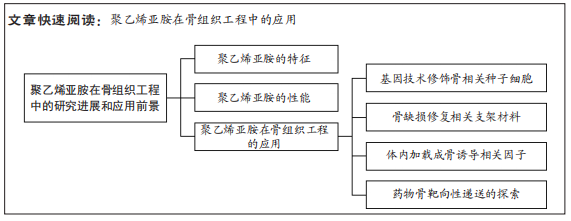
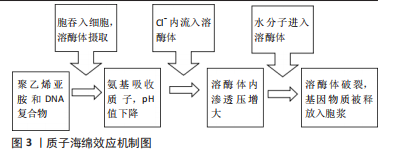
[1] MORE N, KAPUSETTI G. Piezoelectric material-a promising approach for bone and cartilage regeneration. Med Hypotheses. 2017;108:10-16.
[2] WINKLER T, SASS FA, DUDA GN, et al. A review of biomaterials in bone defect healing, remaining shortcomings and future opportunities for bone tissue engineering: the unsolved challenge. Bone Jt Res. 2018; 7(3):232-243.
[3] YANG Y, SONG X, LI X, et al. Recent progress in biomimetic additive manufacturing technology:from materials to functional structures. Adv Mater. 2018;30(36):1706539.
[4] Amara M, Kerdjoudj H. Modification of the cation exchange resin properties by impregnation in polyethyleneimine solutions:
application to the separation of metallic ions. Talanta. 2003;60(5):991-1001.
[5] 吴慎剑,刘源岗,王士斌.PEI用于磁性纳米颗粒载药及联合载药抗肿瘤的研究进展[J].材料导报,2015,29(13):89-92,111.
[6] 刘云,潘杰,董伟,等.半乳糖基化壳聚糖-聚乙烯亚胺递送siRNA对肝癌耐药细胞BEL7402/5-Fu中MRE11表达的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(6):934-939.
[7] HUSSAIN Z, PEI R. Necessities, opportunities, and challenges for tympanic membrane perforation scaffolding-based bioengineering. Biomed Mater Bristol Engl. 2020. doi:10.1088/1748-605X/abcf5d.
[8] HONG SJ, AHN MH, SANGSHETTI J, et al. Sugar alcohol-based polymeric gene carriers: synthesis, properties and gene therapy applications. Acta Biomater. 2019;97:105-115.
[9] ZHU J, LI H, XIONG Z, et al. Polyethyleneimine-coated manganese oxide nanoparticles for targeted tumor PET/MR imaging. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(41):34954-34964.
[10] ZHANG B, DUAN Q, LI Y, et al. A “Turn-on” fluorescent probe for glutathione detection based on the polyethylenimine-carbon dots-Cu2+ system. J Photochem. Photobiol B. 2019;197:111532.
[11] WANG X, LI Y, HAN R, et al. Demineralized bone matrix combined bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, bone morphogenetic protein-2 and transforming growth factor-β3 gene promoted pig cartilage defect repair. PLoS One. 2014;9(12):e116061.
[12] 俞莉敏,马俊轩,李继云,等.稳定表达人骨形态发生蛋白2基因骨组织工程种子细胞的构建[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(17): 2722-2728.
[13] BOUSSIF O, LEZOUALC HF, ZANTA MA, et al. A versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: polyethylenimine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92(16):7297-7301.
[14] BRONICH T, KABANOV AV, MARKY LA. A thermodynamic characterization of the interaction of a cationic copolymer with DNA. J Phys Chem B. 2001;105(25):6042-6050.
[15] KARIMOV M, APPELHANS D, EWE A, et al. The combined disulfide cross-linking and tyrosine-modification of very low molecular weight linear PEI synergistically enhances transfection efficacies and improves biocompatibility. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2021;161:56-65.
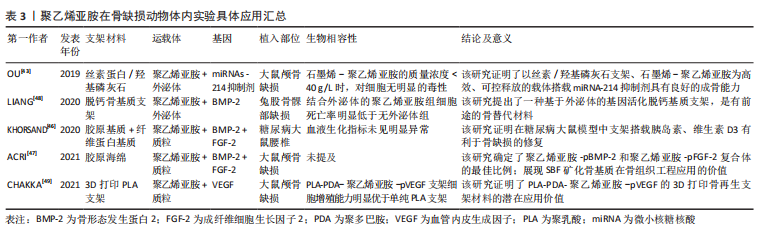
[16] KHORSAND B, ELANGOVAN S, HONG L, et al. A comparative study of the bone regenerative effect of chemically modified RNA encoding BMP-2 or BMP-9. AAPS J. 2017;19(2):438-446.
[17] JIANG HL, ISLAM MA, XING L, et al. Degradable polyethylenimine-based gene carriers for cancer therapy. Curr Chem Cham. 2017;375(2):34.
[18] KUBCZAK M, MICHLEWSKA S, KARIMOV M, et al. Unmodified and tyrosine-modified polyethylenimines as potential carriers for siRNA: biophysical characterization and toxicity. Int J Pharm. 2022;614:121468.
