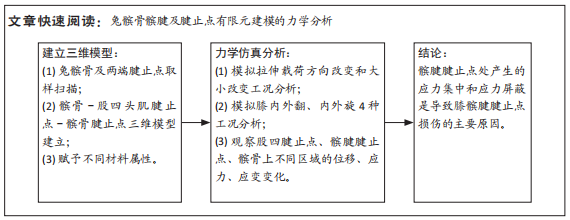
1.1 设计 通过有限元分析兔髌骨髌腱Mirco-CT扫描重建模型,分析髌骨髌腱结合部应力特点。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2021年11月在北京体育大学,运动医学与康复学院钟楼实验室完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 实验动物 成年健康雌性新西兰大白兔(18周龄),体质量(2.6±0.1) kg,普通级,购买自北京兴隆养殖场,实验动物机构许可证号:110108600078158,单独饲养,每天12 h光照,自由饮水,自由饮食,温度(20±2) ℃。骨骼肌肉发育正常,无膝关节损伤,以左侧膝关节的髌骨和肌腱为研究对象。此次实验已获得北京体育大学动物伦理委员会批准(批准文号:2015022)。实验过程遵循了国际兽医学编辑协会《关于动物伦理与福利的作者指南共识》和本地及国家法规。
1.3.2 仪器和软件 Micro-CT仪器:skyscan 1072(美国GE公司),台式图形工作站(Precision T7810),Mimics 20.0(比利时Materialise公司),Geomagic Studio 2014(美国Raindop Geomagic公司),Solidworks 2020(法国Dassault公司),Ansys Workbench 19.0(美国ANSYS公司)。
1.4 实验步骤 此次研究的实验数据建立在前期研究基础上[14-15],用已知的致慢性损伤运动载荷以及肌腱所能承受的最大载荷来进行力学模拟[16],从而观察髌骨髌腱区域应力特征的变化。
1.4.1 样本取材与Micro-CT二维图像获取 腹腔注射10%戊巴比妥钠(1.5 mL/kg,Sigma,美国)将兔子麻醉处死后,将兔子整个股四头肌肌腱-髌骨-髌腱的骨和腱止点取下,放入容器内固定后进行Micro-CT(skyscan 1072,GE,美国)扫描。扫描参数:射线管电流159 μA,电压59 kV,扫描物体长度121 mm,扫描分辨率9 μm,曝光时间600 ms,扫描角度180°。扫描后将全部图像以TIF格式进行储存。
1.4.2 骨-腱三维模型构建 将TIF格式的CT二维图片导入到Mimics 20.0(比利时Materialise公司)中,经过区域增长、孔隙填充、蒙板编辑、光顺、计算3D、布尔运算等步骤初步重建髌骨和两端腱止点两部分三维模型,输出为Binary二进制格式的STL文件(图1)。随后将文件再导入Geomagic Studio中通过多边形和曲面计算形成理想的NURBS曲面模型,包括轮廓线阶段、曲面片和格栅阶段、曲面阶段等(图2),最终导入SolidWorks生成实体模型,通过装配步骤组成骨-肌腱装配体(图3)。

