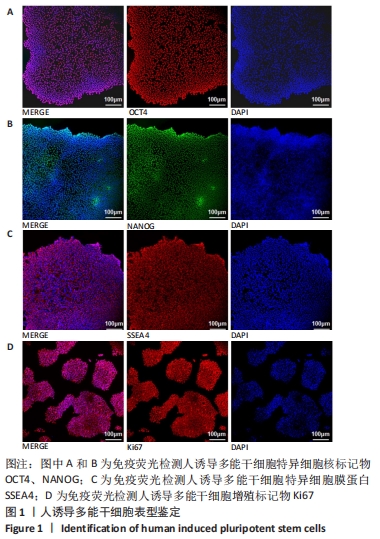
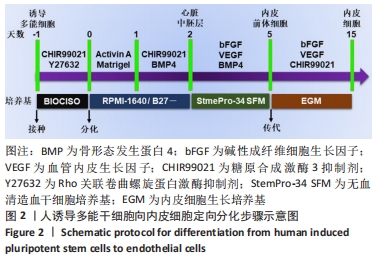
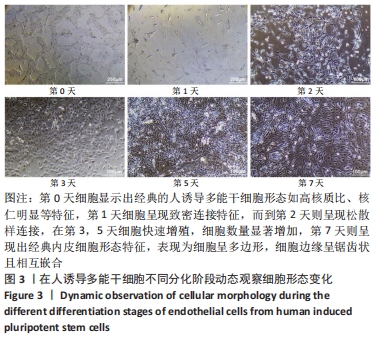
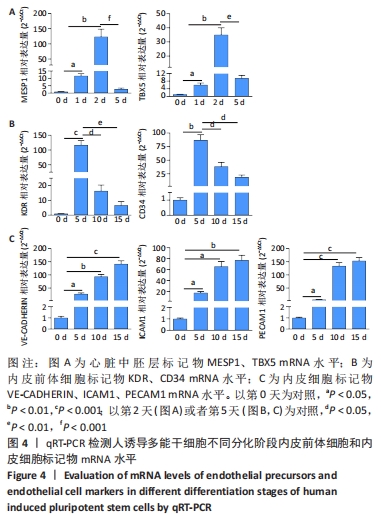
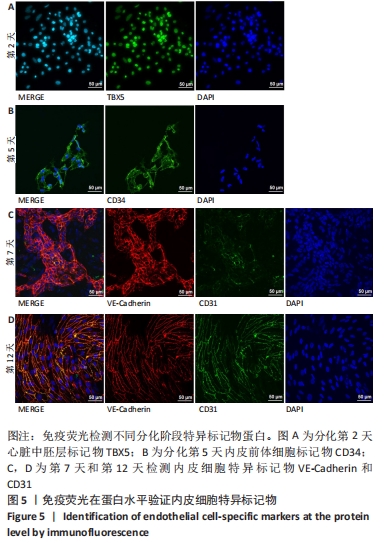
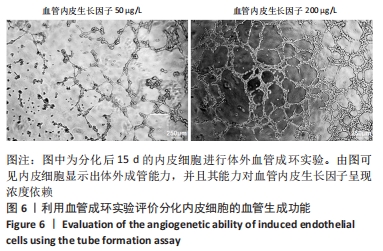
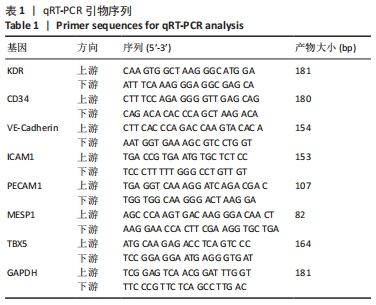
[1] DI BERNARDINI E, CAMPAGNOLO P, MARGARITI A, et al. Endothelial lineage differentiation from induced pluripotent stem cells is regulated by microRNA-21 and transforming growth factor β2 (TGF-β2) pathways. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(6):3383-3393.
[2] KRÜGER-GENGE A, BLOCKI A, FRANKE RP, et al. Vascular Endothelial Cell Biology: An Update. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(18):4411.
[3] SENA CM, PEREIRA AM, SEIÇA R. Endothelial dysfunction - a major mediator of diabetic vascular disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013; 1832(12):2216-2231.
[4] 严 拓,刘雅文,吴灿,等.人工血管研究现状与应用优势[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(30):4849-4854.
[5] 张家庆,王武军,闫玉生.小口径人工血管材料应用进展[J].实用医学杂志,2014,30(21):3520-3521.
[6] XU L, VARKEY M, JORGENSEN A, et al. Bioprinting small diameter blood vessel constructs with an endothelial and smooth muscle cell bilayer in a single step. Biofabrication. 2020;12(4):045012.
[7] SFRISO R, ZHANG S, BICHSEL CA, et al. 3D artificial round section micro-vessels to investigate endothelial cells under physiological flow conditions. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):5898.
