中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (6): 857-861.doi: 10.12307/2023.794
• 骨与关节生物力学 bone and joint biomechanics • 上一篇 下一篇
发育性髋关节发育不良患者髋臼发育程度与脊柱-骨盆参数的相关性
林天烨1,2,张文胜1,2,何晓铭1,2,何敏聪1,2,李子祺1,2,陈镇秋3,张庆文1,2,何 伟1,2,魏秋实1,2
- 1广东省中医骨伤研究院,广东省广州市 510405;2广州中医药大学第三附属医院,广东省广州市 510405;3广州中医药大学第一附属医院,广东省广州市 510000
Correlation between acetabular development and spinopelvic parameters in patients with developmental dysplasia of the hip
Lin Tianye1, 2, Zhang Wensheng1, 2, He Xiaoming1, 2, He Mincong1, 2, Li Ziqi1, 2, Chen Zhenqiu3, Zhang Qingwen1, 2, He Wei1, 2, Wei Qiushi1, 2
- 1Guangdong Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine Bone Trauma, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 2Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 3First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
发育性髋关节发育不良:是由于髋关节发育缺陷或滞后导致髋臼或股骨头的大小、形态、方向发生异常,进而影响髋臼、股骨头等骨性或关节囊、韧带及肌肉等髋周软组织的病变。随着发育性髋关节发育不良的病程进展,髋外翻、股骨头覆盖不足、股骨前倾角增加、髋臼浅和股骨颈缩短等严重畸形会出现。脊柱-骨盆参数:脊柱与骨盆在解剖结构上相连接、共同维持躯干平衡,两者的参数相互关联、协调、匹配;当脊柱或骨盆发生疾患时,骨盆或脊柱会发生相应的代偿,从而维持躯干平衡,脊柱-骨盆参数可评估代偿程度的参数,主要包括骨盆倾斜角、骨盆投射角、骶骨倾斜角、胸椎后凸角、胸腰椎后凸角、腰椎前凸角和矢状位躯干偏移等。
背景:在发育性髋关节发育不良的相关研究中,大部分集中于髋关节畸形,目前缺乏髋臼发育不良对脊柱影响的报道。
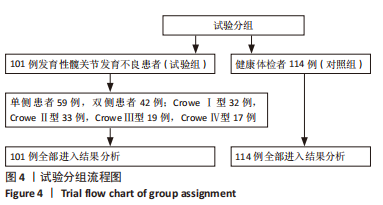
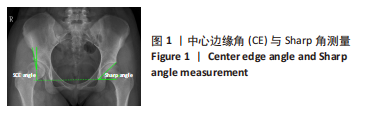
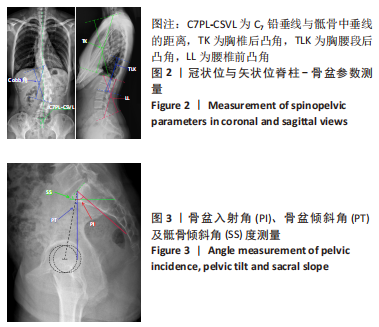
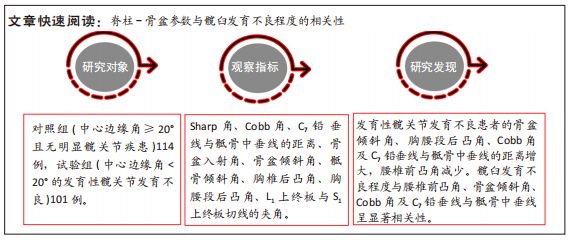
目的:探讨发育性髋关节发育不良患者冠状位及矢状位脊柱-骨盆参数代偿情况,并探讨髋臼发育程度与脊柱-骨盆参数的相关性。方法:选择2018年1月至 2022年6月于广州中医药大学第三附属医院就诊的发育性髋关节发育不良患者101例(试验组),选择同期健康体检者114例(对照组),两组均拍摄冠状位及矢状位脊柱全长X射线片,获取以下脊柱-骨盆参数:腰椎前凸角、骨盆前倾角、胸腰椎后凸角、Cobb角及C7铅垂线与骶骨中垂线的距离、骶骨倾斜角、骨盆入射角、胸椎后凸角,对比两组受试对象脊柱-骨盆参数差异;另外,对比单侧、双侧以及不同Crowe分型发育性髋关节发育不良患者的脊柱-骨盆参数差异,采用Pearson相关分析探讨髋臼发育程度(Sharp角)与脊柱-骨盆参数的相关性。
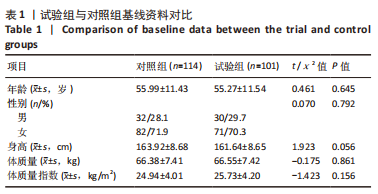
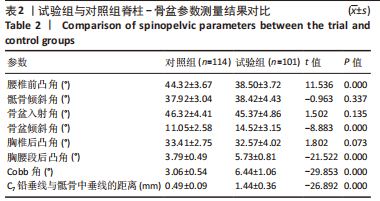
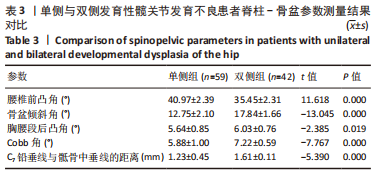
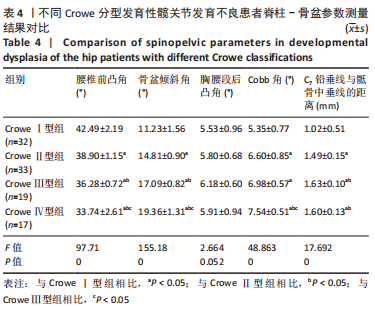
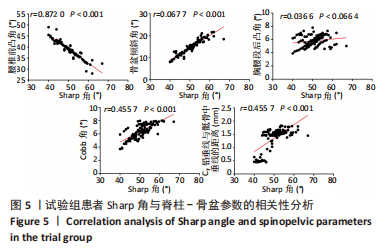
结果与结论:①在矢状位上,试验组腰椎前凸角小于对照组(P < 0.05),骨盆倾斜角、胸腰段后凸角大于对照组(P < 0.05);在冠状位上,试验组Cobb角、C7铅垂线与骶骨中垂线的距离大于对照组(P < 0.05);两组间其余脊柱-骨盆参数测量值比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05);②双侧发育性髋关节发育不良患者的腰椎前凸角小于单侧发育性髋关节发育不良患者(P < 0.05),骨盆倾斜角、胸腰段后凸角、Cobb角及C7铅垂线与骶骨中垂线的距离均大于单侧发育性髋关节发育不良患者(P < 0.05);③腰椎前凸角随着Crowe分型严重程度的增加而减少(P < 0.05),骨盆倾斜角随着Crowe分型严重程度的增加而增加(P < 0.05);④ Pearson相关分析显示,Sharp角与腰椎前凸角呈负相关(P < 0.05),骨盆前倾角、Cobb角及C7铅垂线与骶骨中垂线呈正相关(P < 0.05);⑤结果显示,发育性髋关节发育不良患者的骨盆倾斜角、胸腰段后凸角、Cobb角及C7铅垂线与骶骨中垂线的距离增大,腰椎前凸角减少;髋臼发育不良程度与腰椎前凸角、骨盆倾斜角、Cobb角及C7铅垂线与骶骨中垂线呈显著的相关性。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0286-5425 (林天烨)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: