及碱性磷酸酶活性、骨钙素活性、成骨相关基因和蛋白的表达,具有良好骨修复应用前景。BABILOTTE等[54]制备的聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物/羟基磷灰石多孔支架具有良好的生物相容性,与脂肪干细胞、骨髓间充质干细胞共培养可观察到较高的细胞存活率,并能维持细胞增殖;材料植入大鼠皮下见轻度炎症反应,与聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物支架相比,细胞在聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物-羟基磷灰石10%支架中的碱性磷酸酶活性更强,可使脂肪干细胞的钙沉积显著增加。CUI等[55]制得聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物/羟基磷灰石/聚乳酸支架,并将载有人骨形态发生蛋白4基因片段的质粒载体与支架复合,在电刺激下具有可控的基因释放和表达,实现了人骨形态发生蛋白4在严格控制下的表达,可显著促进细胞增殖、成骨分化;将支架植入骨缺损处可加速兔子桡骨缺损的骨愈合。感染是创伤或肿瘤切除后大块骨缺损骨不连的关键原因之一。YANG等[56]发现季铵化壳聚糖接枝的聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物/羟基磷灰石支架具有良好的抗菌和骨传导性能,X射线片、显微CT、微生物学和组织病理学分析发现,季铵化壳聚糖接枝的聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物/羟基磷灰石支架对SD大鼠股骨干缺损感染模型和新西兰白兔髁突缺损感染模型表现出显著增强的抗感染和促进骨再生能力。
2.2.3 羟基磷灰石/聚己内酯 因良好的生物相容性、缓慢的降解性、与其他聚酯相比酸性分解产物较少以及承重应用的潜力,聚己内酯已被广泛用于骨组织工程领域,但其存在表面疏水和缺乏骨传导性等缺点,不利于细胞的黏附和增殖。聚己内酯可以与各种无机物、聚合物或水凝胶混合,以改善其性能或制出新的基于聚己内酯的复合材料[57-58]。
GóMEZ-LIZáRRAGA等[59]将生物来源的羟基磷灰石与聚己内酯混合制得多孔支架,体外细胞实验表明与纯聚己内酯支架、合成羟基磷灰石/聚己内酯支架相比,生物羟基磷灰石/聚己内酯多孔支架具有更好的生物活性,可显著促进成骨细胞的黏附、存活和增殖。JI等[60]合成纳米羟基磷灰石/聚己内酯复合支架用作甲壳素水凝胶载体,RT-PCR检测结果显示,当间充质干细胞被包裹在甲壳素水凝胶中时,与成骨相关的骨钙素、骨桥蛋白表达水平显著增加;复合支架与巨噬细胞共同培养实验发现,骨形态发生蛋白2、转化生长因子β1和前列腺素E2的基因表达水平均升高,纳米羟基磷灰石/聚己内酯与羟基丙基甲壳素水凝胶杂化支架可通过促进成骨和免疫调节有效地促进血管生成和成骨诱导,具有良好的骨再生应用前景。急性骨软骨缺陷和/或宿主对植入材料的炎症反应,将导致组织修复和再生的性能下降[61-62]。白细胞介素4作为一种抗炎因子已被用于关节疾病的治疗[63]。GONG等[64]制造了一种双层支架,上层是负载白细胞介素4的甲基丙烯酸明胶支架,下层是多孔聚己内酯-羟基磷灰石支架,体外实验表明,这两层都支持细胞的黏附和增殖,因为下层促进了成骨分化,而上层的白细胞介素4则缓解了炎症对小鼠软骨细胞的负面影响;在兔骨软骨缺损修复模型中,植入16 周后与未处理组(11±1)和纯双层支架组(16±1)相比,加载白细胞介素4的双层支架组获得了最高的组织学评分(24±2),显著促进了软骨和软骨下骨的再生。这种双层支架为骨软骨修复和再生提供了一种支架制造和组合策略。HAN等[65]制得含有转化生长因子β1和骨形态发生蛋白7(表层)、胰岛素样生长因子1(中层)和羟基磷灰石(深层)的多层载细胞因子聚己内酯/羟基磷灰石支架,可实现细胞因子持续释放并诱导细胞定向分化;兔股骨髁间骨软骨损伤修复实验发现,12 周时复合支架表面形成了光滑的软骨,与周围组织很好地结合在一起,支架表面的胶原蛋白明显多于空白组和简单支架组。
2.2.4 羟基磷灰石/聚氨基酸 聚氨基酸与人多肽胶原蛋白结构相似,可在人体组织中代谢并与二氧化碳和水一起排出体外,具有良好的生物相容性,已被广泛应用于外科缝合线、人造皮肤、药物或基因递送系统。聚氨基酸虽然具有优异的性能,但从仿生学的角度来看,这种单一的聚合物很少被直接用作骨修复材料。既往研究证明,生物活性颗粒的存在可以赋予聚合物生物活性[66],因此通过将生物活性无机化合物和聚合物基质结合在一起,可得到改性的骨修复材料。
FAN等[67]采用原位熔融缩聚法制备了聚氨基酸、羟基磷灰石和硫酸钙的三元复合材料,材料在体外可促进MG-63细胞的增殖,并使细胞在材料表面良好的铺展;材料植入绵羊尺骨缺损处表现出良好的生物相容性和骨传导性,在植入24 周时材料被新形成的骨完全包裹,骨和植入物之间没有明显的边界,已实现了缺损区域的完全骨整合,这为聚氨基酸/羟基磷灰石/硫酸钙复合材料作为负重骨替代材料的临床应用提供了可能。薛有地等[68]探讨了聚氨基酸/纳米羟基磷灰石/硫酸钙融合器在山羊腰椎椎间融合中的作用,比较各组术后椎间融合高度、CT三维重建融合评分、生物力学测试、组织学及扫描电镜观察,结果显示,术后24 周,聚氨基酸/纳米羟基磷灰石/硫酸钙组达骨性融合,融合器界面新骨形成并与宿主骨连接较紧密,融合效果与自体骨类似,融合器表面虽可见微降解,但融合效果优于钛合金融合器;将聚氨基酸/纳米羟基磷灰石/硫酸钙融合器、聚醚醚酮融合器植入单节段腰椎融合术患者椎间,对比两组患者术后各时间点融合节段椎间隙高度、融合节段前凸曲度、Oswestry功能障碍指数及CT三维重建的Brantigan植骨融合分级,研究发现术后3,6,12 个月时,两组患者融合节段椎间隙高度、融合节段前凸曲度及Oswestry功能障碍指数均较术前显著改善,但两组间差异无统计学意义,12 个月时两组植骨融合率均可达90%;中期临床随访发现,术后各观察指标较术前显著改善,但两组间无显著差异,术后12,36 个月,聚氨基酸/纳米羟基磷灰石/硫酸钙融合器组的植骨融合率分别达95%,100%,与聚醚醚酮融合器组比较差异无统计学意义,证实聚氨基酸/纳米羟基磷灰石/硫酸钙融合器用于腰椎融合术可获得与聚醚醚酮融合器相似的、满意的早中期临床疗效[69-70]。
