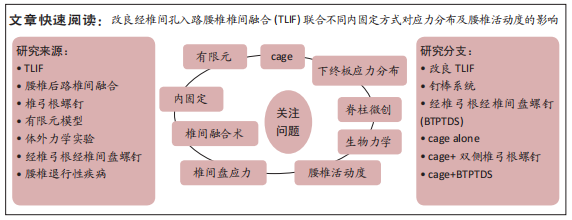
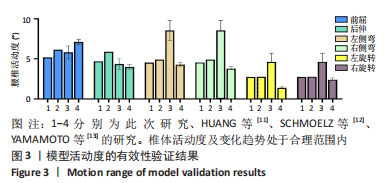
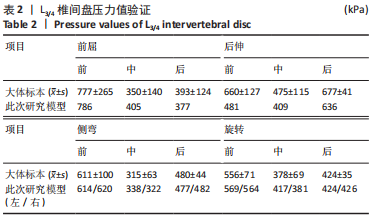
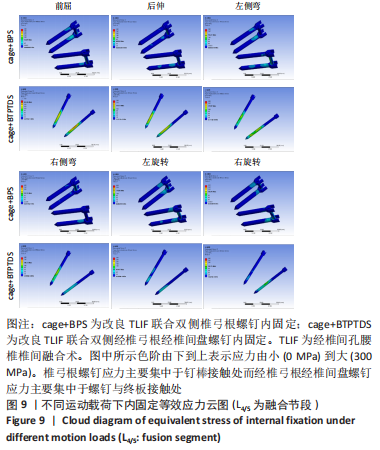
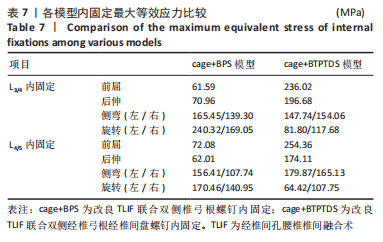
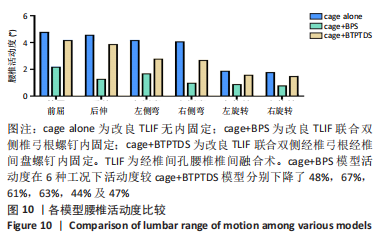
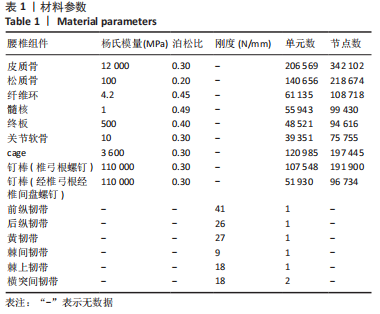
[1] MENG B, BUNCH J, BURTON D, et al. Lumbar interbody fusion: recent advances in surgical techniques and bone healing strategies. Eur Spine J. 2021;30(1):22-33.
[2] UÇAR BY, ÖZCAN Ç, POLAT Ö, et al. Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion For Lumbar Degenerative Disease: Patient Selection And Perspectives. Orthop Res Rev. 2019;11:183-189.
[3] KIM CH, EASLEY K, LEE JS, et al. Comparison of Minimally Invasive Versus Open Transforaminal Interbody Lumbar Fusion. Global Spine J. 2020;10(2 Suppl):143s-150s.
[4] ROSINSKI A, ODEH K, UNGUREAN V JR, et al. Non-Pedicular Fixation Techniques for the Treatment of Spinal Deformity: A Systematic Review. JBJS Rev. 2020;8(5):e0150.
[5] WU AM, HARRIS JA, HAO JC, et al. Biomechanical properties of posterior transpedicular-transdiscal oblique lumbar screw fixation with novel trapezoidal lateral interbody spacer: an in vitro human cadaveric model. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(11):2873-2882.
[6] BELYTSCHKO T, ANDRIACCHI T, SCHULTZ A, et al. Analog studies of forces in the human spine: computational techniques. J Biomech. 1973;6(4):361-371.
[7] LU T, LU Y. Comparison of Biomechanical Performance Among Posterolateral Fusion and Transforaminal, Extreme, and Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Finite Element Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2019;129:e890-e899.
[8] PINTAR FA, YOGANANDAN N, MYERS T, et al. Biomechanical properties of human lumbar spine ligaments. J Biomech. 1992;25(11):1351-1356.
[9] ROSINSKI AA, MITTAL A, ODEH K, et al. Alternatives to traditional pedicle screws for posterior fixation of the degenerative lumbar spine. JBJS Rev. 2021;9(7):e20.