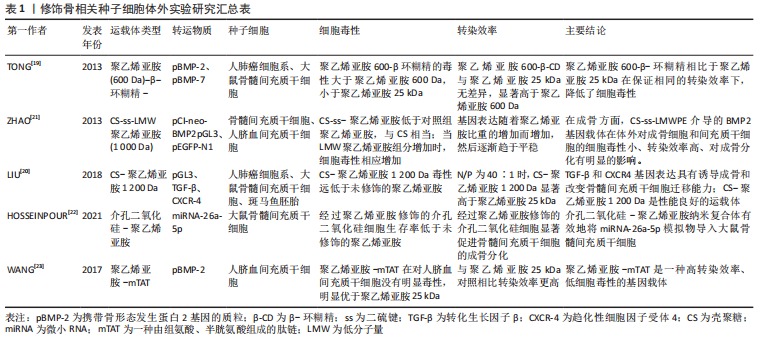
[19] TONG H, WANG C, HUANG Y, et al. Polyethylenimine600-β-cyclodextrin: a promising nanopolymer for nonviral gene delivery of primary mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:1935-1946.
[20] LIU M, ZHANG L, ZHAO Q, et al. Lower-molecular-weight chitosan-treated polyethyleneimine: a practical strategy for gene delivery to mesenchymal stem cells. cellular physiology and biochemistry. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(4):1255-1269.
[21] ZHAO X, LI Z, PAN H, et al. Enhanced gene delivery by chitosan-disulfide-conjugated LMW-PEI for facilitating osteogenic differentiation. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(5):6694-6703.
[22] HOSSEINPOUR S, CAO Y, LIU J, et al. Efficient transfection and long-term stability of Rno-miRNA-26a-5p for osteogenic differentiation by large pore sized mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J Mater Chem. 2021; 9(9):2275-2284.
[23] WANG Y, YOU C, WEI R, et al. Modification of human umbilical cord blood stem cells using polyethylenimine combined with modified TAT peptide to enhance BMP-2 production. BioMed Res Int. 2017; 2017:2971413.
[24] ATLURI K, SEABOLD D, HONG L, et al. Nanoplex-mediated codelivery of fibroblast growth factor and bone morphogenetic protein genes promotes osteogenesis in human adipocyte-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Pharm. 2015;12(8):3032-3042.
[25] ACRI T M, LAIRD NZ, GEARY SM, et al. Effects of calcium concentration on nonviral gene delivery to bone marrow-derived stem cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(12):2256-2265.
[26] REZNIKOV N, BILTON M, LARI L, et al. Fractal-like hierarchical organization of bone begins at the nanoscale. Science. 2018;360(6388): eaao2189.
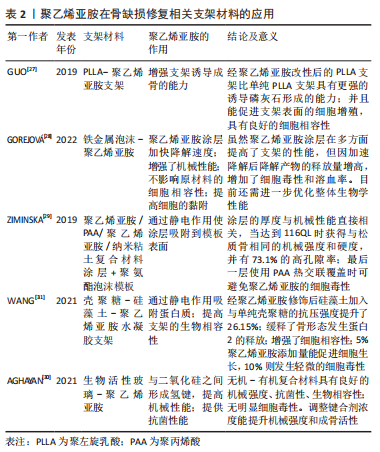
[27] GUO R, CHEN S, XIAO X. Fabrication and characterization of poly (ethylenimine) modified poly (l-Lactic acid) nanofibrous scaffolds. J Biomater Sci Polym. 2019;30(16):1523-1541.
[28] GOREJOVÁ R, ORIŇAKOVÁ R, MACKO J, et al. Electrochemical Behavior, Biocompatibility and Mechanical Performance of Biodegradable Iron with PEI Coating. J Biomed. Mater Res A. 2022;110(3):659-671.
[29] ZIMINSKA M, CHALANQUI MJ, CHAMBERS P, et al. Nanocomposite-coated porous templates for engineered bone scaffolds: a parametric study of layer-by-layer assembly conditions. Biomed Mater Bristol Engl. 2019;14(6):065008.
[30] AGHAYAN M, ALIZADEH P, KESHAVARZ M. Multifunctional polyethylene imine hybrids decorated by silica bioactive glass with enhanced mechanical properties, antibacterial, and osteogenesis for bone repair. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;131:112534.
[31] WANG X, LI Y, REN W, et al. PEI-Modified Diatomite/chitosan composites as bone tissue engineering scaffold for sustained release of BMP-2. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2021;32(10):1337-1355.
[32] STERZENBACH T, HELBIG R, HANNIG C, et al. Bioadhesion in the oral cavity and approaches for biofilm management by surface modifications. Clin Oral Investig. 2020;24(12):4237-4260.
[33] BEYTH N, YUDOVIN-FARBER I, BAHIR R, et al. Antibacterial activity of dental composites containing quaternary ammonium polyethylenimine nanoparticles against streptococcus mutans. Biomaterials. 2006;27(21): 3995-4002.
[34] 朱敏闻,孙兵,李志耀,等.增强成骨及抗菌性能的鱼胶原/聚乙烯亚胺电纺膜用于牙周组织修复[J].组织工程与重建外科,2021, 17(2):102-107.
