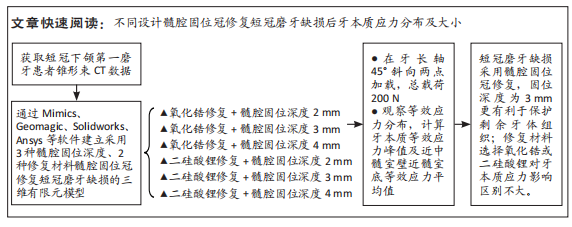
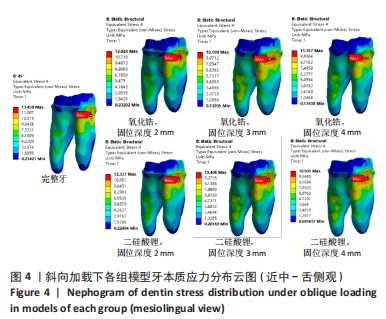
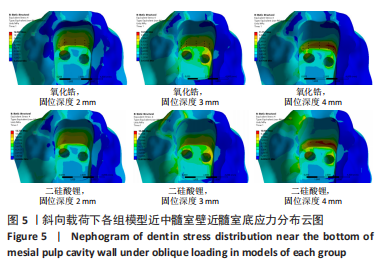
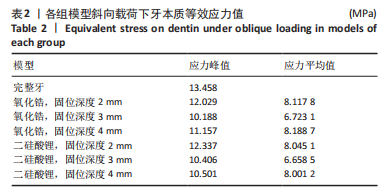
[1] 粟猛,屈直.不同制备形态对短冠磨牙髓腔固位冠抗折性影响的研究[J].口腔医学研究,2021,37(2):118-121.
[2] PARKER MH, GUNDERSON RB, GARDNER FM, et al. Quantitative determination of taper adequate to provide resistance form: concept of limiting taper. J Prosthet Dent. 1988;59(3):281-288.
[3] 田宇,张亚庆,吕海鹏,等.后牙椅旁CAD/CAM修复洞型分类的思考[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2016,26(10):581-588.
[4] BINDL A, MORMANN WH. clinical evaluation of adhesively placed Cerec endo—crowns after 2 years—preliminary result. Adhes Dent. 1999;1(3):255-265.
[5] HARALUR SB, ALAMREY AA, ALSHEHRI SA, et al. Effect of different preparation designs and all ceramic materials on fracture strength of molar endocrowns. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2020;18:588079489.
[6] DARTORA NR, DE CONTO FM, MORIS I, et al. Effect of Intracoronal Depth of Teeth Restored with Endocrowns on Fracture Resistance: In Vitro and 3-dimensional Finite Element Analysis. J Endod. 2018; 44(7):1179-1185.
[7] 李米雪子,张琛.椅旁计算机辅助设计/计算机辅助制作髓腔固位冠修复根管治疗后磨牙的临床考量[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2021, 48(3):274-279.
[8] 包旭东.椅旁计算机辅助设计与辅助制作嵌体冠粘接修复大面积缺损根管治疗牙的利与弊[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2018,53(4):221-225.
[9] 张珑,李芳萍,杨柏松,等.不同材料嵌体修复邻牙合(Ⅱ类)洞型的三维有限元研究[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2015,36(2): 201-205.
[10] JIANG WM, BO HM, YONGCHUN GM, et al. Stress distribution in molars restored with inlays or onlays with or without endodontic treatment: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Prosthet Dent. 2010; 103(1):6-12.
[11] 殷金萍,王静,孙亚丽,等.动态载荷下不同材料修复非龋性颈部缺损有限元分析[J].口腔医学研究, 2021,37(9):820-824.
[12] 贾洪诚,王璇.髓室固位形在短临床冠修复中的应用[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2010,11(2):90-91.
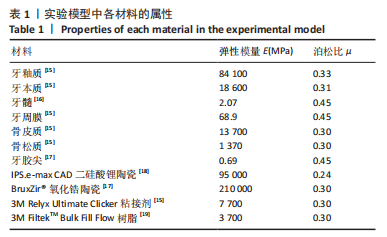
[13] 王惠芸.我国人牙的测量和统计[J].中华口腔科杂志,1959,7(3): 149-155.