[10] 文兵, 杜瑛, 胡良波,等. 磁共振对 BMI 正常人群髓核体积的测量与临床应用研究[J]. 中国医学计算机成像杂志,2016,22(4): 346-350.
[11] HUANG YP, DU CF, CHENG CK, et al. Preserving posterior complex can prevent adjacent segment disease following posterior lumbar interbody fusion surgeries: a finite element analysis. PLoS One. 2016; 11(11):e0166452.
[12] SCHMOELZ W, ERHART S, UNGER S, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of a posterior non-fusion instrumentation of the lumbar spine. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(5):939-945.
[13] YAMAMOTO I, PANJABI MM, CRISCO T, et al. Three-dimensional movements of the whole lumbar spine and lumbosacral joint. 1989; 14(11):1256-1260.
[14] TENG I, HAN J, PHAN K, et al. A meta-analysis comparing alif, plif, tlif and llif. J Clin Neurosci. 2017;44:11-17.
[15] MOBBS RJ, PHAN K, MALHAM G, et al. Lumbar interbody fusion: techniques, indications and comparison of interbody fusion options including PLIF, TLIF, MI-TLIF, OLIF/ATP, LLIF and ALIF. J Spine Surg. 2015; 1(1):2-18.
[16] 孙继芾, 黄永辉, 左华,等. 改良 TLIF 治疗腰椎不稳伴腰椎管狭窄症[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(23):2138-2141.
[17] TARAWNEH AM, SALEM KM. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing the accuracy and clinical outcome of pedicle screw placement using robot-assisted technology and conventional freehand technique. Global Spine J. 2021;11(4):575-586.
[18] HIYAMA A, KATOH H, SAKAI D, et al. Short-Term Comparison Between Unilateral Versus Bilateral Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Fixation in Short-Level Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion–A Prospective Randomized Study. Global Spine J. 2022;21925682221146500.
[19] SONG T, WELLINGTON KH, YE T. Lumbar pedicle cortical bone trajectory screw. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(21):3808-3813.
[20] 姜伟, 袁峰. 单侧椎弓根螺钉联合经椎板关节突螺钉与双侧椎弓根螺钉固定治疗下腰椎退行性疾病: 2 年随访[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(19):2973-2979.
[21] 唐强, 廖烨晖, 唐超,等. 椎间融合器的置入方式对腰椎融合效果的影响. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2019,29(12):1071-1079.
[22] EGUCHI Y, ORITA S, YAMADA H, et al. Pilot study of oblique lumbar interbody fusion using mobile percutaneous pedicle screw and validation by a three-dimensional finite element assessment. J Clin Neurosci. 2020;76:74-80.
[23] 魏源标, 郭惠智, 张顺聪. 皮质骨轨迹螺钉固定对相邻节段影响的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(18):2799-2804.
[24] 杨洋, 王洋, 叶晓健. 椎弓根皮质骨轨迹螺钉固定技术的研究进展[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2015,25(7):659-662.
[25] MATSUKAWA K, YATO Y, HYNES RA, et al. Cortical Bone Trajectory for Thoracic Pedicle Screws. Clin Spine Surg. 2017;30(5):E497-E504.
[26] 潘爱星, 刘玉增, 海涌,等. 腰椎皮质骨螺钉联合椎弓根螺钉固定对融合节段应力影响的有限元分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2022, 32(1):67-74.
[27] ABDU WA, WILBER RG, EMERY SE. Pedicular transvertebral screw fixation of the lumbosacral spine in spondylolisthesis. A new technique for stabilization. Spine. 1994;19(6):710-715.
[28] ZAGRA A, GIUDICI F, MINOIA L, et al. Long-term results of pediculo-body fixation and posterolateral fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. 2009;18:151-155.
[29] GROB D, HUMKE T, DVORAK J. Direct pediculo-body fixation in cases of spondylolisthesis with advanced intervertebral disc degeneration. Eur Spine J. 1996;5:281-285.
[30] AONO H, TAKENAKA S, TOBIMATSU H, et al. Adjacent-segment disease after L3-4 posterior lumbar interbody fusion: does L3-4 fusion have cranial adjacent-segment degeneration similar to that after L4-5 fusion? J Neurosurg Spine. 2020;33(4):455-460.
[31] 钟建斌, 张凯伦, 赵波捷. 腰椎邻椎病的危险因素及治疗进展[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志,2020,9(7):555-559.
[32] YUAN C, ZHOU J, WANG L, et al. Adjacent segment disease after minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar diseases: incidence and risk factors. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):982.
[33] DU CF, CAI XY, GUI W, et al. Does oblique lumbar interbody fusion promote adjacent degeneration in degenerative disc disease: A finite element analysis. Comput Biol Med. 2021;128:104122. |