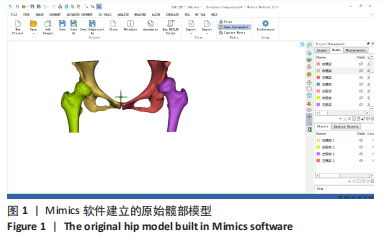
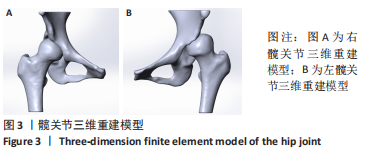
[1] ZHANG H, ZHOU J, GUAN J, et al. How to restore rotation center in total hip arthroplasty for developmental dysplasia of the hip by recognizing the pathomorphology of acetabulum and Harris fossa? J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):339.
[2] ZHANG S, DOUDOULAKIS KJ, KHURWAL A, et al. Developmental dysplasia of the hip. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2020;81(7):1-8.
[3] YUASA T, MAEZAWA K, KANEKO K, et al. Rotational acetabular osteotomy for acetabular dysplasia and osteoarthritis: a mean follow-up of 20 years. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017;137(4):465-469.
[4] FÜRNSTAHL P, CASARI FA, ACKERMANN J, et al. Computer-assisted femoral head reduction osteotomies: an approach for anatomic reconstruction of severely deformed Legg-Calvé-Perthes hips. A pilot study of six patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):759.
[5] HÅBERG Ø, FOSS OA, LIAN ØB, et al. Is foot deformity associated with developmental dysplasia of the hip? Bone Joint J. 2020;102-b(11): 1582-1586.
[6] BENEDETTI MG, CAVAZZUTI L, AMABILE M, et al. Abductor muscle strengthening in THA patients operated with minimally-invasive anterolateral approach for developmental hip dysplasia. Hip Int. 2021; 31(1):66-74.
[7] 赵资坚,张荣臻,蔡史健,等.3D打印技术在发育性髋关节发育不良继发骨性关节炎全髋关节置换术中的应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2022,37(4):346-350.
[8] ZHANG H, LIU Y, DONG Q, et al. Novel 3D printed integral customized acetabular prosthesis for anatomical rotation center restoration in hip arthroplasty for developmental dysplasia of the hip crowe type III: A Case Report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(40):e22578.
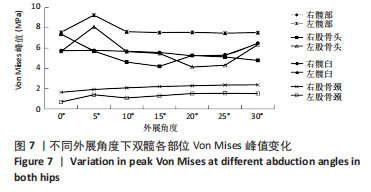
[9] 张美超,史风雷,赵卫东,等.髋关节外展不同角度股骨颈应力分布的有限元分析[J].第一军医大学学报,2005,25(10):1244-1246.
[10] 张海峰,宋翠荣,赵文涛,等.髋关节外展角度对股骨颈应力分布的影响[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2016,33(2):274-278.
[11] 田丰德,赵德伟,郭林,等.步幅大小及髋关节外展角度对坏死股骨头影响的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(17): 3052-3055.
[12] 杜秀利,陈岚,徐根林,等.有限元分析在全髋关节置换术中的应用[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2009,26(2):429-432.
[13] 田丰德,赵德伟,李东怡,等.三维有限元法分析成人髋关节发育不良重建髋臼的生物力学特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(35): 5642-5647.
[14] 张馨元,丁晓红,段朋云,等.基于骨骼材料分布特征的髋关节有限元模型建立及其应力分析[J].北京生物医学工程,2020,39(5): 462-469.
[15] 高耀东,段宇星,郭鹏年,等.基于髋关节CT图像三维实体髋骨重建及髋骨承受力数据有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2019, 23(28):4564-4569.
[16] BIXBY SD, MILLIS MB. The borderline dysplastic hip: when and how is it abnormal? Pediatr Radiol. 2019;49(12):1669-1677.
[17] HARTOFILAKIDIS G, STAMOS K, KARACHALIOS T, et al. Congenital hip disease in adults. Classification of acetabular deficiencies and operative treatment with acetabuloplasty combined with total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78(5):683-692.
[18] FUJII M, NAKASHIMA Y, SATO T, et al. Acetabular tilt correlates with acetabular version and coverage in hip dysplasia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(10):2827-2835.