2.2.5 羟基磷灰石/聚乙烯醇 聚乙烯醇由于高亲水性、渗透性、生物降解性、生物相容性、柔韧性以及可与其他生物聚合物混合的能力,在支架生产中具有巨大的潜力。
安田田等[71]以丝素蛋白、聚乙烯醇和羟基磷灰石为原料,通过正交实验探索了三者的最佳配比,采用3D打印制得丝素蛋白/聚乙烯醇/羟基磷灰石多孔支架,孔隙率为(55.0±1.5)%,孔隙相互连通,有利于营养物质的运输和骨细胞的黏附、迁移,且支架具有良好的细胞相容性,在体外可促进成骨细胞的增殖。李蕾等[72]将丝素蛋白/聚乙烯醇/羟基磷灰石支架植入羊下颌骨缺损处评估了支架的降解性,研究发现该支架具有一定的降解性,植入3 个月后近乎完全降解,并被新生的骨组织和纤维组织代替,且在降解过程中引起的炎症反应较轻,具有良好的生物相容性。李耀明等[73]通过正交实验发现,3%乙酸、5%壳聚糖溶液、羟基磷灰石∶聚乳酸质量比=1∶6、羟基磷灰石/聚乳酸∶壳聚糖溶液∶聚乙烯醇凝胶=2 g∶1 g∶1.4 mL,采用3D打印技术制备的壳聚糖/聚乳酸/羟基磷灰石/聚乙烯醇骨支架具有良好的力学性能,最大抗压强度可达6 MPa,满足松质骨的力学要求,可起到良好的支撑作用,其孔隙率为52%,可满足营养输送和细胞黏附增殖的要求;同时支架具有一定的降解性,体外降解10 周后抗压强度仍达4.36 MPa,可起到良好的支撑作用,但降解性有待进一步提高。受骨骼有序多孔纳米结构的启发,仿生功能化多孔生物材料被认为是很有前景的骨再生替代品。为了实现相关的仿生多孔结构,LIU等[74]采用快速冷冻干燥法制备了同时含有改性碳纳米管和羟基磷灰石的聚乙烯醇基仿生骨气凝胶支架,支架可增强MC3T3-E1细胞的黏附、分化和成骨基因表达;进一步将气凝胶支架植入SD大鼠颅骨缺损模型评价其体内成骨性能,8 周后的Micro-CT表征和骨含量分析共同表明该气凝胶支架在不含细胞因子的情况下能加速骨再生。

| [1] SALHOTRA A, SHAH HN, LEVI B, et al. Mechanisms of bone development and repair. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(11):696-711. [2] JI XF, YUAN X, MA LM, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-loaded thermosensitive hydroxypropyl chitin hydrogel combined with a three-dimensional-printed poly(ε-caprolactone) /nano-hydroxyapatite scaffold to repair bone defects via osteogenesis, angiogenesis and immunomodulation. Theranostics. 2020;10(2):725-740. [3] PALIERSE E, HÉLARY C, KRAFFT JM, et al. Baicalein-modified hydroxyapatite nanoparticles and coatings with antibacterial and antioxidant properties. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;118:111537. [4] BHARADWAZ A, JAYASURIYA AC. Recent trends in the application of widely used natural and synthetic polymer nanocomposites in bone tissue regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;110:110698. [5] BARROS J, FERRAZ MP, AZEREDO J, et al. Alginate-nanohydroxyapatite hydrogel system: Optimizing the formulation for enhanced bone regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;105:109985. [6] REDDY MSB, PONNAMMA D, CHOUDHARY R, et al. A comparative review of natural and synthetic biopolymer composite scaffolds. Polymers (Basel). 2021;13(7):1105. [7] RAY S, ADELNIA H, TA HT. Collagen and the effect of poly-l-lactic acid based materials on its synthesis. Biomater Sci. 2021;9(17): 5714-5731. [8] OU MM, HUANG XF. Influence of bone formation by composite scaffolds with different proportions of hydroxyapatite and collagen. Dent Mater. 2021;37(4):e231-e244. [9] 李冬梅,刘新晖,李庆星.纳米羟基磷灰石/胶原复合材料修复猪下颌骨缺损后血管内皮生长因子的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019,23(26): 4148-4153. [10] YU L, ROWE DW, PERERA IP, et al. Intrafibrillar mineralized collagen-hydroxyapatite-based scaffolds for bone regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(16):18235-18249. [11] LEE D, WUFUER M, KIM I, et al. Sequential dual-drug delivery of BMP-2 and alendronate from hydroxyapatite-collagen scaffolds for enhanced bone regeneration. