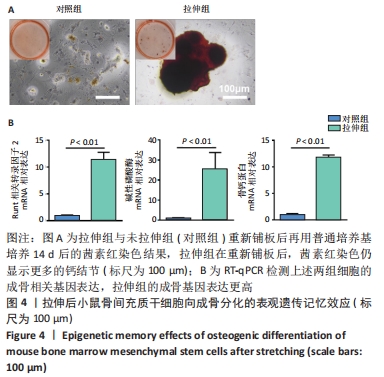
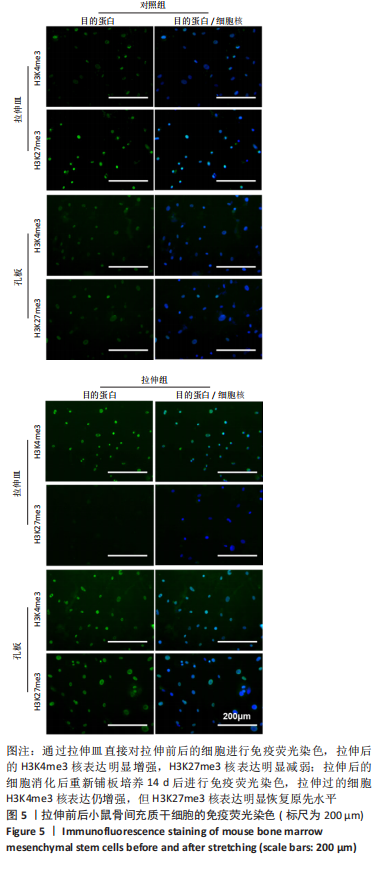
[1] BLABER EA, DVOROCHKIN N, TORRES ML, et al. Mechanical unloading of bone in microgravity reduces mesenchymal and hematopoietic stem cell-mediated tissue regeneration. Stem Cell Res. 2014;13(2):181-201.
[2] VINING KH, MOONEY DJ. Mechanical forces direct stem cell behaviour in development and regeneration. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017;18(12): 728-742.
[3] FU X, LIU G, HALIM A, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Migration and Tissue Repair. Cells. 2019;8(8):784.
[4] 张晓梅,彭旭,魏诗航,等.力学刺激调控骨髓间充质细胞向软骨的分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(45):6834-6840.
[5] ZHAO C, LI Y, WANG X, et al. The Effect of Uniaxial Mechanical Stretch on Wnt/beta-Catenin Pathway in Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J Craniofac Surg. 2017;28(1):113-117.
[6] YU L, CAI Y, WANG H, et al. Biomimetic bone regeneration using angle-ply collagen membrane-supported cell sheets subjected to mechanical conditioning. Acta Biomater. 2020;112:75-86.
[7] YANG C, TIBBITT MW, BASTA L, et al. Mechanical memory and dosing influence stem cell fate. Nat Mater. 2014;13(6):645-652.
[8] CAKOUROS D, GRONTHOS S. Epigenetic Regulators of Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell Lineage Determination. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020; 18(5):597-605.
[9] BLOCK T, EL-OSTA A. Epigenetic programming, early life nutrition and the risk of metabolic disease. Atherosclerosis. 2017;266:31-40.
[10] SUI BD, ZHENG CX, LI M, et al. Epigenetic Regulation of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Homeostasis. Trends Cell Biol. 2020;30(2):97-116.
[11] YE L, FAN Z, YU B, et al. Histone Demethylases KDM4B and KDM6B Promote Osteogenic Differentiation of Human MSCs. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;23(6):898-899.
[12] NAYAK A, VIALE-BOURONCLE S, MORSCZECK C, et al. The SUMO-specific isopeptidase SENP3 regulates MLL1/MLL2 methyltransferase complexes and controls osteogenic differentiation. Mol Cell. 2014; 55(1):47-58.
[13] ROJAS A, AGUILAR R, HENRIQUEZ B, et al. Epigenetic Control of the Bone-master Runx2 Gene during Osteoblast-lineage Commitment by the Histone Demethylase JARID1B/KDM5B. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(47): 28329-28342.
[14] LU Y, GAO H, ZHANG M, et al. Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor-Transfected Placenta-Derived Versus Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Cells for Treating Spinal Cord Injury. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:1800-1811.
[15] 陈迟迟,张雨,何家辰,等.肥胖小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(24):3846-3851.
[16] CHEN X, YAN J, HE F, et al. Mechanical stretch induces antioxidant responses and osteogenic differentiation in human mesenchymal stem cells through activation of the AMPK-SIRT1 signaling pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2018;126:187-201.
[17] KESHTKAR S, AZARPIRA N, GHAHREMANI MH. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: novel frontiers in regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):63.
[18] LIN Z, TANG X, WAN J, et al. Functions and mechanisms of circular RNAs in regulating stem cell differentiation. RNA Biol. 2021;18(12):2136-2149.
[19] DAS D, FLETCHER RB, NGAI J. Cellular mechanisms of epithelial stem cell self-renewal and differentiation during homeostasis and repai. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2020;9(1):e361.
[20] WU T, YIN F, WANG N, et al. Involvement of mechanosensitive ion channels in the effects of mechanical stretch induces osteogenic differentiation in mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(1):284-293.
[21] Man K, Joukhdar H, Manz XD, et al. Bone tissue engineering using 3D silk scaffolds and human dental pulp stromal cells epigenetic reprogrammed with the selective histone deacetylase inhibitor MI192. Cell Tissue Res. 2022;388(3):565-581.
[22] ERMOLAEVA M, NERI F, ORI A, et al. Cellular and epigenetic drivers of stem cell ageing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(9):594-610.
[23] RYALL JG, CLIFF T, DALTON S, et al. Metabolic Reprogramming of Stem Cell Epigenetics. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;17(6):651-662.
[24] REN R, OCAMPO A, LIU GH, et al. Regulation of Stem Cell Aging by Metabolism and Epigenetics. Cell Metab. 2017;26(3):460-474.
[25] HUPPERTZ S, SENGER K, BROWN A, et al. KDM6A, a histone demethylase, regulates stress hematopoiesis and early B-cell differentiation. Exp Hematol. 2021;99:32-43 e13.
[26] CHAKRABORTY AA, LAUKKA T, MYLLYKOSKI M, et al. Histone demethylase KDM6A directly senses oxygen to control chromatin and cell fate. Science. 2019;363(6432):1217-1222.
[27] SHI YG, TSUKADA Y. The discovery of histone demethylases. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013;5(9):a017947.
[28] LE HQ, GHATAK S, YEUNG CY, et al. Mechanical regulation of transcription controls Polycomb-mediated gene silencing during lineage commitment. Nat Cell Biol. 2016;18(8):864-875.
[29] LI Y, GE C, FRANCESCHI RT. MAP Kinase-Dependent RUNX2 Phosphorylation Is Necessary for Epigenetic Modification of Chromatin During Osteoblast Differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 2017;232(9):2427-2435.
[30] RUMMUKAINEN P, TARKKONEN K, DUDAKOVIC A, et al. Lysine-Specific Demethylase 1 (LSD1) epigenetically controls osteoblast differentiation. PLoS One. 2022;17(3):e0265027.
[31] SUZUKI J, MARUYAMA S, TAMAUCHI H, et al. Gfi1, a transcriptional repressor, inhibits the induction of the T helper type 1 programme in activated CD4 T cells. Immunology. 2016;147(4):476-487.
[32] GE W, SHI L, ZHOU Y, et al. Inhibition of osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stromal cells by retinoblastoma binding protein 2 repression of RUNX2-activated transcription. Stem Cells. 2011;29(7): 1112-1125.
|