[35] SUN Y, ZHAO YQ, ZENG Q, et al. Dual-functional implants with antibacterial and osteointegration-promoting performances. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(40):36449-36457.
[36] BOULAND C, PHILIPPART P, DEQUANTER D, et al. Cross-talk between mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) and endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) in bone regeneration. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:674084.
[37] LI Y, LIU Y, BAI H, et al. Sustained release of VEGF to promote angiogenesis and osteointegration of three-dimensional printed biomimetic titanium alloy implants. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9: 757767.
[38] YANG YP, GADOMSKI BC, BRUYAS A, et al. Investigation of a prevascularized bone graft for large defects in the ovine tibia. Tissue Eng Part A. 2021;27(23–24):1458-1469.
[39] WANG XT, LIU PY, TANG JB. PDGF gene therapy enhances expression of VEGF and BFGF genes and activates the NF-κB gene in signal pathways in ischemic flaps. Plast. Reconstr Surg. 2006;117(1):129.
[40] HADJIZADEH A. Acetaldehyde plasma polymer-coated PET fibers for endothelial cell patterning: chemical, topographical, and biological analysis. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2010;94(1):11-21.
[41] GIGLIOBIANCO G, CHONG CK, MACNEIL S. Simple surface coating of electrospun Poly-L-Lactic acid scaffolds to induce angiogenesis. J Biomater Appl. 2015;30(1):50-60.
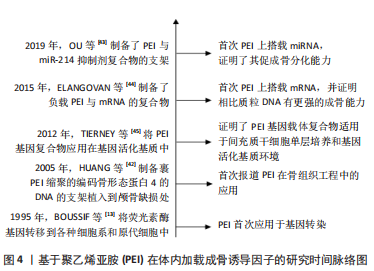
[42] HUANG YC, SIMMONS C, KAIGLER D, et al. Bone regeneration in a rat cranial defect with delivery of PEI-condensed plasmid DNA encoding for bone morphogenetic protein-4 (BMP-4). Gene Ther. 2005;12(5): 418-426.
[43] OU L, LAN Y, FENG Z, et al. Functionalization of SF/HAP scaffold with GO-PEI-MiRNA inhibitor complexes to enhance bone regeneration through activating transcription factor 4. Theranostics. 2019;9(15):4525-4541.
[44] ELANGOVAN S, KHORSAND B, DO AV, et al. Chemically modified RNA activated matrices enhance bone regeneration. J Control Release. 2015;218:22-28.
[45] TIERNEY EG, DUFFY GP, HIBBITTS AJ, et al. The development of non-viral gene-activated matrices for bone regeneration using polyethyleneimine (PEI) and collagen-based scaffolds. J Control Release Off J Control Release Soc. 2012;158(2):304-311.
[46] KHORSAND B, ACRI TM, DO AV, et al. A multi-functional implant induces bone formation in a diabetic model. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020; 9(18):e2000770.
[47] ACRI TM, LAIRD NZ, JAIDEV LR, et al. Nonviral gene delivery embedded in biomimetically mineralized matrices for bone tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part A. 2021;27(15-16):1074-1083.
[48] LIANG Z, LUO Y, LV Y. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles mediate BMP2 gene delivery and enhance bone regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(30):6378-6389.
[49] CHAKKA JL, ACRI T, LAIRD NZ, et al. Polydopamine functionalized VEGF gene-activated 3D printed scaffolds for bone regeneration. RSC Adv. 2021;11(22):13282-13291.
[50] 刘锌,杜斌,孙光权,等.多孔β磷酸三钙-聚吡咯-生物素-淫羊藿素微球复合支架促进骨髓间充质干细胞的募集[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(34):5532-5537.
[51] 向海滨,李新霞,梁求真,等.特异性骨靶向纳米递药系统的优势与临床可应用性[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(4):612-618.
[52] FORTE L, SARDA S, COMBES C, et al. Hydroxyapatite functionalization to trigger adsorption and release of risedronate. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017;160:493-499.
[53] PLESSELOVA S, GARCIA-CEREZO P, BLANCO V, et al. Polyethylenimine–bisphosphonate–cyclodextrin ternary conjugates: supramolecular systems for the delivery of antineoplastic drugs. J Med Chem. 2021; 64(16):12245-12260.
[54] DUAN J, DONG J, ZHANG T, et al. Polyethyleneimine-functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles for systemic siRNA delivery in experimental arthritis. Nanomed. 2014;9(6):789-801.
[55] GONG M, LIU H, SUN N, et al. Polyethylenimine-dextran-coated magnetic nanoparticles loaded with miR-302b suppress osteosarcoma in vitro and in vivo. Nanomed. 2020;15(7):711-723.
[56] AEINEH N, SALEHI F, AKRAMI M, et al. Glutathione conjugated polyethylenimine on the surface of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles as a theranostic agent for targeted and controlled curcumin delivery. J Biomater Sci Polym. 2018;29(10):1109-1125.
[57] BRICOUT N, CHAI F, SOBOCINSKI J, et al. Immobilisation of an anti-platelet adhesion and anti-thrombotic drug (EP224283) on polydopamine coated vascular stent promoting anti-thrombogenic properties. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;113:110967. |