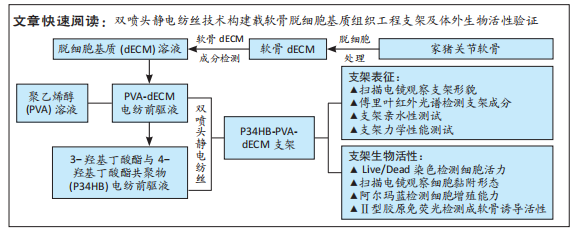
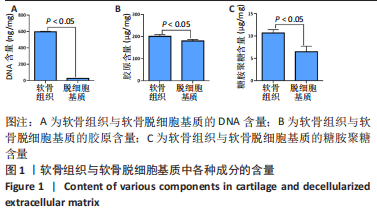
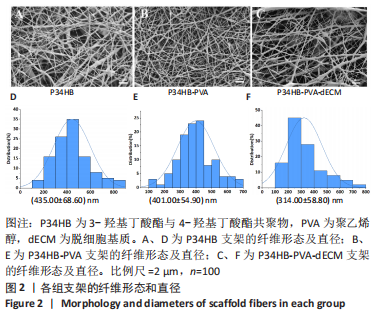
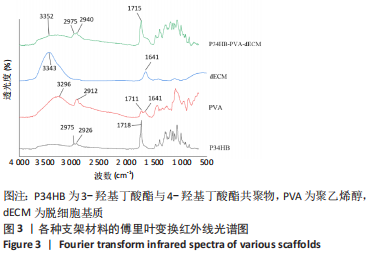
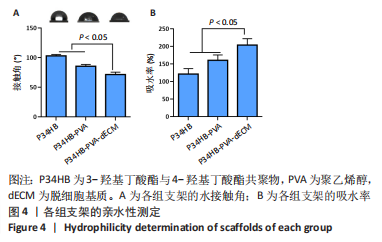
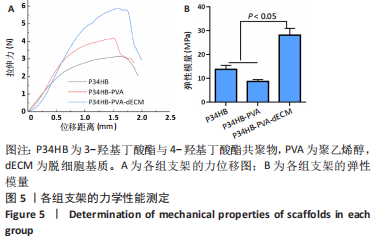
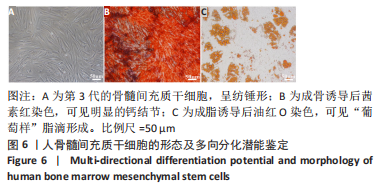
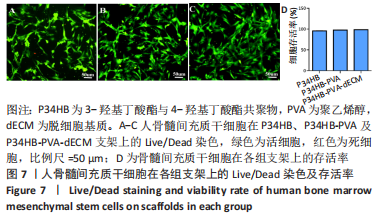
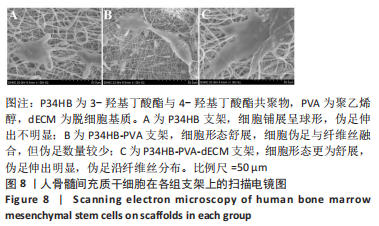
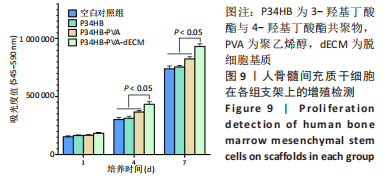
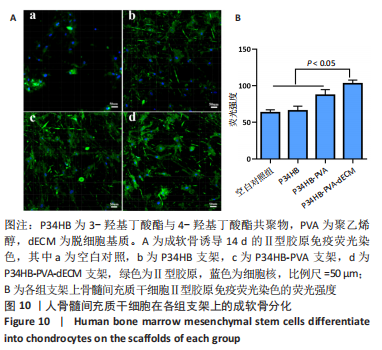
[1] ZHANG FX, LIU P, DING W, et al. Injectable mussel-Inspired highly adhesive hydrogel with exosomes for endogenous cell recruitment and cartilage defect regeneration. Biomaterials. 2021;278:121169.
