[1] GUPTA R, AMBASTA RK, KUMAR P. Multifaced role of protein deacetylase sirtuins in neurodegenerative disease. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022;132:976-997.
[2] WANG J, ZHANG XN, FANG JN, et al. The mechanism behind activation of the Nod-like receptor family protein 3 inflammasome in Parkinson’s disease. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(4):898-904.
[3] WALDTHALER J, VINDING MC, ERIKSSON A, et al. Neural correlates of impaired response inhibition in the antisaccade task in Parkinson’s disease. Behav Brain Res. 2022;422:113763.
[4] MIZRAHI-KLIGER AD, FELDMANN LK, KUHN AA, et al. Etiologies of insomnia in Parkinson’s disease -Lessons from human studies and animal models. Exp Neurol. 2022;350:113976.
[5] SCHRAG A, ZHELEV SS, HOTHAM S, et al. Heterogeneity in progression of prodromal features in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2019;64:275-279.
[6] MARRAS C, BECK JC, BOWER JH, et al. Prevalence of Parkinson’s disease across North America. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2018;4:21.
[7] QIU J, CHEN Y, ZHUO J, et al. Urolithin A promotes mitophagy and suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV2 microglial cells and MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease model. Neuropharmacology. 2022;207:108963.
[8] OZGEN S, KRIGMAN J, ZHANG R, et al. Significance of mitochondrial activity in neurogenesis and neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(4):741-747.
[9] CHAU E, KIM J R. alpha-synuclein-assisted oligomerization of beta-amyloid (1-42). Arch Biochem Biophys. 2022;717:109120.
[10] NGUYEN TT, NGUYEN TTD, TRAN NM, et al. Lipid-based nanocarriers via nose-to-brain pathway for central nervous system disorders. Neurochem Res. 2022;47(3):552-573.
[11] YU H, SUN T, AN J, et al. Potential roles of exosomes in Parkinson’s disease:from pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment to prognosis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:86.
[12] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020. doi:10.1126/science.aau6977.
[13] ARAUJO-ABAD S, SACEDA M, DE JUAN ROMERO C. Biomedical application of small extracellular vesicles in cancer treatment. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022;182:114117.
[14] SIDORYK-WEGRZYNOWICZ M, DABROWSKA-BOUTA B, SULKOWSKI G, et al. Nanosystems and exosomes as future approaches in treating multiple sclerosis. Eur J Neurosci. 2021;54(9):7377-404.
[15] 卫宇帆,樊飞燕,李双利,等.外泌体及间充质干细胞源性外泌体在帕金森病诊治中的未来[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(25): 4076-4083.
[16] 周丽娜,王洪新.外泌体在帕金森病中的研究进展[J].中华神经医学杂志,2021,20(12):1270-1274.
[17] WAN Y, LIU B, LEI H, et al. Nanoscale extracellular vesicle-derived DNA is superior to circulating cell-free DNA for mutation detection in early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 2018;29(12):2379-2383.
[18] ZHANG Y, LIU Y, LIU H, et al. Exosomes: biogenesis, biologic function and clinical potential. Cell Biosci. 2019;9:19.
[19] GAO P, LI X, DU X, et al. Diagnostic and therapeutic potential of exosomes in neurodegenerative diseases. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021; 13:790863.
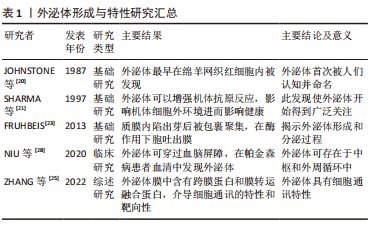
[20] JOHNSTONE RM, ADAM M, HAMMOND JR, et al. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem. 1987;262(19): 9412-9420.
[21] SHARMA S, MILLER PW, STOLINA M, et al. Multicomponent gene therapy vaccines for lung cancer:effective eradication of established murine tumors in vivo with interleukin-7/herpes simplex thymidine kinase-transduced autologous tumor and ex vivo activated dendritic cells. Gene Ther. 1997;4(12):1361-1370.