[14] 刘潇,陈曦,李宝,等.夹层技术不同充填材料和咬合角度对非龋性颈部缺损牙体应力分布的影响[J]. 口腔医学研究,2022,38(5): 447-453.
[15] GONG Q, HUANG L, LUO J, et al. The practicability of different preparation of mandibular molar restored by modified endocrown with intracanal extension: Computational analysis using finite element models. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022;226:107178.
[16] LUO X, RONG Q, LUAN Q, et al. Effect of partial restorative treatment on stress distributions in non-carious cervical lesions: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. BMC Oral Health. 2022;22(1):607.
[17] DARWICH MA, ALJAREH A, ALHOURI N, et al. Biomechanical Assessment of Endodontically Treated Molars Restored by Endocrowns Made from Different CAD/CAM Materials. Materials (Basel). 2023;16(2):764.
[18] ZAMZAM H, OLIVARES A, FOK A. Load capacity of occlusal veneers of different restorative CAD/CAM materials under lateral static loading. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2021;115:104290.
[19] ANTUNES JC, MERCURI E, FRANCO A, et al. Bulk Fill flow resin contraction using 3D finite element model and calibration by Fiber Bragg Grating measurement. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2020;23(14):1127-1137.
[20] DIANA HH, OLIVEIRA JS, FERRO MC, et al. Stress Distribution in Roots Restored with Fiber Posts and An Experimental Dentin Post-3D:FEA. Braz Dent J. 2016;27(2):223-227.
[21] YANG S, CHUNG H. Three-dimentional finite element analysis of a mandibular premolar with reduced periodontal support under a non-axial load. Oral Biol Res. 2019;43(4):313-326.
[22] AHMIĆ VUKOVIĆ A, JAKUPOVIĆ S, ZUKIĆ S, et al. Occlusal Stress Distribution on the Mandibular First Premolar - FEM Analysis. Acta Med Acad. 2019;48(3):255-261.
[23] 邹蕴.根管治疗后下颌第一磨牙髓腔固位冠修复的三维有限元分析[D].沈阳:中国医科大学,2016.
[24] 李智,徐永祥,包旭东,等.垫底树脂和固位深度对树脂基纳米陶瓷髓腔固位冠修复磨牙抗折性能的影响[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2022,54(1):95-99.
[25] 阮文豪.椅旁CAD/CAM不同覆盖形式嵌体修复根管治疗后下颌磨牙的生物力学分析[D].广州:南方医科大学,2019.
[26] ZHANG Y, LAI H, MENG Q, et al. The synergetic effect of pulp chamber extension depth and occlusal thickness on stress distribution of molar endocrowns: a 3-dimensional finite element analysis. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2022;33(7):56.
[27] DE KUIJPER MCFM, CUNE MS, TROMP Y, et al. Cyclic loading and load to failure of lithium disilicate endocrowns: Influence of the restoration extension in the pulp chamber and the enamel outline.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2020;105:103670.
[28] 陈丽洁.辅助固位形对全冠预备体应力分布的影响[D].西安:第四军医大学,2008.
[29] ZAMZAM H, OLIVARES A, FOK A. Load capacity of occlusal veneers of different restorative CAD/CAM materials under lateral static loading. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2021;115:104290.
[30] 张国梅,祝军,胡杨,等.E-Max瓷嵌体三维有限元模型粘接界面应力分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(4):537-541.
[31] GUAZZATO M, ALBAKRY M, RINGER SP, et al. Strength, fracture toughness and microstructure of a selection of all-ceramic materials. Part II. Zirconia-based dental ceramics. Dent Mater. 2004;20(5):449-456.
[32] 赵信义.口腔材料学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2020.
[33] 陈栋.根管治疗后上颌前磨牙修复方式的三维有限元比较研究[D].广州:南方医科大学口腔临床医学,2008. |