[1] THEODORE N. Degenerative Cervical Spondylosis. N Engl J Med. 2020; 383(2):159-168.
[2] JITIN B. Cervical Spondylosis and Atypical Symptoms. Neurol India. 2021;69(3):602-603.
[3] MA M, ZHANG SM. Progress on cervical spondylosis in youths. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2014;27(9):792-795.
[4] 王远政,刘洋,陈富,等.下颈椎前路椎弓根螺钉置入相关的解剖学观察[J].重庆医科大学学报,2012,37(12):1063-1068.
[5] 赵刘军,徐荣明,华群,等.下颈椎前路椎弓根螺钉最佳进钉点和进钉方向的影像学研究及其临床运用[J].中国骨伤,2012,25(12): 1030-1035.
[6] 李松柏,张远金,孙法瑞.后路单开门联合椎间孔切开术治疗混合型颈椎病[J].局解手术学杂志2016,25(6):432-434.
[7] MAO JZ, AGYEI JO, GHANNAM MM, et al. Navigation-Guided Subaxial Cervical Pedicle Screws in Revision Spine Surgery: 2-Dimensional Operative Video. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown). 2021;20(4):E312-E313.
[8] SOLIMAN MAR, KHAN S, RUGGIERO N, et al. Complications associated with subaxial placement of pedicle screws versus lateral mass screws in the cervical spine: systematic review and meta-analysis comprising 1768 patients and 8636 screws. Neurosurg Rev. 2022;45(3):1941-1950.
[9] HEY HWD, ZHUO WH, TAN YHJ, et al. Accuracy of freehand pedicle screws versus lateral mass screws in the subaxial cervical spine. Spine Deform. 2020;8(5):1049-1058.
[10] CHEN C, KIM WK. The application of micro-CT in egg-laying hen bone analysis: introducing an automated bone separation algorithm. Poult Sci. 2020;99(11):5175-5183.
[11] HALM S, HABERTHÜR D, EPPLER E, et al. Micro-CT imaging of Thiel-embalmed and iodine-stained human temporal bone for 3D modeling. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021;50(1):33.
[12] ZENZES M, ZASLANSKY P. Micro-CT data of early physiological cancellous bone formation in the lumbar spine of female C57BL/6 mice. Sci Data. 2021;8(1):132.
[13] WELSH H, NELSON AJ, VAN DER MERWE AE, et al. An Investigation of Micro-CT Analysis of Bone as a New Diagnostic Method for Paleopathological Cases of Osteomalacia. Int J Paleopathol. 2020;31: 23-33.
[14] RITMAN EL. Current status of developments and applications of micro-CT. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2011;13:531-552.
[15] PERILLI E, PARKINSON IH, REYNOLDS KJ. Micro-CT examination of human bone: from biopsies towards the entire organ. Ann Ist Super Sanita. 2012;48(1):75-82.
[16] TASSANI S, PERILLI E. On local micro-architecture analysis of trabecular bone in three dimensions. Int Orthop. 2013;37(8):1645-1646.
[17] ZHANG ZM, LI ZC, JIANG LS, et al. Micro-CT and mechanical evaluation of subchondral trabecular bone structure between postmenopausal women with osteoarthritis and osteo porosis. Osteoporos Int. 2010; 21(8):1383-1390.
[18] XIAO ZF, HE JB, SU GY, et al. Osteoporosis of the vertebra and osteochondral remodeling of the endplate causes intervertebral disc degeneration in ovariectomized mice.Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20:1-15.
[19] DENIS F. The three column spine and its significance in the classification of acute thoracolumbar spinal injuries. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1983; 8(8):817-831.
[20] AEBI M, NAZARIAN S. Classification of injuries of the cervical spine. Orthopade. 1987;16(1):27-36.
[21] 李路,唐文.下颈椎后路椎弓根钉置钉:人工智能发展将如何提高治疗效果[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(3):474-479.
[22] 郑昌坤,徐佳隆,吴建军.下颈椎椎弓根螺钉内固定技术应用研究进展[J].脊柱外科杂志,2021,19(3):203-207.
[23] 李杰,赵刘军,干开丰,等.下颈椎两节段椎体次全切后前路椎弓根螺钉固定系统重建稳定性有限元模型的建立[J].中国骨伤,2022, 35(2):178-185.
[24] SONG D, SHUJAAT S, HUANG Y, et al. Effect of platelet-rich and platelet-poor plasma on 3D bone-to-implant contact: a preclinical micro-CT study. Int J Implant Dent. 2021;7(1):11.
[25] KIM Y, BRODT MD, TANG SY, et al. MicroCT for Scanning and Analysis of Mouse Bones. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2230:169-198.
[26] GANESHAARAJ G, KAUSHALYA S, KONDARAGE AI, et al. Semantic Segmentation of Micro-CT Images to Analyze Bone Ingrowth into Biodegradable Scaffolds. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2022; 2022:3830-3833
[27] ARıCAN G, ÖZMERIÇ A, FıRAT A, et al. Micro-ct findings of concentrated growth factors (cgf) on bone healing in masquelet’s technique-an experimental study in rabbits. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022; 142(1):83-90.