[22] LI S, CHEN L. Exosomes in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol. 2022;12:793432.
[23] FRUHBEIS C, FROHLICH D, KUO WP, et al. Extracellular vesicles as mediators of neuron-glia communication. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013; 7:182.
[24] SOARES MARTINS T, MARCALO R, DA CRUZ ESCB, et al. Novel exosome biomarker candidates for alzheimer’s disease unravelled through mass spectrometry analysis. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. doi:10.1007/s12035-022-02762-1.
[25] ZHANG H, XING J, DAI Z, et al. Exosomes: the key of sophisticated cell-cell communication and targeted metastasis in pancreatic cancer. Cell Commun Signal. 2022;20(1):9.
[26] AGLIARDI C, GUERINI FR, MELONI M, et al. Alpha-synuclein as a biomarker in Parkinson’s disease:focus on neural derived extracelluar vesicles. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(7):1503-1504.
[27] FU Y, JIANG C, TOFARIS G K, et al. Facile impedimetric analysis of neuronal exosome markers in parkinson’s disease diagnostics. Anal Chem. 2020;92(20):13647-13651.
[28] NIU M, LI Y, LI G, et al. A longitudinal study on alpha-synuclein in plasma neuronal exosomes as a biomarker for Parkinson’s disease development and progression. Eur J Neurol. 2020;27(6):967-974.
[29] YOUSIF G, QADRI S, HAIK M, et al. Circulating exosomes of neuronal origin as potential early biomarkers for development of stroke. Mol Diagn Ther. 2021;25(2):163-180.
[30] WEI Z X, XIE G J, MAO X, et al. Exosomes from patients with major depression cause depressive-like behaviors in mice with involvement of miR-139-5p-regulated neurogenesis. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2020;45(6):1050-1058.
[31] JIANG R, RONG C, KE R, et al. Differential proteomic analysis of serum exosomes reveals alterations in progression of Parkinson disease. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(41):e17478.
[32] CHOI WS, KIM HW, TRONCHE F, et al. Conditional deletion of Ndufs4 in dopaminergic neurons promotes Parkinson’s disease-like non-motor symptoms without loss of dopamine neurons. Sci Rep. 2017;7:44989.
[33] JANKOVIC J, TAN EK. Parkinson’s disease:etiopathogenesis and treatment. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2020;91(8):795-808.
[34] LATIF S, JAHANGEER M, MAKNOON RAZIA D, et al. Dopamine in Parkinson’s disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2021;522:114-126.
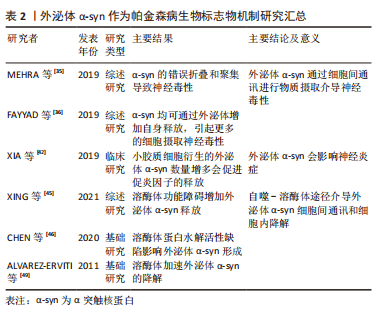
[35] MEHRA S, SAHAY S, MAJI SK. alpha-Synuclein misfolding and aggregation:Implications in Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2019;1867(10):890-908.
[36] FAYYAD M, SALIM S, MAJBOUR N, et al. Parkinson’s disease biomarkers based on alpha-synuclein. J Neurochem. 2019;150(5):626-636.
[37] FAN RZ, GUO M, LUO S, et al. Exosome release and neuropathology induced by alpha-synuclein:new insights into protective mechanisms of Drp1 inhibition. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019;7(1):184.
[38] GUO M, WANG J, ZHAO Y, et al. Microglial exosomes facilitate alpha-synuclein transmission in Parkinson’s disease. Brain. 2020;143(5): 1476-1497.
[39] HAN C, XIONG N, GUO X, et al. Exosomes from patients with Parkinson’s disease are pathological in mice. J Mol Med (Berl). 2019; 97(9):1329-1344.
[40] SI X, TIAN J, CHEN Y, et al. Central nervous system-derived exosomal alpha-synuclein in serum may be a biomarker in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience. 2019;413:308-316.
[41] GUO M, HAO Y, FENG Y, et al. Microglial exosomes in neurodegenerative disease. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021;14:630808.