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):746. [12] ZAKHIREH S, BARAR J, ADIBKIA K, et al. Bioactive chitosan-based organometallic scaffolds for tissue engineering and regeneration. Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2022;380(2):13. [13] 卢育南,张信照,林斌斌,等.柚皮苷-壳聚糖/羟基磷灰石复合支架修复大鼠颅骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(28):4441-4445. [14] LI LM, YU ML, LI Y, et al. Synergistic anti-inflammatory and osteogenic n-HA/resveratrol/chitosan composite microspheres for osteoporotic bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2020;6(5):1255-1266. [15] XIE K, ZHOU ZA, GUO Y, et al. Long-term prevention of bacterial infection and enhanced osteoinductivity of a hybrid coating with selective silver toxicity. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8(5):e1801465. [16] GRITSCH L, MAQBOOL M, MOURIÑO V, et al. Chitosan/hydroxyapatite composite bone tissue engineering scaffolds with dual and decoupled therapeutic ion delivery: copper and strontium. J Mater Chem B. 2019; 7(40):6109-6124. [17] SIKKEMA R, KEOHAN B, ZHITOMIRSKY I. Alginic acid polymer-hydroxyapatite composites for bone tissue engineering. Polymers (Basel). 2021;13(18):3070. [18] MAHMOUD EM, SAYED M, EL-KADY AM, et al. In vitro and in vivo study of naturally derived alginate/hydroxyapatite bio composite scaffolds. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;165(Pt A):1346-1360. [19] BARROS J, FERRAZ MP, AZEREDO J, et al. Alginate-nanohydroxyapatite hydrogel system: Optimizing the formulation for enhanced bone regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;105:109985. [20] HASANI-SADRABADI MM, SARRION P, POURAGHAEI S, et al. An engineered cell-laden adhesive hydrogel promotes craniofacial bone tissue regeneration in rats. Sci Transl Med. 2020;12(534):eaay6853. [21] FAROKHI M, MOTTAGHITALAB F, SAMANI S, et al. Silk fibroin/hydroxyapatite composites for bone tissue engineering. Biotechnol Adv. 2018;36(1):68-91. [22] ZHAO ZH, MA XL, ZHAO B, et al. Naringin-inlaid silk fibroin/hydroxyapatite scaffold enhances human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell-based bone regeneration. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(7):e13043. [23] NIE L, ZHANG H, REN AS, et al. Nano-hydroxyapatite mineralized silk fibroin porous scaffold for tooth extraction site preservation. Dent Mater. 2019;35(10):1397-1407. [24] SALEEM M, RASHEED S, YOUGEN C. Silk fibroin/hydroxyapatite scaffold: a highly compatible material for bone regeneration. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2020;21(1):242-266. [25] 李智,谭春华,蔡贤华,等.