1.1 设计 材料学表征实验和细胞学体外实验,组间比较采用t检验。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2020年12月至2022年7月在徐州医科大学口腔医学院实验室完成。
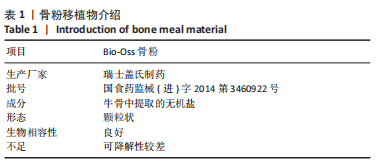
1.3 材料 Bio-Oss骨粉移植物介绍见表1。
α-MEM培养基、BCA血清(Gibco,美国);胎牛血清(四季青,中国);0.25%胰酶细胞消化液、青/链霉素双抗、CCK-8细胞活性检测试剂盒、DEPC水、SBF模拟体液(Vicmed,中国);碱性磷酸酶检测试剂盒、BCA蛋白定量试剂盒(碧云天,中国);碱性磷酸酶活性检测试剂盒(南京建成,中国);Primer引物、茜素红染色及定量检测试剂盒(上海生工,中国);RNA提取试剂盒、反转录试剂盒、实时定量PCR 试剂盒(Takara,日本)。
实时荧光定量PCR仪(Roche,瑞士);倒置相差显微镜(Olympus,日本);酶标仪(Biotek,美国);氢氧化钙、磷酸、致孔剂(国药,中国);场发射扫描电子显微镜(Teneo VS,FEI,美国);十二烷基硫酸钠、PBS(碧云天,中国)。
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 亚微米拓扑结构磷酸钙陶瓷的制备 以氢氧化钙和磷酸为原料,将磷酸溶液以恒定的速率逐滴滴加到氢氧化钙悬浮液中,在室温下熟化6周后,对浆液进行过滤、干燥和研磨,得到亚微米级磷酸三钙陶瓷粉末。随后将磷酸三钙陶瓷粉末至于1%蒸馏水和致孔剂的混合溶液中,在60 ℃下发泡得到磷酸三钙陶瓷生胚。将生胚在1 050 ℃下烧结8 h,得到大块磷酸三钙陶瓷材料,并在破碎后,筛分出尺寸范围为1.0-2.0 mm的磷酸钙陶瓷颗粒。所有样品均用去离子水超声清洗、烘干,并在高压釜中灭菌后使用。
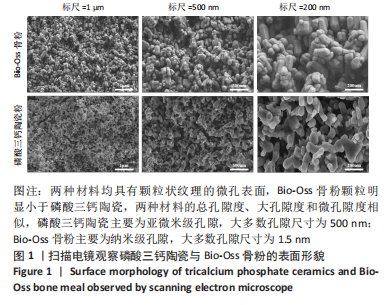
1.4.2 扫描电镜检测 取磷酸三钙陶瓷和Bio-Oss骨粉两组样品,分别在室温下干燥,喷金后扫描电镜下观察两组样品的表面形貌,并拍照记录。
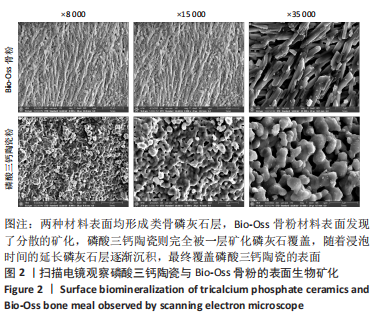
1.4.3 生物矿化实验 取磷酸三钙陶瓷和Bio-Oss骨粉两组样品,分别置于15 mL的离心管中,管中加入1.5倍浓度的模拟体液,置于37 ℃摇床中。每2 d更换新鲜模拟体液,浸泡7 d后取出,用去离子水冲洗,室温下烘干,喷金后扫描电镜下观察。
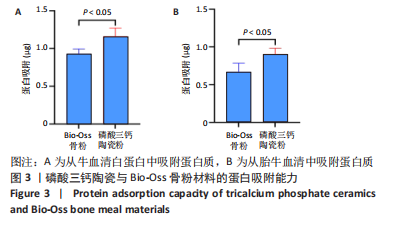
1.4.4 蛋白吸附实验 将磷酸三钙陶瓷和Bio-Oss骨粉两组样品置于48孔板中,分别向每孔加入500 µL的1%牛血清白蛋白或胎牛血清。37 ℃浸泡24 h后,用PBS冲洗3次,随后每孔中加500 µL 1%的十二烷基硫酸钠提取样品表面吸附的蛋白。采用BCA法检测试剂盒测定不同样品表面的蛋白提取量。
