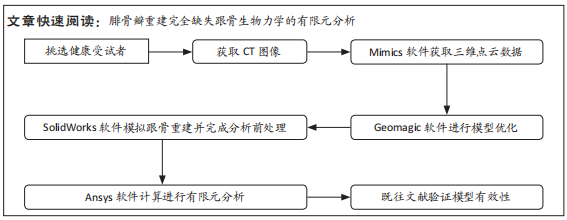
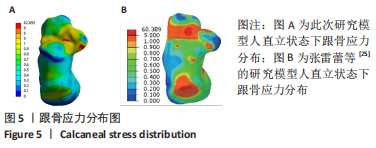
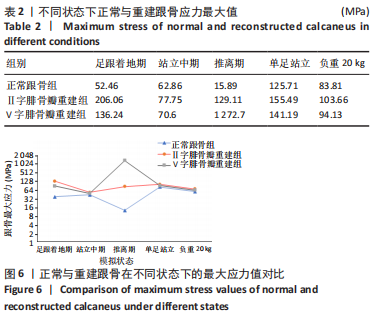
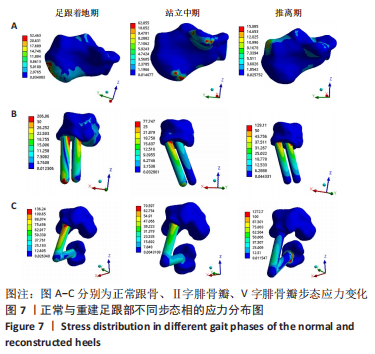
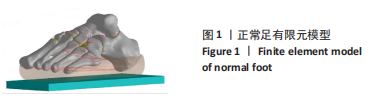
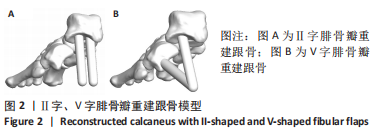
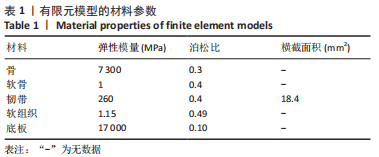
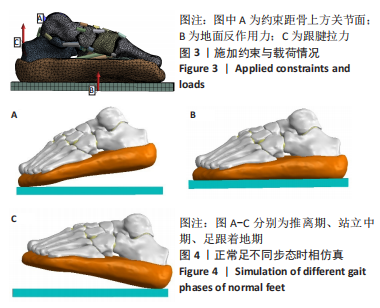
[1] 章浩伟,吕琳,倪明.跟骨骨折髓内固定治疗的研究进展[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2021,23(5):458-460.
[2] 蔡锦方,刘晓平.带骨复合皮瓣修复足跟与足底缺损[J].中华显微外科杂志, 1989,12(2):70-71.
[3] 周仁鹏,梅劲,潘庆祥,等.Ⅱ型与Ⅴ型腓骨瓣修复跟骨缺失初期再造跟骨稳定性的比较[J]. 解剖学报,2011,42(3):410-414.
[4] 唐茂林,吴石头.逆行岛状Ⅴ型腓骨肌皮瓣修复后足缺损的应用解剖[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2000,18(2):110-112.
[5] 郭德亮,潘朝晖,张伟旭. 吻合血管腓骨移植重建全跟骨缺损一例[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2002,4(1):64.
[6] MEI J, WU S, YANG Z, et al. Functional total heel reconstruction with a fibular osteomyocutaneous flap. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2010;26(6):367-373.
[7] LI J, WANG Z. Surgical treatment of malignant tumors of the calcaneus. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2014;104(1):71-76.
[8] 李朝旭,王锐英,唐际存.并联腓骨组织瓣修复足跟骨及软组织缺损[J].中华显微外科杂志,2014,37(6):528-530.
[9] 袁炜庆,杨渊.游离腓骨复合组织瓣修复足部骨与软组织缺损九例[J].中华显微外科杂志,2021,44(6):659-662.