仿生大孔骨支架的制备及生物相容性评估[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(14):2223-2227. [26] SONG JE, TRIPATHY N, LEE DH, et al. Quercetin inlaid silk fibroin/hydroxyapatite scaffold promotes enhanced osteogenesis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(39):32955-32964. [27] KO E, LEE JS, KIM H, et al. Electrospun silk fibroin nanofibrous scaffolds with two-stage hydroxyapatite functionalization for enhancing the osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(9):7614-7625. [28] TABAGHT FE, AZZAOUI K, ELIDRISSI A, et al. New nanostructure based on hydroxyapatite modified cellulose for bone substitute, synthesis, and characterization. Int J Polym Mater. 2021;70(6):437-448. [29] 杨蕾.细菌纤维素/羟基磷灰石复合材料的制备及性能研究[D].南京:南京理工大学,2021. [30] 付冉冉.纤维素基复合材料的制备与抗菌性能研究[D].天津:天津工业大学,2018. [31] HE X, FAN X, FENG W, et al. Incorporation of microfibrillated cellulose into collagen-hydroxyapatite scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;115:385-392. [32] AO C, NIU Y, ZHANG X, et al. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun cellulose/nano-hydroxyapatite nanofibers for bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;97:568-573. [33] DAUGELA P, PRANSKUNAS M, JUODZBALYS G, et al. Novel cellulose/hydroxyapatite scaffolds for bone tissue regeneration: In vitro and in vivo study. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(5):1195-1208. [34] 南晓茹.丝素蛋白/纳米羟基磷灰石/透明质酸复合支架的制备及性能研究[D].太原:山西医科大学,2021. [35] 郭倩楠.明胶-透明质酸-纳米羟基磷灰石支架材料修复大鼠颌骨缺损的实验研究[D].唐山:华北理工大学,2019. [36] KACZMAREK B, SIONKOWSKA A, GOŁYŃSKA M, et al. In vivo study on scaffolds based on chitosan, collagen, and hyaluronic acid with hydroxyapatite. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;118(Pt A):938-944. [37] SADAT-SHOJAI M. Electrospun Polyhydroxybutyrate/Hydroxyapatite Nanohybrids: Microstructure and Bone Cell Response. J Mater Sci Technol. 2016;32(10):1013-1020. [38] KARAHALILOĞLU Z, ERCAN B, TAYLOR EN, et al. Antibacterial Nanostructured Polyhydroxybutyrate Membranes for Guided Bone Regeneration. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2015;11(12):2253-2263. [39] 管东华,林映荷,黄建生,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚羟基丁酸酯骨组织工程支架的制备及性能表征[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(25):3983-3989. [40] 宋越.静电纺丝法制备骨组织工程PHB和nHAP/PHB复合纤维支架及其结构和性能的研究[D].西安:西北大学,2012. [41] SADAT-SHOJAI M, KHORASANI MT, JAMSHIDI A, et al. Nano-hydroxyapatite reinforced polyhydroxybutyrate composites: a comprehensive study on the structural and in vitro biological properties. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013;33(5):2776-2787. [42] SENATOV F, ANISIMOVA N, KISELEVSKIY M, et al. Polyhydroxybutyrate/Hydroxyapatite Highly Porous Scaffold for Small Bone Defects Replacement in the Nonload-bearing Parts. J Bionic Eng. 2017;14(4):648-658. [43] CHEN Z, SONG Y, ZHANG J, et al. Laminated electrospun nHA/PHB-composite scaffolds mimicking bone extracellular matrix for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;72:341-351. [44] DONNALOJA F, JACCHETTI E, SONCINI M, et al. Natural and synthetic polymers for bone scaffolds optimization. Polymers (Basel). 2020;12(4):905. [45] DIEZ-ESCUDERO A, ANDERSSON B, PERSSON C, et al. Hexagonal pore geometry and the presence of hydroxyapatite enhance deposition of mineralized bone matrix on additively manufactured polylactic acid scaffolds. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;125:112091. [46] ZIMINA A, SENATOV F, CHOUDHARY R, et al. Biocompatibility and physico-chemical properties of highly porous PLA/HA scaffolds for bone reconstruction. Polymers (Basel). 2020;12(12):2938. [47] 刘冬,秦虎,汪永新,等.3D打印羟基磷灰石/聚乳酸网状复合物修复颅骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(6):833-837. [48] ZHANG HF, MAO XY, ZHAO DY, et al. Three dimensional printed polylactic acid-hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds for prefabricating vascularized tissue engineered bone:an in vivo bioreactor model. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):15255. [49] HUANG YH, JAKUS AE, JORDAN SW, et al. Three-dimensionally printed hyperelastic bone scaffolds accelerate bone regeneration in critical-size calvarial bone defects. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019;143(5):1397-1407. [50] YE KQ, LIU DH, KUANG HZ, et al. Three-dimensional electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds displaying bone morphogenetic protein-2-derived peptides for the promotion of osteogenic differentiation of stem cells and bone regeneration. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2019;534:625-636. [51] WANG X, ZHANG GL, QI F, et al. Enhanced bone regeneration using an insulin-loaded nano-hydroxyapatite/collagen/PLGA composite scaffold. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;13:117-127. [52] WU N, LIU J, MA WB, et al. Degradable calcium deficient hydroxyapatite/poly(lactic-glycolic acid copolymer) bilayer scaffold through integral molding 3D printing for bone defect repair. Biofabrication. 2021;13(2):10. [53] 王德欣,许战武,裴国献.骨髓间充质干细胞在淫羊藿苷/羟基磷灰 石/聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物支架上的成骨[J].中国组织工程研究,2020, 24(25):3974-3980. [54] BABILOTTE J, MARTIN B, GUDURIC V, et al. Development and characterization of a PLGA-HA composite material to fabricate 3D-printed scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;118:111334. [55] CUI LG, ZHANG J, ZOU J, et al. Electroactive composite scaffold with locally expressed osteoinductive factor for synergistic bone repair upon electrical stimulation. Biomaterials. 