[2] WANG S, YANG L, CAI B, et al. Injectable hybrid inorganic nanoscaffold as rapid stem cell assembly template for cartilage repair. Natl Sci Rev. 2022; 9(4):nwac037.
[3] AL-QURAYSHI Z, WAFA EI, ROSSI MEYER MK, et al. Tissue engineering the pinna: comparison and characterization of human decellularized auricular biological scaffolds. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2021;4(9):7234-7242.
[4] ORTH P, GAO L, MADRY H. Microfracture for cartilage repair in the knee: a systematic review of the contemporary literature. Knee Surg Sport Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(3):670-706.
[5] TIAN G, JIANG S, LI J, et al. Cell-free decellularized cartilage extracellular matrix scaffolds combined with interleukin 4 promote osteochondral repair through immunomodulatory macrophages: in vitro and in vivo preclinical study. Acta Biomater. 2021;127:131-145.
[6] BLUM JC, SCHENCK TL, BIRT A, et al. Artificial decellularized extracellular matrix improves the regenerative capacity of adipose tissue derived stem cells on 3D printed polycaprolactone scaffolds. J Tissue Eng. 2021;12: 20417314211022242.
[7] 胡秋羽,杨龙,杨勇,等.聚己二酸丁二醇酯-对苯二甲酸丁二醇酯/Ⅰ型胶原取向纤维促进前交叉韧带断裂后腱-骨愈合[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(27):4314-4319.
[8] XUE J, WU T, DAI Y, et al. Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: Methods, materials, and applications. Chem Rev. 2019;119(8):5298-5415.
[9] BARHOUM A, PAL K, RAHIER H, et al. Nanofibers as new-generation materials: from spinning and nano-spinning fabrication techniques to emerging applications. Appl Mater Today. 2019;(17):1-35.
[10] KANIUK Ł, STACHEWICZ U. Development and advantages of biodegradable PHA polymers based on electrospun PHBV fibers for tissue engineering and other biomedical applications. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021;7(12):5339-5362.
[11] BASNETT P, MATHARU RK, TAYLOR CS, et al. Harnessing polyhydroxyalkanoates and pressurized gyration for hard and soft tissue engineering. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13:32624-32639.
[12] YE C, HU P, MA MX, et al. PHB/PHBHHx scaffolds and human adipose-derived stem cells for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2009;30(26):4401-4406.
[13] 刘鋆,杨龙,王伟宇,等.聚 3-羟基丁酸酯 4-羟基丁酸酯/聚乙二醇/氧化石墨烯组织工程支架的制备和性能评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(22):3466-3472.
[14] MA MX, LIU Q, YE C, et al. Preparation of P3HB4HB/(Gelatin + PVA) composite scaffolds by coaxial electrospinning and its biocompatibility evaluation. Biomed Res Int. 2017;(2017):9251806.
[15] MONZAVI SM, KAJBAFZADEH AM, SABETKISH S, et al. Extracellular matrix scaffold using decellularized Cartilage for hyaline cartilage regeneration. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1345:209-223.
[16] CHEN M, FENG Z, GUO W, et al. PCL-MECM- Based hydrogel hybrid scaffolds and meniscal fibrochondrocytes promote whole meniscus regeneration in a rabbit meniscectomy model. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(44): 41626-41639.
[17] IRANI M, NODEH SM. PVA/kappa-carrageenan/Au/camptothecin/pegylated-polyurethane/paclitaxel nanofibers against lung cancer treatment. RSC Adv. 2022;12(25):16310-16318.
[18] YANG L, ZHAO Y, CUI DB, et al. Coaxial bioelectrospinning of P34HB/PVA microfibers biomimetic scaffolds with simultaneity cell-laden for improving bone regeneration. Mater Design. 2022;213:110349.
[19] 赵超尘.脱细胞基质覆层壳聚糖纤维载体的制备和生物学评价[D].广州:南方医科大学,2020.
[20] LIU HW, SU WT, LIU CY, et al. Highly organized porous gelatin-based scaffold by microfluidic 3D-foaming technology and dynamic culture for cartilage tissue engineering. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(15):8449.