1.4.5 人牙周膜干细胞的分离培养 收集徐州医科大学附属口腔医院口腔颌面外科门诊18-22周岁健康成年患者因正畸需要拔除的前磨牙,牙齿无龋坏、无牙髓疾病、无根尖周疾病,行拔除前以体积分数75%乙醇充分消毒牙体周围组织。实验已获得供者知情同意,实验获得徐州市口腔医院伦理委员会批准(伦理号:2021-018)。
将牙齿样本立即置入4 ℃预冷的完全培养基中(含1%青霉素、链霉素和体积分数10%胎牛血清的α-MEM 培养基)。在超净工作台内将拔除的牙齿置于培养皿中,用PBS冲洗液反复冲洗,用无菌11号手术刀片刮取根中1/3牙周韧带,修剪组织块约1 mm3大小,加入3 g/L的Ⅰ型胶原酶置于37 ℃环境中;1 h后收集至离心管中,800 r/min离心5 min,离心后弃上清液,以完全培养基吹匀沉淀,平铺于培养皿底部。置37 ℃、体积分数为5%CO2孵箱中进行培养,2 d后首次换液,以后每隔3 d换液。当细胞从组织块周围爬出且密度达到90%后,用0.25%胰蛋白酶消化传代,取第3代人牙周膜干细胞进行实验[10-11]。
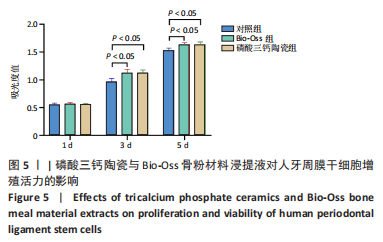
1.4.6 两种材料浸提液对人牙周膜干细胞增殖的影响 无菌条件下分别取Bio-Oss和磷酸三钙陶瓷两种骨粉颗粒,将骨粉颗粒分别加入含完全培养基浸泡(质量浓度为0.1 g/mL), 37 ℃下浸泡48 h后获得浸提液,过滤后备用。
将人牙周膜干细胞以2×107 L-1的细胞浓度接种至24孔板内,每孔接种1 mL细胞悬液。培养24 h细胞贴壁后,将原培养液分别更换为两种材料浸提液(1 mL),对照组继续使用原培养液(1 mL)。分别培养1,3,5 d后,PBS洗涤,每孔加入200 µL含10%CCK-8工作液的α-MEM培养基。37 ℃避光孵育2 h后,将100 µL的溶液转移到96孔板上,使用酶标仪在450 nm波长下测定吸光度值。
1.4.7 两种材料对人牙周膜干细胞成骨分化的影响
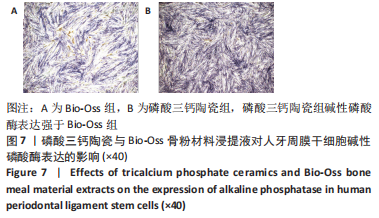
碱性磷酸酶染色:将人牙周膜干细胞以2×104/孔接种在24孔板内,每孔接种1 mL细胞悬液。培养24 h细胞贴壁后,将原培养液分别更换为两种材料浸提液。培养7 d后,吸出原有培养基,以PBS洗涤3次,40 g/L多聚甲醛固定30 min,以PBS洗涤,随后每孔加入碱性磷酸酶显色剂避光染色30 min,以PBS洗涤,光学显微镜观察下并拍摄图像。
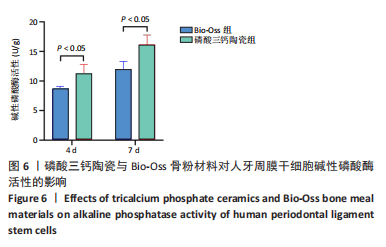
碱性磷酸酶活性检测:取生长状态良好的第3代人牙周膜干细胞,以2×104/孔的细胞密度接种在两种材料上,在培养第4,7天时,吸去原培养基,以PBS轻轻洗涤3遍,每孔加入100 μL的1%TritonX-100,置于冰上裂解30 min,反复吹打收集至1.5 mL离心管中,4 ℃下12 000 r/mmin离心10 min,取上清液,然后根据BCA蛋白定量试剂盒的使用要求,在562 nm波长下测定各孔的吸光度值。利用标准孔的吸光度值绘制标准曲线,根据吸光度值测算各组待测样品的蛋白浓度。根据碱性磷酸酶试剂盒说明,制备一个标准孔和空白孔。接着将30 μL的各组待测液加入96孔板,在每孔中分别加入50 μL的缓冲液和基质液,37 ℃避光孵育15 min。然后每孔加入150 μL的显色液,混匀,去除气泡,在520 nm波长下测定各孔的吸光度值。
