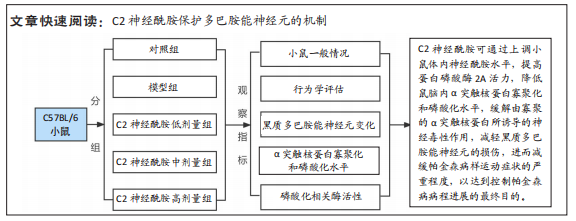
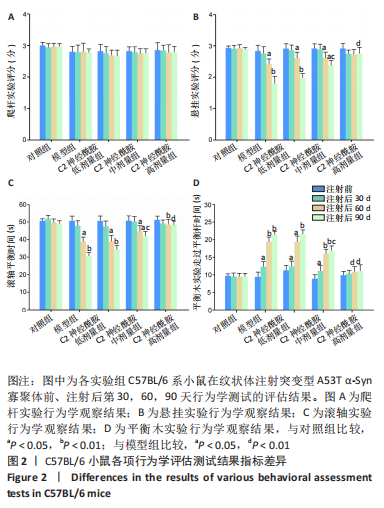
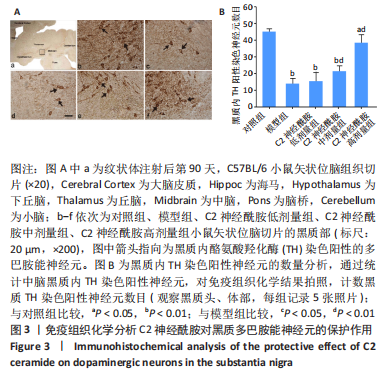
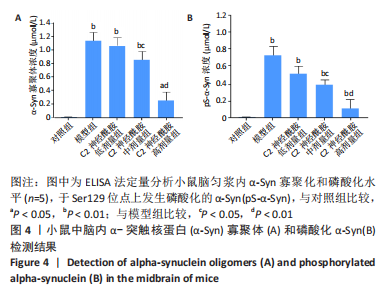
[1] MONTEMURRO N, ALIAGA N, GRAFF P, et al. New targets and new technologies in the treatment of parkinson’s disease: a narrative review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(14):8799.
[2] COSTA HN, ESTEVES AR, EMPADINHAS N, et al. Parkinson’s disease: a multisystem disorder. Neurosci Bull. 2023;39(1):113-124.
[3] MYERS PS, O’DONNELL JL, JACKSON JJ, et al. Proteinopathy and longitudinal cognitive decline in Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2022;99(1):e66-e76.
[4] SIMON C, SOGA T, OKANO HJ, et al. α-Synuclein-mediated neurodegeneration in dementia with Lewy bodies: the pathobiology of a paradox. Cell Biosci. 2021;11(1):196.
[5] BARBA L, PAOLINI PAOLETTI F, BELLOMO G, et al. Alpha and beta synucleins: from pathophysiology to clinical application as biomarkers. Mov Disord. 2022;37(4):669-683.
[6] BELL R, THRUSH RJ, CASTELLANA-CRUZ M, et al. N-terminal acetylation of α-synuclein slows down its aggregation process and alters the morphology of the resulting aggregates. Biochemistry. 2022;61(17):1743-1756.
[7] SALAMON A, ZADORI D, SZPISJAK L, et al. The genetic background of Parkinson’s disease and novel therapeutic targets. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2022;26(10):827-836.
[8] GUHATHAKURTA S, SONG MK, BASU S, et al. Regulation of αlpha-synuclein gene (SNCA) by epigenetic modifier TET1 in Parkinson disease. Int Neurourol J. 2022;26(Suppl 2):S85-S93.