[21] XI Y, GE J, GUO Y, et al. Biomimetic elastomeric polypeptidebased nanofibrous matrix for overcoming multidrug-resistant bacteria and enhancing full-thickness wound healing/skin regeneration. ACS Nano. 2018; 12:10772-10784.
[22] ZELINKA A, ROELOFS AJ, KANDEL RA, et al. Cellular therapy and tissue engineering for cartilage repair. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(12): 1547-1560.
[23] ZHANG Q, NETTLESHIP I, SCHMELZER E, et al. Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine therapies for cell senescence in bone and cartilage. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2020;26(1):64-78.
[24] KIM HS, MANDAKHBAYAR N, KIM HW, et al. Protein-reactive nanofibrils decorated with cartilage-derived decellularized extracellular matrix for osteochondral defects. Biomaterials. 2021;269:120214.
[25] HONG J, YEO M, YANG GH, et al. Cell-electrospinning and its application for tissue engineering. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:6208.
[26] XING H, LEE H, LUO L, et al. Extracellular matrix-derived biomaterials in engineering cell function. Biotechnol Adv. 2020;42:107421.
[27] FIORDALISI M, SILVA AJ, BARBOSA M, et al. Decellularized scaffolds for intervertebral disc regeneration. Trends Biotechnol. 2020;38(9):947-951.
[28] GAO S, CHEN M, WANG P, et al. An electrospun fiber reinforced scaffold promotes total meniscus regeneration in rabbit meniscectomy model. Acta Biomater. 2018;73:127-140.
[29] ZHANG X, CHEN X, HONG H, et al. Decellularized extracellular matrix scaffolds: Recent trends and emerging strategies in tissue engineering. Bioact Mater. 2021;23(10):15-31.
[30] ROTHRAUFF BB, COLUCCINO L, GOTTARDI R, et al. Efficacy of thermoresponsive, photocrosslinkable hydrogels derived from decellularized tendon and cartilage extracellular matrix for cartilage tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(1):e159-e170.
[31] GAO S, GUO W, CHEN M, et al. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun nanofibers composed of decellularized meniscus extracellular matrix and polycaprolactone for meniscus tissue engineering. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5(12):2273-2285.
[32] MISZUK JM, XU T, YAO Q, et al. Functionalization of PCL-3D electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds for improved BMP2-induced bone formation. Appl Mater Today. 2018;10:194-202.
[33] 蒲丛丛,何建新,崔世忠,等.电场对双喷头喷气静电纺纳米纤维成形的影响[J].材料导报,2013,27(7):86-89.
[34] 任浩征,潘超,许迎,等.ZnO 表面改性 Zn-Cu 组织工程支架的研究[J].表面技术,2021,50(2):58-65.
[35] LI X, LIU M, CHEN F, et al. Design of hydroxyapatite bioceramics with micro-/nano-topographies to regulate the osteogenic activities of bone morphogenetic protein-2 and bone marrow stromal cells. Nanoscale. 2020; 12(13):7284-7300.
[36] GIRAO AF, SEMITELA A, PEREIRA AL, et al. Microfabrication of a biomimetic arcade-like electrospun scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering applications. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2020;31(8):69.
[37] GRESHAM RCH, BAHNEY CS, LEACH JK. Growth factor delivery using extracellular matrix-mimicking substrates for musculoskeletal tissue engineering and repair. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(7):1945-1956.
[38] ZHU W, CAO L, SONG C, et al. Cell-derived decellularized extracellular matrix scaffolds for articular cartilage repair. Int J Artif Organs. 2021;44(4):269-281.
[39] SHAHVERDI F, BARATI A, SALEHI E, et al. Biaxial electrospun nanofibers based on chitosan-poly (vinyl alcohol) and poly (Ɛ-caprolactone) modified with CeAlO3 nanoparticles as potential wound dressing materials. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;221:736-750.
[40] PEDRAM RAD Z, MOKHTARI J, ABBASI M, et al. Calendula officinalis extract/PCL/Zein/Gum arabic nanofibrous bio-composite scaffolds via suspension, two-nozzle and multilayer electrospinning for skin tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;135:530-543.
|