2020;230:119617. [56] YANG Y, CHU LY, YANG SB, et al. Dual-functional 3D-printed composite scaffold for inhibiting bacterial infection and promoting bone regeneration in infected bone defect models. Acta Biomater. 2018;79:265-275. [57] MOSTAFAVI A, ABUDULA T, RUSSELL CS, et al. In situ printing of scaffolds for reconstruction of bone defects. Acta Biomater. 2021;127:313-326. [58] PETRETTA M, GAMBARDELLA A, DESANDO G, et al. Multifunctional 3D-printed magnetic polycaprolactone/hydroxyapatite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Polymers(Basel). 2021;13(21):3825. [59] GÓMEZ-LIZÁRRAGA KK, FLORES-MORALES C, DEL PRADO-AUDELO ML, et al. Polycaprolactone- and polycaprolactone/ceramic-based 3D-bioplotted porous scaffolds for bone regeneration: A comparative study. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;79:326-335. [60] JI XF, YUAN X, MA LM, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-loaded thermosensitive hydroxypropyl chitin hydrogel combined with a three-dimensional-printed poly(ε-caprolactone) /nano-hydroxyapatite scaffold to repair bone defects via osteogenesis, angiogenesis and immunomodulation. Theranostics. 2020;10(2):725-740. [61] HACHIM D, LOPRESTI ST, YATES CC, et al. Shifts in macrophage phenotype at the biomaterial interface via IL-4 eluting coatings are associated with improved implant integration. Biomaterials. 2017;112:95-107. [62] ZHOU FF, ZHANG XZ, CAI DD, et al. Silk fibroin-chondroitin sulfate scaffold with immuno-inhibition property for articular cartilage repair. Acta Biomater. 2017;63:64-75. [63] PAN LH, ZHANG YH, CHEN N, et al. Icariin regulates cellular functions and gene expression of osteoarthritis patient-derived human fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(12):2656. [64] GONG L, LI J, ZHANG JW, et al. An interleukin-4-loaded bi-layer 3D printed scaffold promotes osteochondral regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2020;117:246-260. [65] HAN Y, LIAN MF, SUN BB, et al. Preparation of high precision multilayer scaffolds based on Melt Electro-Writing to repair cartilage injury. Theranostics. 2020;10(22):10214-10230. [66] ZHAO X, ZHOU L, LI Q, et al. Biomimetic mineralization of carboxymethyl chitosan nanofibers with improved osteogenic activity in vitro and in vivo. Carbohyd Polym. 2018;195:225-234. [67] FAN X, REN H, LUO X, et al. Mechanics, degradability, bioactivity, in vitro, and in vivo biocompatibility evaluation of poly(amino acid)/hydroxyapatite/calcium sulfate composite for potential load-bearing bone repair. J Biomater Appl. 2016;30(8):1261-1272. [68] 薛有地,宋跃明,刘立岷,等.