[42] XIA Y, ZHANG G, HAN C, et al. Microglia as modulators of exosomal alpha-synuclein transmission. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(3):174.
[43] BRUCK D, WENNING GK, STEFANOVA N, et al. Glia and alpha-synuclein in neurodegeneration: a complex interaction. Neurobiol Dis. 2016;85:262-274.
[44] SARKAR S, DAMMER EB, MALOVIC E, et al. Molecular signatures of neuroinflammation induced by alphasynuclein aggregates in microglial cells. Front Immunol. 2020;11:33.
[45] XING H, TAN J, MIAO Y, et al. Crosstalk between exosomes and autophagy: a review of molecular mechanisms and therapies. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(5):2297-308.
[46] CHEN HX, LIANG FC, GU P, et al. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells repair a Parkinson’s disease model by inducing autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(4):288.
[47] FUSSI N, HOLLERHAGE M, CHAKROUN T, et al. Exosomal secretion of alpha-synuclein as protective mechanism after upstream blockage of macroautophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(7):757.
[48] STEFANIS L, EMMANOUILIDOU E, PANTAZOPOULOU M, et al. How is alpha-synuclein cleared from the cell? J Neurochem. 2019;150(5):577-590.
[49] ALVAREZ-ERVITI L, SEOW Y, SCHAPIRA AH, et al. Lysosomal dysfunction increases exosome-mediated alpha-synuclein release and transmission. Neurobiol Dis. 2011;42(3):360-367.
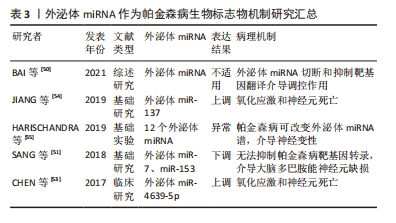
[50] BAI Y, SU X, PIAO L, et al. Involvement of astrocytes and microrna dysregulation in neurodegenerative diseases: from pathogenesis to therapeutic potential. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021;14:556215.
[51] SANG Q, LIU X, WANG L, et al. CircSNCA downregulation by pramipexole treatment mediates cell apoptosis and autophagy in Parkinson’s disease by targeting miR-7. Aging (Albany NY). 2018;10(6):1281-1293.
[52] LU S, YANG X, WANG C, et al. Current status and potential role of circular RNAs in neurological disorders. J Neurochem. 2019;150(3): 237-248.
[53] CHEN Y, GAO C, SUN Q, et al. MicroRNA-4639 Is a regulator of DJ-1 expression and a potential early diagnostic marker for parkinson’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2017;9:232.
[54] JIANG Y, LIU J, CHEN L, et al. Serum secreted miR-137-containing exosomes affects oxidative stress of neurons by regulating OXR1 in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res. 2019;1722:146331.
[55] HARISCHANDRA DS, ROKAD D, NEAL ML, et al. Manganese promotes the aggregation and prion-like cell-to-cell exosomal transmission of alpha-synuclein. Sci Signal. 2019. doi:10.1126/scisignal.aau4543.
[56] HARISCHANDRA DS, GHAISAS S, ROKAD D, et al. Environmental neurotoxicant manganese regulates exosome-mediated extracellular miRNAs in cell culture model of Parkinson’s disease: relevance to alpha-synuclein misfolding in metal neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology. 2018;64:267-277.
[57] PANICKER N, GE P, DAWSON VL, et al. The cell biology of Parkinson’s disease. J Cell Biol. 2021. doi:10.1083/jcb.202012095.
[58] ZHANG K, ZHU SO, LI JM, et al. Targeting autophagy using small-molecule compounds to improve potential therapy of Parkinson’s disease. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021;11(10):3015-3034.
[59] ZHAO ZH, CHEN ZT, ZHOU RL, et al. Increased DJ-1 and alpha-synuclein in plasma neural-derived exosomes as potential markers for Parkinson’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018;10:438.
[60] FRASER KB, MOEHLE MS, ALCALAY RN, et al. Urinary LRRK2 phosphorylation predicts parkinsonian phenotypes in G2019S LRRK2 carriers. Neurology. 2016;86(11):994-999.