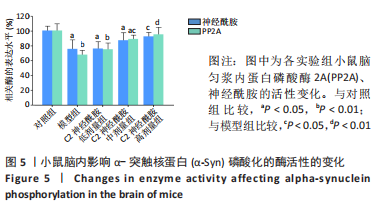
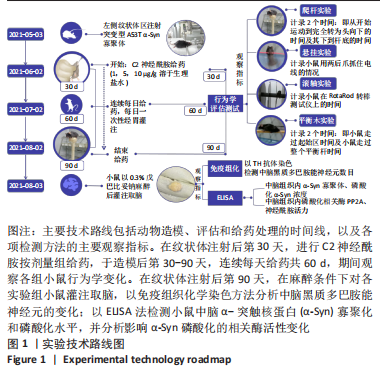
[9] 王鹏,历春,王海鹏,等.Alpha-突触核蛋白寡聚体致帕金森病小鼠模型的行为学变化[J].中国老年学杂志,2016,36(21):5227-5230.
[10] GHANEM SS, MAJBOUR NK, VAIKATH NN, et al. α-Synuclein phosphorylation at serine 129 occurs after initial protein deposition and inhibits seeded fibril formation and toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022;119(15):e2109617119.
[11] WANG R, WANG Y, QU L, et al. Iron-induced oxidative stress contributes to α-synuclein phosphorylation and up-regulation via polo-like kinase 2 and casein kinase 2. Neurochem Int. 2019;125:127-135.
[12] SHIN WH, CHUNG KC. Death-associated protein kinase 1 phosphorylates α-synuclein at Ser129 and exacerbates rotenone-induced toxic aggregation of α-synuclein in dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells. Exp Neurobiol. 2020;29(3): 207-218.
[13] LASHUEL HA, MAHUL-MELLIER AL, NOVELLO S, et al. Revisiting the specificity and ability of phospho-S129 antibodies to capture alpha-synuclein biochemical and pathological diversity. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2022; 8(1):136.
[14] DENT SE, KING DP, OSTERBERG VR, et al. Phosphorylation of the aggregate-forming protein alpha-synuclein on serine-129 inhibits its DNA-bending properties. J Biol Chem. 2022;298(2):101552.
[15] KAWAHATA I, FINKELSTEIN DI, FUKUNAGA K. Pathogenic impact of α-synuclein phosphorylation and its kinases in α-synucleinopathies. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(11):6216.
[16] UEDA S, NISHIHARA M, HIOKA Y, et al. Polo-like kinase 2 plays an essential role in cytoprotection against MG132-induced proteasome inhibition via phosphorylation of serine 19 in HSPB5. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(19):11257.
[17] ZHANG C, NI C, LU H. Polo-like kinase 2: from principle to practice. Front Oncol. 2022;12(8):956225.
[18] TIAN H, LU Y, LIU J, et al. Leucine carboxyl methyltransferase downregulation and protein phosphatase methylesterase upregulation contribute toward the inhibition of protein phosphatase 2A by α-synuclein. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018;10:173.
[19] DEHGHAN A, PINTO RC, KARAMAN I, et al. Metabolome-wide association study on ABCA7 indicates a role of ceramide metabolism in Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022;119(43):e2206083119.
[20] ZHUO C, ZHAO F, TIAN H, et al. Acid sphingomyelinase/ceramide system in schizophrenia: implications for therapeutic intervention as a potential novel target. Transl Psychiatry. 2022;12(1):260.
[21] ZHANG Y, JI S, ZHANG X, et al. Human CPTP promotes growth and metastasis via sphingolipid metabolite ceramide and PI4KA/AKT signaling in pancreatic cancer cells. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18(13):4963-4983.
[22] PLOTEGHER N, BUBACCO L, GREGGIO E, et al. Ceramides in Parkinson’s disease: from recent evidence to new hypotheses. Front Neurosci. 2019; 13:330.
[23] CLARK AR, OHLMEYER M. Protein phosphatase 2A as a therapeutic target in inflammation and neurodegeneration. Pharmacol Ther. 2019;201(9):181-201.
[24] CUSTODIA A, ARAMBURU-NÚÑEZ M, CORREA-PAZ C, et al. Ceramide metabolism and Parkinson’s disease-therapeutic targets. Biomolecules. 2021;11(7):945.
[25] 韩燕银.C2-神经酰胺抑制α-synuclein聚集的研究[D].桂林:桂林医学院,2019.