聚氨基酸/纳米羟基磷灰石/硫酸钙融合器在山羊腰椎椎间融合中的作用研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2015,29(8):972-977. [69] 马龙冰,贾云兵,宋跃明,等.聚氨基酸/纳米羟基磷灰石/硫酸钙椎间融合器在腰椎融合术中的初步应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2016,30(3):328-335. [70] 陈伟,杨曦,宋跃明,等.聚氨基酸/纳米羟基磷灰石/硫酸钙椎间融合器植骨融合治疗下腰椎退行性疾病的中期临床随访[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2020,13(1):22-27. [71] 安田田,许燕,周建平,等.基于3D打印技术SF/PVA/HA复合骨支架的制备及表征[J].燕山大学学报,2021,45(5):409-414+423. [72] 李蕾,刘小元,张凯,等.3D打印丝素蛋白/聚乙烯醇/纳米羟基磷灰石支架体内降解的研究[J].口腔医学,2021,41(11):966-971. [73] 李耀明,姜宏,石永芳.壳聚糖/聚乳酸/羟基磷灰石/聚乙烯醇复合材料骨支架的制备及表征[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(18):2888-2893. [74] LIU S, LI D, CHEN X, et al. Biomimetic cuttlebone polyvinyl alcohol/carbon nanotubes/hydroxyapatite aerogel scaffolds enhanced bone regeneration. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022;210:112221. [75] 齐军强,郭超,牛东阳,等.金属离子掺杂羟基磷灰石骨修复材料的特性及应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(21):3415-3422. |
| [1] | 杨玉芳, 杨芷姗, 段棉棉, 刘毅恒, 唐正龙, 王 宇. 促红细胞生成素在骨组织工程中的应用及前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1443-1449. |
| [2] | 白 晨, 杨文骞, 孟志超, 王宇泽. 损伤前交叉韧带修复及促进移植物愈合的策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1457-1463. |
| [3] | 代越星, 郑利钦, 吴敏辉, 李志鸿, 李少彬, 郑德声, 林梓凌. 血管数量对小血管网计算流体力学的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1206-1210. |
| [4] | 王姗姗, 舒 晴, 田 峻. 物理因子促进干细胞的成骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1083-1090. |
| [5] | 张克凡, 石 辉. 细胞因子治疗骨关节炎的研究现状及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [6] | 王嘉旎, 陈俊宇. 金属离子促血管生成机制及在骨组织工程中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 804-812. |
| [7] | 代慧娟, 王钊鑫, 白布加甫·叶力思, 孙江伟, 古丽再努·依不拉音, 尼加提·吐尔逊. 三种咬合关系中树脂陶瓷冠和二氧化锆全瓷冠种植修复的生物力学差异[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 657-663. |
| [8] | 王 武, 樊晓磊, 谢 杰, 胡懿郃, 曾 敏. 羟基磷灰石-聚乙烯醇/胶原-壳聚糖-明胶复合水凝胶修复兔骨软骨缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 682-689. |
| [9] | 王建春, 杨树青, 苏 欣, 王宏远. 不同含量B2O3对生物活性玻璃支架力学性能与生物活性的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 712-716. |
| [10] | 兰伟伟, 于耀东, 黄 棣, 陈维毅. Mg-Zn-Ca合金的体外降解行为[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 717-723. |
| [11] | 周晓文, 符祖昶, 黄 飞, 艾建国, 赵 枫. 单平面胫骨骨搬移中骨水泥分段填塞封堵骨缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 736-740. |
| [12] | 朱礼威, 王江玥, 白 丁. 纳米复合甲基丙烯酰明胶水凝胶在不同骨缺损环境中应用的价值[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 753-758. |
| [13] | 杨雨晴, 陈志宇. 早期短暂M1巨噬细胞在骨组织工程中的作用及应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(4): 594-601. |
| [14] | 周世博, 关健斌, 俞 兴, 赵 赫, 杨永栋, 刘 涛. 股骨骨缺损动物模型制备现状及特点[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(4): 633-638. |
| [15] | 戴 京, 刘沙沙, 沈明敬. 负载外泌体的可注射水凝胶修复种植体周围骨缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 347-354. |