[10] 李振,魏小龙,王本亮,等.腓骨复合组织瓣逆行转移再造足跟1例[J].实用手外科杂志,2021,35(1):130-131.
[11] 潘朝晖,王剑利,蒋萍萍,等.三种不同骨瓣重建跟骨缺损的有限元及临床分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2005,7(6):529-532.
[12] 潘朝晖,王剑利,蒋萍萍,等.游离髂骨重建跖骨缺损的三维有限元及临床分析[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2005,19(5):358-360.
[13] WANG CW, MUHEREMU A, BAI JP. Use of three-dimensional finite element models of the lateral ankle ligaments to evaluate three surgical techniques. J Int Med Res. 2018;46(2):699-709.
[14] 白啸天,霍洪峰.足踝功能的生物力学测评:构建足静态和动态评价指标[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(17):2747-2754.
[15] WANG Y, Li Z, WONG DW, et al. Finite element analysis of biomechanical effects of total ankle arthroplasty on the foot. J Orthop Translat. 2017; (12):55-65.
[16] THOMPSON JC.邱贵兴,高鹏,主译.奈特简明骨科学彩色图谱[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2007.
[17] Akrami M, QIAN Z, ZOU Z, et al. Subject-specific finite element modelling of the human foot complex during walking: sensitivity analysis of material properties, boundary and loading conditions. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2018;17(2):559-576.
[18] 何晓宇, 王朝强, 周之平,等.三维有限元方法构建足部健康骨骼与常见疾病模型及生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(9):1410-1415.
[19] LI J, WEI Y, WEI M. Finite Element Analysis of the Effect of Talar Osteochondral Defects of Different Depths on Ankle Joint Stability. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26: e921823.
[20] HSU CY, GUNG WY, SHIH LS, et al. Using an optimization approach to design an insole for lowering plantar fascia stress-A finite element study. Ann Biomech Eng. 2008;(36):1345-1352.
[21] 张峻霞,高昆,谢兵.步态分析研究综述[J].包装工程,2022,43(10):41-53.
[22] CHEN TL, WONG DW, WANG Y, et al. Foot arch deformation and plantar fascia loading during running with rearfoot strike and forefoot strike: A dynamic finite element analysis. J Biomech. 2019;(83):260-272.
[23] 冯洋,王冬梅,刘安民,等.足踝步态模拟机动力学特性仿真及实验验证[J].医用生物力学,2014,29(5):393-398.
[24] 章浩伟,陈亮,杨俊彦,等.基于有限元法对足跟痛在推离期的生物力学研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2020,39(2):190-196.
[25] 张雷蕾,王盟圣,徐大伟,等.足部三维有限元建模及其多姿态生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(30):4799-4804.
[26] 华祥,陈辉,刘华渝.跟骨创伤性骨髓炎的手术及非手术治疗进展[J].创伤外科杂志,2021,23(9):710-713.
[27] 窦义臣,宣昭鹏,傅东升,等.游离腓骨皮瓣移植重建小腿长段骨及软组织缺损[J].实用手外科杂志,2021,35(4):447-450.
[28] OZOLS D, BLUMS K, KRUMINS M, et al. Entire calcaneus reconstruction with pedicled composite fibular growth plate flap in a pediatric patient.Microsurgery. 2021;41(3):280-285.
[29] 徐光华. 跆拳道运动对跟骨形态及其骨皮质与骨小梁结构影响[D]. 太原:中北大学,2021.
[30] WOLFF J. The Classic: On the Inner Architecture of Bones and its Importance for Bone Growth: (Ueber die innere Architectur der Knochen und ihre Bedeutung für die Frage vom Knochenwachsthum). Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(4):1056-1065.
[31] 张来福,卢承印,王孝辉,等. 3D打印辅助Masquelet膜诱导技术治疗跟骨骨缺损的疗效研究[J].创伤外科杂志,2021,23(7):507-511.
[32] 孙琪博,陈默迪,邰国梁,等. 带神经股前外穿支削薄皮瓣修复足踝大面积创面[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2022,30(14):1307-1310.
|