1.4.3 模型受力网格划分 通过参考过往研究成果,将SolidWorks中的骨-腱装配体在Workbench中打开,选择静态结构分析进行网格划分,分别选取0.01,0.02,0.03,0.04,0.06,0.08 mm等6个不同大小的网格进行收敛性分析比较,综合考虑网格精度和计算效率,将网格单元大小设置为0.02 mm,整体网格划分出71 394个节点(nodes),41 212个四面体单元(elements)。
1.4.4 定义材料属性及设置边界条件 髌腱在上端与股四头肌相连,附着于髌骨表面。膝关节在进行屈伸运动时,髌骨为支点在关节面上进行滑动,髌腱受到到上下纵向牵拉力的影响,因此选择髌腱和股四头肌腱止点与髌骨上下端的接触面,将接触面的接触类型设置为Bonded(牢固结合)接触。在髌骨上选择髌骨与股骨接触滑动的区域,两关节面之间的接触定义为摩擦接触,摩擦系数为0.1。在对材料属性赋值方面,目前常用灰度赋值法和均一赋值法两种,材料赋值法是将生成模型导入Mimics中根据赋值公式对模型的材料参数赋值,均一赋值法在有限元软件中对材料参数直接赋值,两种方法各有优缺点。刘波[16]在对兔髌腱的体外加载实验中计算出准确的兔髌腱弹性模量E=226.47 MPa,在此次建模仿真实验中,与灰度赋值法相比,在Workbench中赋予准确的弹性模量值更接近于真实情况。根据过往研究和报告结果分别赋予髌骨模型和腱止点模型的材料属性[16-20],设置髌骨弹性模量为10 950 MPa,泊松比为0.30,腱止点弹性模量为226.47 MPa,泊松比为0.40。
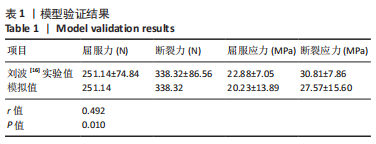
1.4.5 模型验证 在刘波[16]的循环加载、应力松弛以及断裂实验中,得出兔髌腱的弹性模量E为226.47 MPa,断裂实验中的屈服应力为(22.88±7.05) MPa,断裂应力为(30.81±7.86) MPa;所对应的屈服力为(251.14±74.84) N,断裂力为(338.32±86.56) N。为了和实际实验条件相吻合,将有限元模型中的髌骨和股四头肌腱止点端都设置为固定约束,由髌腱腱止点端受力以模拟加载时胫骨平台的受力。对髌腱腱止点端施加屈服力、断裂力,求解得到相应的应力,对髌腱腱止点的端面和腱止点与髌骨接触区各随机取共60个节点的值,算出平均应力值,将平均应力值和实验值比较,若实验值与模拟值相近且具有线性关系,则说明该模型得到的数据与实际相比有效性和可靠性较高(图4)。

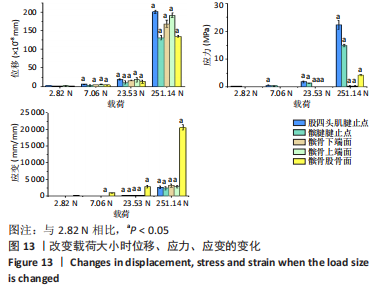
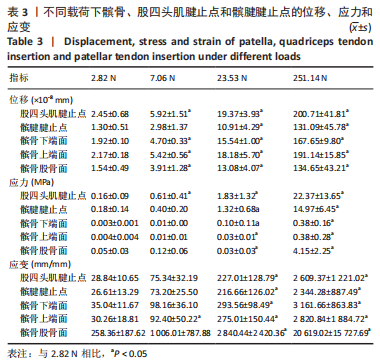
1.4.6 应力测试 在WANG等[11,14-15,21]对兔子进行损伤造模研究腱病的实验中,测得最大伸膝力为23.53 N,损伤阈强度为(7.06±0.71) N,损伤后低强度恢复训练的强度为(2.82±0.28) N。而刘波[16]通过拉断实验得出兔髌腱的屈服力为(251.14±74.84) N。为了分析全面,在有限元分析中对模型施加的载荷大小分别为2.82,7.06,23.53以及251.14 N。
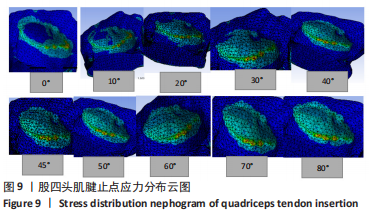