骨缺损是骨科医生经常面临的问题,因自体骨及异体骨存在的缺点,人工骨修复材料作为骨组织再生的替代选择应运而生。人骨的主要成分是磷酸钙矿物质和含有Ⅰ型胶原纤维的有机基质,羟基磷灰石是骨的主要无机质成分,已被证实具有良好的细胞亲和力,可促进成骨细胞的黏附和增殖,并直接与骨结合,已被广泛用作骨移植的替代材料[3]。然而,由于羟基磷灰石的易碎性、不耐疲劳以及在多孔羟基磷灰石网络中形成的新骨不能承受重塑所需的机械负荷,其临床应用受到限制。聚合物因具有良好的生物相容性、韧性和降解性,与羟基磷灰石复合可提高材料的机械性能、生物活性,被广泛研究并应用于骨组织的修复与再生[4-5]。该文对各种羟基磷灰石/聚合物复合材料的最新研究进展及其应用进行综述,旨在为骨修复材料的基础研究和临床应用提供参考。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在2023年4月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 2010年1月至2023年4月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 应用计算机检索PubMed、Web of Science、中国知网及万方数据库中的相关文献。
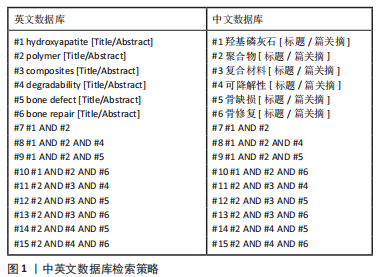
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“羟基磷灰石,聚合物,复合材料,可降解性,骨缺损,骨修复”,英文检索词“hydroxyapatite,polymer,composites,degradability,bone defect,bone repair”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著、综述和病例报告。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 无。
1.1.7 检索策略 中英文数据库的检索策略,见图1。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①有关羟基磷灰石/聚合物的文献;②与骨修复或骨组织工程有关的文献;③相关性高且权威的文献;④他引次数高的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①重复性研究;②与骨修复、骨组织工程无关的文献;③非核心期刊文献。
1.3 文献质量评估和数据的提取 通过文献泛读和精读,依据纳入和排除标准,最后选入文献75 篇进行综述。文献筛选流程图,见图2。
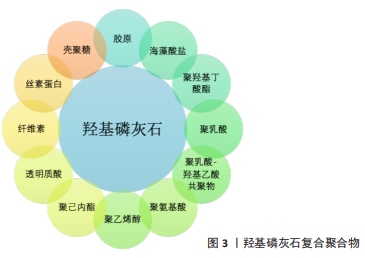
 创伤、炎症、肿瘤、退行性疾病等骨缺损原因具有多样性、复杂性,骨修复重建又是一个各种细胞因子、许多相关蛋白共同调节骨形成、骨吸收和血管生成的复杂连续过程,为得到理想的骨修复材料,未来可从以下方面探索:①改进制备工艺,如3D打印、交联、涂层技术或多技术联合制备材料等;②通过离子掺杂(锶、铜、锌、银、镁等)、表面修饰或多元复合(如羟基磷灰石/磷酸三钙/聚合物、羟基磷灰石/生物玻璃/聚合物等)增强材料机械强度[75];③负载活性因子(骨形态发生蛋白、血管内皮生长因子、成纤维细胞生长因子等)、细胞(骨髓/脂肪间充质干细胞等)、促骨生成药物(槲皮素、淫羊藿苷、柚皮苷等)、抗生素(庆大霉素、异烟肼等)、抗癌药(多柔比星等)等,构建多功能复合材料等。随着新技术的出现、组织工程学和材料学的发展,相信未来骨修复材料必将取得重大进展,满足临床需求,为广大患者带来福音。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
创伤、炎症、肿瘤、退行性疾病等骨缺损原因具有多样性、复杂性,骨修复重建又是一个各种细胞因子、许多相关蛋白共同调节骨形成、骨吸收和血管生成的复杂连续过程,为得到理想的骨修复材料,未来可从以下方面探索:①改进制备工艺,如3D打印、交联、涂层技术或多技术联合制备材料等;②通过离子掺杂(锶、铜、锌、银、镁等)、表面修饰或多元复合(如羟基磷灰石/磷酸三钙/聚合物、羟基磷灰石/生物玻璃/聚合物等)增强材料机械强度[75];③负载活性因子(骨形态发生蛋白、血管内皮生长因子、成纤维细胞生长因子等)、细胞(骨髓/脂肪间充质干细胞等)、促骨生成药物(槲皮素、淫羊藿苷、柚皮苷等)、抗生素(庆大霉素、异烟肼等)、抗癌药(多柔比星等)等,构建多功能复合材料等。随着新技术的出现、组织工程学和材料学的发展,相信未来骨修复材料必将取得重大进展,满足临床需求,为广大患者带来福音。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
羟基磷灰石:是人体骨组织的主要无机质成分,其钙/磷比为1.67,与自然骨组织相似,可与人体骨组织通过羟基键合,且有一定的降解性,可释放钙、磷离子刺激或诱导骨组织生成,促进骨缺损局部修复,具有良好的生物相容性,但其脆性高、降解速度慢及骨诱导性、成血管活性等较弱,限制了其在临床上的单独使用。聚合物:包括天然聚合物和人工合成聚合物,在结构上与细胞外基质类似,具有良好的生物相容性、可调控的降解性、细胞因子和药物缓释性、骨传导性,常与其他材料复合制备新材料用于细胞因子和药物的缓释、骨组织缺损的修复等。
由于骨缺损的发生不断上升,临床治疗中对骨修复移植物的需求也持续增加。自体骨和异体骨移植因其存在的缺点,临床应用受限。随着骨组织工程和材料科学的发展进步,人工骨修复材料得到广泛研究。基于天然骨组织无机物-有机物复合的组成特点,以仿生天然骨的组成、结构和功能为理念,结合羟基磷灰石和聚合物的优点,羟基磷灰石基聚合物复合材料得到研究者的关注。既往多为聚合物复合羟基磷灰石的制备、不同制备方法对复合材料理化性能的影响、某一聚合物改性羟基磷灰石的复合材料理化性能和生物活性的研究等,未对不同聚合物复合羟基磷灰石用于骨缺损修复的力学性能、体内外成骨活性进行系统的综述研究。该文对常见天然聚合物和合成聚合物复合羟基磷灰石的制备、复合材料的力学性能、体内外生物相容性、骨诱导性和成骨能力等进行了综述,旨在为羟基磷灰石基聚合物材料用于骨修复的基础研究和临床应用提供参考。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||