[28] NIKODEM A. Correlations between structural and mechanical properties of human trabecular femur bone. Acta Bioeng Biomech. 2012;14(2): 37-46.
[29] GOULET RW, GOLDSTEIN SA, CIARELLI MJ, et al. The relationship between the structural and orthogonal compressive properties of trabecular bone. J Biomech. 1994;27(4):375-389.
[30] DING M, OVERGAARD S. 3-D microarchitectural properties and rodand plate-like trabecular morphometric properties of femur head cancellous bones in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and osteoporosis. J Orthop Translat. 2021;28:159-168.
[31] BARRETT JM, MCKINNON C, CALLAGHAN JP. Cervical spine joint loading with neck flexion. Ergonomics. 2020;63(1):101-108.
[32] RIEGER R, AUREGAN JC, HOC T. Micro-finite-element method to assess elastic properties of trabecular bone at micro- and macroscopic level. Morphologie. 2018;102(336):12-20.
[33] WANG J, ZHOU B, LIU XS, et al. Trabecular plates and rods determine elastic modulus and yield strength of human trabecular bone. Bone. 2015;72:71-80.
[34] PERILLI E, PARKINSON IH, TRUONG LH, et al. Modic (endplate) changes in the lumbar spine: bone micro-architecture and remodelling. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(9):1926-1934. |
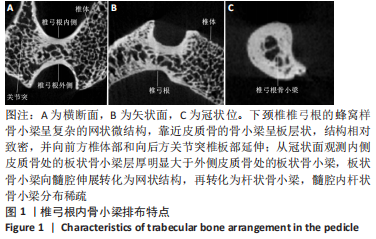
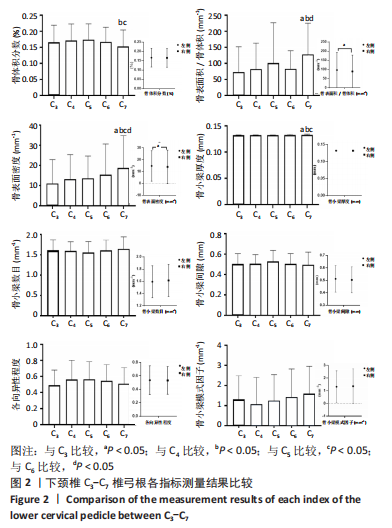

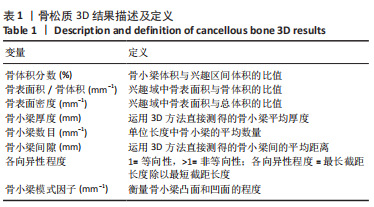
 Micro-CT在评价骨微细结构中已被大量应用,不仅可精确计量标本整体骨量参数,还可测试大量骨结构参数,其中骨体积分数、骨表面积密度、骨小梁厚度、骨小梁数量、骨小梁间隙、各向异性度、骨小梁模式因子是目前最常用的参数。有学者在动物或人体样本上研究了骨微结构参数对骨小梁材料属性产生的影响[28-30],发现其中骨小梁骨体积分数与骨负荷能力、屈服强度密切相关,是评价小梁微观结构的首要指标[31-32]。骨体积分数描述了骨小梁骨量大小,在相同载荷下,较小骨体积分数值的骨小梁在单位体积内承受更多应力,因此更容发生骨小梁断裂而引起损伤。WANG等[33]研究发现,当骨体积分数值减少8%时,骨小梁抗压强度和刚度将分别减少24%和17%。其他一些关于脊柱微CT的研究表明,在一个样本中不同感兴趣区域其微结构不同,骨小梁体积分数较低的区域其结构应力也较低,是该椎体结构的薄弱区
Micro-CT在评价骨微细结构中已被大量应用,不仅可精确计量标本整体骨量参数,还可测试大量骨结构参数,其中骨体积分数、骨表面积密度、骨小梁厚度、骨小梁数量、骨小梁间隙、各向异性度、骨小梁模式因子是目前最常用的参数。有学者在动物或人体样本上研究了骨微结构参数对骨小梁材料属性产生的影响[28-30],发现其中骨小梁骨体积分数与骨负荷能力、屈服强度密切相关,是评价小梁微观结构的首要指标[31-32]。骨体积分数描述了骨小梁骨量大小,在相同载荷下,较小骨体积分数值的骨小梁在单位体积内承受更多应力,因此更容发生骨小梁断裂而引起损伤。WANG等[33]研究发现,当骨体积分数值减少8%时,骨小梁抗压强度和刚度将分别减少24%和17%。其他一些关于脊柱微CT的研究表明,在一个样本中不同感兴趣区域其微结构不同,骨小梁体积分数较低的区域其结构应力也较低,是该椎体结构的薄弱区