[26] 张天华,李永春,李宪伟,等.C2-神经酰胺对间皮瘤细胞裸鼠移植瘤生长的抑制作用[J].现代肿瘤医学,2014,22(9):2038-2043.
[27] CHOONG CJ, MOCHIZUKI H. Neuropathology of α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Neuropathology. 2022;42(2):93-103.
[28] PAN L, LI C, MENG L, et al. Tau accelerates α-synuclein aggregation and spreading in Parkinson’s disease. Brain. 2022;145(10):3454-3471.
[29] TIJMS BM, GOBOM J, REUS L, et al. Pathophysiological subtypes of Alzheimer’s disease based on cerebrospinal fluid proteomics. Brain. 2020; 143(12):3776-3792.
[30] SEPPI K, RAY CHAUDHURI K, COELHO M, et al. Update on treatments for nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease-an evidence-based medicine review. Mov Disord. 2019;34(2):180-198.
[31] ELLIS TD, COLÓN-SEMENZA C, DEANGELIS TR, et al. Evidence for early and regular physical therapy and exercise in Parkinson’s disease. Semin Neurol. 2021;41(2):189-205.
[32] YOO H, LEE J, KIM B, et al. Role of post-translational modifications on the alpha-synuclein aggregation-related pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. BMB Rep. 2022;55(7):323-335.
[33] RAMALINGAM N, JIN SX, MOORS TE, et al. Dynamic physiological α-synuclein S129 phosphorylation is driven by neuronal activity. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2023;9(1):4.
[34] PENG WANG, XIN LI, XURAN LI, et al. Blood plasma of patients with Parkinson’s disease increases alpha-synuclein aggregation and neurotoxicity. Parkinsons Dis. 2016;2016:7596482.
[35] LUNGHI G, CASNNA EV, LOBERTO N, et al. β-glucocerebrosidase deficiency activates an aberrant lysosome-plasma membrane axis responsible for the onset of neurodegeneration. Cells. 2022;11(15):2343.
[36] SMITH L, SCHAPIRA AHV. GBA variants and Parkinson disease: mechanisms and treatments. Cells. 2022;11(8):1261.
[37] SMITH JK, MELLICK GD, SYKES AM. The role of the endolysosomal pathway in α-synuclein pathogenesis in Parkinson’s disease. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023;16:1081426.
[38] 王鹏,李昕,陈予东,等.α-突触核蛋白寡聚体抑制大鼠原代培养神经元突起早期生长[J].首都医科大学学报,2014,35(5):587-591.
[39] TRINGALI C, GIUSSANI P. Ceramide and sphingosine-1-phosphate in neurodegenerative disorders and their potential involvement in therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(14):7806.
[40] DEN HOEDT S, CRIVELLI SM, LEIJTEN FPJ, et al. Effects of sex, age, and apolipoprotein e genotype on brain ceramides and sphingosine-1-phosphate in alzheimer’s disease and control mice. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021;13:765252.
[41] AYUB M, JIN HK, BAE JS. Novelty of sphingolipids in the central nervous system physiology and disease: focusing on the sphingolipid hypothesis of neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(14):7353.
[42] MINGIONE A, PIVARI F, PLOTEGHER N, et al. Inhibition of ceramide synthesis reduces α-synuclein proteinopathy in a cellular model of Parkinson’s disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(12):6469.
[43] BHUMKAR A, MAGNAN C, LAU D, et al. Single-molecule counting coupled to rapid amplification enables detection of α-synuclein aggregates in cerebrospinal fluid of Parkinson’s disease patients. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021;60(21):11874-11883.
[44] POGGIOLINI I, GUPTA V, LAWTON M, et al. Diagnostic value of cerebrospinal fluid alpha-synuclein seed quantification in synucleinopathies. Brain. 2022; 145(2):584-595.
[45] ZHAO X, HE H, XIONG X, et al. Lewy body-associated proteins a-synuclein (a-syn) as a plasma-based biomarker for Parkinson’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:869797. |