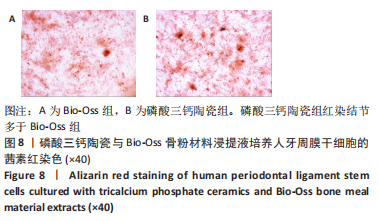
茜素红染色:取Bio-Oss骨粉与磷酸三钙陶瓷两种材料样品,经过高温高压消毒灭菌后置于24孔板中,每孔加入1 mL的完全培养基,浸泡润湿过夜。第2天,取生长状态良好的第3代人牙周膜干细胞,以 2×104/孔的细胞密度接种在24孔板中,每孔分别加入1 mL的Bio-Oss骨粉浸提液或磷酸三钙陶瓷材料浸提液,置于37 ℃、体积分数5%CO2恒温箱中培养。培养到第21天时,吸去原培养液,以PBS漂洗3遍。每孔加入1 mL的40 g/L多聚甲醛固定40 min。吸去固定液,以PBS洗涤。每孔加入1 mL茜素红染色液,染色5 min,吸去染色液,PBS反复漂洗至液体颜色不变红。室温烘干,拍照记录各组材料表面钙结节的染色情况。
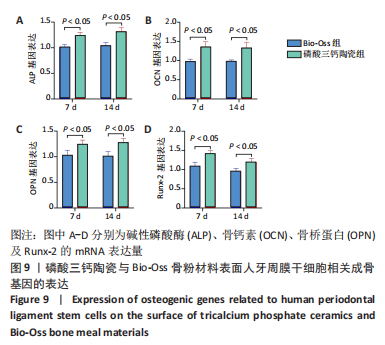
qRT-PCR法检测成骨基因表达:取Bio-Oss骨粉与磷酸三钙陶瓷两种材料样品,经过高温高压消毒灭菌后置于24孔板中,每孔加入1 mL的α-MEM培养基,浸泡润湿过夜。取生长状态良好的第2代人牙周膜干细胞,使用0.25%胰酶消化细胞,离心重悬,利用血球计数板进行计数,以 2×104 /孔的细胞密度接种在两种材料上,每孔加入1 mL 的α-MEM完全培养基,置于 37 ℃、体积分数5%CO2 恒温箱中进行培养。培养第7,14天,吸去每孔中旧培养基,以PBS清洗后,应用180 μL Trizol试剂于冰上静置30 min,随后Trizol 裂解液集中收集到1.5 mL的EP管中,加入氯仿震荡混匀,冰上静置15 min。
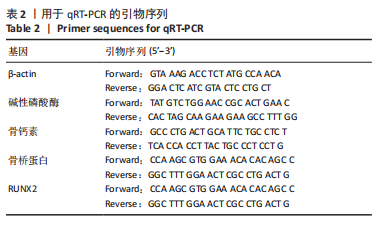
将其放入冷冻离心机中,4 ℃下12 000 r/min离心15 min。将上清液移至新的EP管,加入等量异丙醇沉淀RNA,静置 15 min,再次放入冷冻离心机中在,4 ℃下12 000 r/min离心15 min。吸去上清液后,每管中加入体积分数75%无水乙醇洗涤沉淀,并重复之前的离心操作。吸弃管中体积分数75%无水乙醇,室温晾干沉淀至透明。加入适量的 DEPC 水来充分完全溶解沉淀,使用紫外分光光度计测定 RNA 的浓度和纯度。样本纯度合格后,根据反转录PCR试剂盒的说明书在冰上进行操作,反应条件:37 ℃15 min,85 ℃5 s。随后在实时荧光定量 PCR 仪中进行扩增反应,具体反应条件如下:预变性,95 ℃进行反应 30 s;PCR 扩增反应,95 ℃进行反应 5 s;退火反应,60 ℃进行反应 34 s,共计 45 个循环。以β-actin基因作为内参,采用2-ΔΔCt方法来计算分析碱性磷酸酶、Runx-2、骨桥蛋白和骨钙素基因的相对表达变化,各基因引物序列见表2。
1.5 主要观察指标 磷酸三钙陶瓷、Bio-Oss骨粉对牙周膜干细胞增殖及成骨分化的影响。
1.6 统计学分析 所有数据以x±s表示。采用SPSS 16.0软件对所得数据进行统计学分析,结果采用t检验。P < 0.05时差异有显著性意义。该文统计学方法已经由徐州医科大学生物统计学专家审核。