首先测量最大伸膝力下,膝关节伸直0°,10°,20°,30°,40°,50°,60°,70°,80°条件下的应力情况,随后测试膝关节在30°下内外旋和内外翻的情况。根据过往研究结果和膝关节的运动形式,对肌腱结合部分别施加(7.06±0.71) N拉力和(2.82±0.28) N侧向切力,分别计算5°内翻和10°外翻时下结合部的应力情况,以及在内旋外旋状态下沿髌腱方向的拉力和垂直于髌腱方向的切力。
加载条件主要考虑与实际情况相符合的拉力、内外旋、内外翻等情况,根据以往的研究结果将载荷方向设置为30°,并分别计算不同拉力和不同方向下髌腱结合部区域的应力情况。
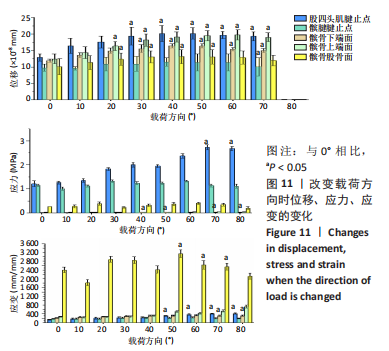
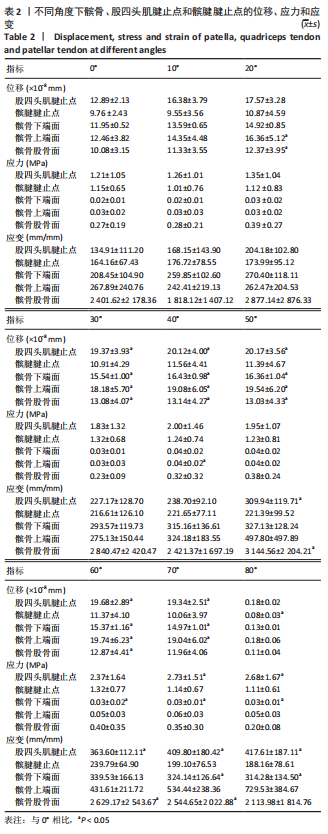
(1)模拟在不同运动形势下施加伸膝力载荷:分别取载荷2.82,7.06,23.53,251.4 N,角度沿髌腱方向分别取0°,10°,20°,30°,40°,50°,60°,70°,80°,分析不同角度和载荷下髌腱和髌骨的应力情况(图5)。

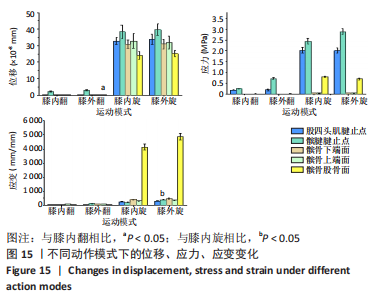
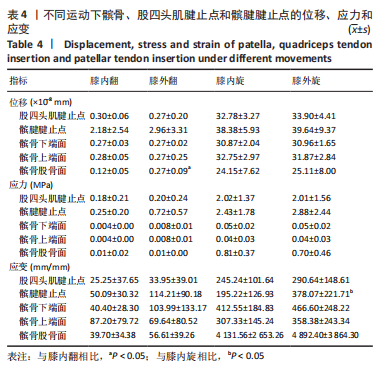
(2)模拟膝关节内外翻时髌骨-腱止点受力情况:膝关节内外翻时,载荷大小取低强度恢复训练的力(2.82±0.28) N,方向设定为与髌腱纵向成角度偏差方向。一般来说人体膝关节的理想下肢力线呈5°-10°的外翻[22],所以外翻模型的载荷设置为10°偏差,而内翻角度较小,设置为5°偏差(图6)。

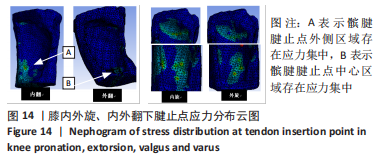
(3)模拟膝关节内外旋时髌骨-腱止点受力情况:在实际情况中,当膝关节发生内外旋时,除了受到拉伸载荷的作用之外,还受到近似垂直于髌腱方向力的作用,此处将力简化分解为沿髌腱方向的拉力和垂直于髌腱方向的切力,拉力大小取7.06 N损伤阈强度,切力则简化为2.32 N(图7)。
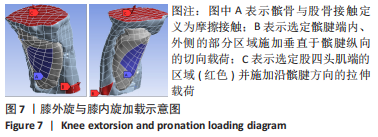
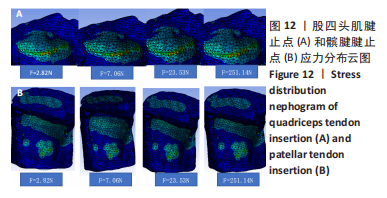
1.5 主要观察指标 观察髌骨与股四头肌腱止点和髌腱腱止点接触区域的等效应力、位移、应变和应力云图变化;观察云图应力分布情况,比较不同大小、方向的载荷以及膝内外翻、内外旋情况下的结果。对有限元模型的目标区域探测数据,每个目标区域随机抽取20个节点的数值,目标区域包括髌骨上与股四头肌肌腱接触的上端面、与髌腱接触的髌骨下端面、与股骨接触的髌骨-股骨面,股四头肌肌腱与髌骨上端面接触的股四头肌腱止点区域、髌腱与髌骨下端面接触的髌腱腱止点区域。
1.6 统计学分析 采用SPSS 20.0对数据进行统计学分析,数据用x±s表示。计量资料符合正态分布,采用单因素ANOVA检验,不符合正态分布则以中位数代表平均水平,采用非参数独立样本检验。P < 0.05代表差异有显著性意义。模型验证采用双变量相关性分析,P < 0.05表示显著相关。文章统计学方法已经北京体育大学生物统计学专家审核。