[61] STREUBEL-GALLASCH L, GIUSTI V, SANDRE M, et al. Parkinson’s Disease-associated LRRK2 interferes with astrocyte-mediated alpha-synuclein clearance. Mol Neurobiol. 2021;58(7):3119-3140.
[62] DE RUS JACQUET A, TANCREDI JL, LEMIRE AL, et al. The LRRK2 G2019S mutation alters astrocyte-to-neuron communication via extracellular vesicles and induces neuron atrophy in a human iPSC-derived model of Parkinson’s disease. Elife. 2021. doi:10.7554/eLife.73062.
[63] MANNA I, QUATTRONE A, DE BENEDITTIS S, et al. Exosomal miRNA as peripheral biomarkers in Parkinson’s disease and progressive supranuclear palsy: a pilot study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2021;93: 77-84.
[64] JIANG C, HOPFNER F, KATSIKOUDI A, et al. Serum neuronal exosomes predict and differentiate Parkinson’s disease from atypical parkinsonism. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2020;91(7):720-729.
[65] DUTTA S, HORNUNG S, KRUAYATIDEE A, et al. alpha-Synuclein in blood exosomes immunoprecipitated using neuronal and oligodendroglial markers distinguishes Parkinson’s disease from multiple system atrophy. Acta Neuropathol. 2021;142(3):495-511.
[66] GOMEZ-MOLINA C, SANDOVAL M, HENZI R, et al. Small extracellular vesicles in rat serum contain astrocyte-derived protein biomarkers of repetitive stress. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019;22(3):232-246.
[67] SAMANTA S, RAJASINGH S, DROSOS N, et al. Exosomes:new molecular targets of diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018;39(4):501-513.
[68] KALIMUTHU S, GANGADARAN P, RAJENDRAN RL, et al. A new approach for loading anticancer drugs into mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome mimetics for cancer therapy. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1116.
[69] BUNGGULAWA EJ, WANG W, YIN T, et al. Recent advancements in the use of exosomes as drug delivery systems. J Nanobiotechnology. 2018;16(1):81.
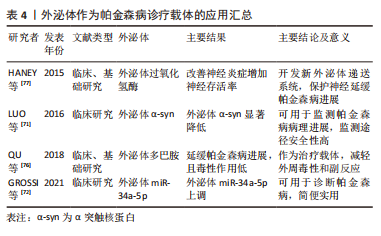
[70] KOJIMA R, BOJAR D, RIZZI G, et al. Designer exosomes produced by implanted cells intracerebrally deliver therapeutic cargo for Parkinson’s disease treatment. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1305.
[71] LUO HT, ZHANG JP, MIAO F. Effects of pramipexole treatment on the alpha-synuclein content in serum exosomes of Parkinson’s disease patients. Exp Ther Med. 2016;12(3):1373-1376.
[72] GROSSI I, RADEGHIERI A, PAOLINI L, et al. MicroRNA34a5p expression in the plasma and in its extracellular vesicle fractions in subjects with Parkinson’s disease: an exploratory study. Int J Mol Med. 2021; 47(2):533-546.
[73] FAROTTI L, PACIOTTI S, TASEGIAN A, et al. Discovery, validation and optimization of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for use in Parkinson’s disease. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2017;17(8):771-780.
[74] MEHTA SH, ADLER CH. Advances in biomarker research in Parkinson’s disease. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2016;16(1):7.
[75] ALAMRI Y, VOGEL R, MACASKILL M, et al. Plasma exosome concentration may correlate with cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2016;4:107-108.
[76] QU M, LIN Q, HUANG L, et al. Dopamine-loaded blood exosomes targeted to brain for better treatment of Parkinson’s disease. J Control Release. 2018;287:156-166.
[77] HANEY MJ, KLYACHKO NL, ZHAO Y, et al. Exosomes as drug delivery vehicles for Parkinson’s disease therapy. J Control Release. 2015;207: 18-30.
[78] ARYANI A, DENECKE B. Exosomes as a nanodelivery system: a key to the future of neuromedicine? Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53(2):818-834. |