[19] 郑炬,张秀娥.高频超声在小儿发育性髋关节发育不良诊断中的应用价值[J].影像研究与医学应用,2022,6(8):71-73.
[20] 陈松浩,张立强,梅玉倩,等.基于不同髋臼前中心边缘角的有限元分析对临界髋关节发育不良的辅助诊断研究[J].医用生物力学, 2021,36(S1):221.
[21] LI L, JIA J, ZHAO Q, et al. Evaluation of femoral head coverage following Chiari pelvic osteotomy in adolescents by three-dimensional computed tomography and conventional radiography. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(5):599-605.
[22] JIA J, LI L, ZHANG L, et al. Three dimensional-CT evaluation of femoral neck anteversion, acetabular anteversion and combined anteversion in unilateral DDH in an early walking age group. Int Orthop. 2012;36(1):119-124.
[23] ZHAO X, CHOSA E, TOTORIBE K, et al. Effect of periacetabular osteotomy for acetabular dysplasia clarified by three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Orthop Sci. 2010;15(5):632-640.
[24] NAKAMURA T, YAMAGUCHI R, WADA A, et al. A longitudinal study for the prediction of the mature acetabular morphology using childhood magnetic resonance imaging. J Orthop Sci. 2021;26(4):644-649.
[25] ZIMMERER A, SCHNEIDER MM, NIETSCHKE R, et al. Is Hip Arthroscopy an Adequate Therapy for the Borderline Dysplastic Hip? Correlation Between Radiologic Findings and Clinical Outcomes. Orthop J Sports Med. 2020;8(5):2325967120920851.
[26] 郭磊,赵玉岩,范广宇,等.髋臼发育不良的生物力学实验研究[J].中国医科大学学报,2001,30(4):277-278.
[27] 李兴,王洪福,罗伟,等.基于术后髋骨CT数据重建个性化骨肌多体动力学模型及步态仿真[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(35): 5685-5690.
[28] 邬培慧,傅明,康焱,等.髋臼CE角及关节作用力方向的生物力学作用[J].第三军医大学学报,2011,33(11):1174-1177.
[29] YANG Y, ZUO J, LIU T, et al. Morphological Analysis of True Acetabulum in Hip Dysplasia (Crowe Classes I-IV) Via 3-D Implantation Simulation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(17):e92.
[30] LIU B, GAO YH, DING L, et al. Computed Tomographic Evaluation of Bone Stock in Patients With Crowe Type III Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip: Implications for Guiding Acetabular Component Placement Using the High Hip Center Technique. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(3): 915-918.
[31] VAFAEIAN B, ADEEB S, EL-RICH M, et al. Hip Joint Contact Pressure Distribution During Pavlik Harness Treatment of an Infant Hip: A Patient-Specific Finite Element Model. J Biomech Eng. 2018;140(7): 071009.
[32] 蔡振存,朴成哲,周宏宇,等.有限元法分析儿童发育不良髋关节“人”字型固定后的应力特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2019, 23(36):5841-5845.
[33] 颜继英.不同材料赋值下股骨静力学有限元模型的力学仿真分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(9):1390-1394.
[34] 陈诺,邱兴,汪帝,等.基于CT灰度值赋予材料属性的马拉松运动员髋关节有限元模型建立及其应力分析[J].中华医学杂志,2022, 102(9):679-682.
[35] HAO Z, WAN C, GAO X, et al. The effect of boundary condition on the biomechanics of a human pelvic joint under an axial compressive load: a three-dimensional finite element model. J Biomech Eng. 2011; 133(10):101006.
[36] 刘欣伟,闫寒,刘中洋,等.包含肌肉、韧带组织的骨盆、髋臼3D有限元模型的构建[J].临床军医杂志,2014,42(4):331-335.
[37] PHILLIPS AT, PANKAJ P, HOWIE CR, et al. Finite element modelling of the pelvis: inclusion of muscular and ligamentous boundary conditions. Med Eng Phys. 2007;29(7):739-748.
[38] ZOU Z, CHÁVEZ-ARREOLA A, MANDAL P, et al. Optimization of the position of the acetabulum in a ganz periacetabular osteotomy by finite element analysis. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(3):472-479. |