[8] LIN Y, GIL CH, YODER MC. Differentiation, Evaluation, and Application of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Endothelial Cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017;37(11):2014-2025.
[9] GNECCHI M, STEFANELLO M, MURA M. Induced pluripotent stem cell technology: Toward the future of cardiac arrhythmias. Int J Cardiol. 2017;237:49-52.
[10] HENDRIKS D, CLEVERS H, ARTEGIANI B. CRISPR-Cas Tools and Their Application in Genetic Engineering of Human Stem Cells and Organoids. Cell Stem Cell. 2020;27(5):705-731.
[11] TAKAHASHI K, YAMANAKA S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126(4):663-676.
[12] RAASCH M, FRITSCHE E, KURTZ A, et al. Microphysiological systems meet hiPSCs technology-New tools for disease modeling of liver infections in basic research and drug development. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019;140:51-67.
[13] TAKAHASHI K, TANABE K, OHNUKI M, et al. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell. 2007; 131(5):861-872.
[14] HAN JK, SHIN Y, KIM HS. Direct Conversion of Cell Fate and Induced Endothelial Cells. Circ J. 2021 Nov 3. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-21-0703. Online ahead of print.
[15] TANI H, TOHYAMA S, KISHINO Y, et al. Production of functional cardiomyocytes and cardiac tissue from human induced pluripotent stem cells for regenerative therapy. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2022;164:83-91.
[16] WANG J, REN H, LIU Y, et al. Bioinspired Artificial Liver System with hiPSCs-Derived Hepatocytes for AcuteLiver Failure Treatment. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(23):e2101580.
[17] MOKHAMES Z, REZAIE Z, ARDESHIRYLAJIMI A, et al. Efficient smooth muscle cell differentiation of iPS cells on curcumin-incorporated chitosan/collagen/polyvinyl-alcohol nanofibers. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2020;56(4):313-321.
[18] OKANO H, YAMANAKA S. iPS cell technologies: significance and applications to CNS regeneration and disease. Mol Brain. 2014;7:22.
[19] ZHANG Y, LI H, WANG J, et al. Generation of three iPSC lines (XACHi007-A, XACHi008-A, XACHi009-A) from a Chinese family with long QT syndrome type 5 with heterozygous c.226G>A (p.D76N) mutation in KCNE1gene. Stem Cell Res. 2020;45:101798.
[20] GENTILE MT, PASTORINO O, BIFULCO M, et al. HUVEC Tube-formation Assay to Evaluate the Impact of Natural Products on Angiogenesis. J Vis Exp. 2019;(148). doi: 10.3791/58591.
[21] PALPANT NJ, PABON L, FRIEDMAN CE, et al. Generating high-purity cardiac and endothelial derivatives from patterned mesoderm using human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Protoc. 2017;12(1):15-31.
[22] KATTMAN SJ, WITTY AD, GAGLIARDI M, et al. Stage-specific optimization of activin/nodal and BMP signaling promotes cardiac differentiation of mouse and human pluripotent stem cell lines. Cell Stem Cell. 2011;8(2):228-240.
[23] XU PF, HOUSSIN N, FERRI-LAGNEAU KF, et al. Construction of a vertebrate embryo from two opposing morphogen gradients. Science. 2014;344(6179):87-89.
[24] KENNEDY CC, BROWN EE, ABUTALEB NO, et al. Development and Application of Endothelial Cells Derived From Pluripotent Stem Cells in Microphysiological Systems Models. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:625016.
[25] YODER MC. Differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into endothelial cells. Curr Opin Hematol. 2015;22(3):252-257.
[26] NELSON EA, QIU J, CHAVKIN NW, et al. Directed Differentiation of Hemogenic Endothelial Cells from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. J Vis Exp. 2021;(169):10.3791/62391.
[27] WANG K, LIN RZ, HONG X, et al. Robust differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into endothelial cells via temporal modulation of ETV2 with modified mRNA. Sci Adv. 2020;6(30):eaba7606.
[28] CHOI KD, YU J, SMUGA-OTTO K, et al. Hematopoietic and endothelial differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells. 2009;27:559-567.
[29] BELAIR DG, WHISLER JA, VALDEZ J, et al. Human vascular tissue models formed from human induced pluripotent stem cell derived endothelial cells. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2015;11(3):511-525.
[30] ADAMS WJ, ZHANG Y, CLOUTIER J, et al. Functional vascular endothelium derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Reports. 2013;1:105-113.
[31] LEVENBERG S, GOLUB JS, AMIT M, et al. Endothelial cells derived from human embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(7): 4391-4396.
[32] IKUNO T, MASUMOTO H, YAMAMIZU K, et al. Efficient and robust differentiation of endothelial cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells via lineage control with VEGF and cyclic AMP. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0173271.
[33] LIAN X, BAO X, AL-AHMAD A, et al. Efficient differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells to endothelial progenitors via small-molecule activation of WNT signaling. Stem Cell Reports. 2014;3:804-816.
|