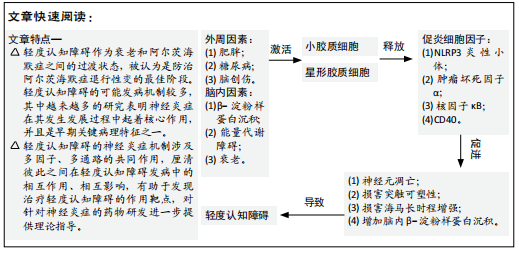
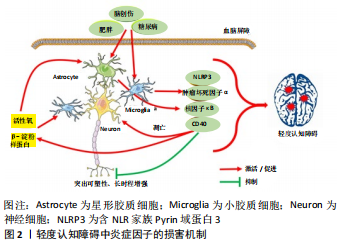
[1] 赵梦琦,廖红.神经炎症与疾病中的认知功能障碍的关系研究进展[J].中国药科大学学报,2019,50(4):497-504.
[2] PETERSEN RC. Mild cognitive impairment as a diagnostic entity. J Intern Med. 2004;256(3):183-194.
[3] CARRO E, BARTOLOME F, BERMEJO-PAREJA F, et al. Early diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease based on salivary lactoferrin. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2017;8:131-138.
[4] PETERSEN R. How early can we diagnose Alzheimer disease (and is it sufficient)?The 2017 Wartenberg lecture. Neurology. 2018;91(9): 395-402.
[5] YANG QQ, ZhOU JW. Neuroinflammation in the central nervous system: Symphony of glial cells. Glia. 2019;67(6):1017-1035.
[6] FAN Z, BROOKS DJ, OKELLO A, et al. An early and late peak in microglial activation in Alzheimer’s disease trajectory. Brain. 2017;140(3):792-803.
[7] SIUDA J, PATALONG-OGIEWA M, ŻMUDA W, et al. Cognitive impairment and BDNF serum levels. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2017;51(1):24-32.
[8] SHEN XN, NIU LD, WANG YJ, et al. Inflammatory markers in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment: a meta-analysis and systematic review of 170 studies. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2019;90(5):590-598.
[9] MAGAKI S, MUELLER C, DICKSON C, et al. Increased production of inflammatory cytokines in mild cognitive impairment. Experimental Gerontology. 2007;42(3):233-240.
[10] TUPPO EE, ARIAS HR. The role of infammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005;37(2):289-305.
[11] PILLAI JA, MAXWELL S, BENA J, et al. Key inflammatory pathway activations in the MCI stage of Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2019;6(7):1248-1262.
[12] HENEKA MT, CARSON MJ, EL KHOURY J, et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14(4):388-405.
[13] PUGAZHENTHI S, QIN L, REDDY PH. Common neurodegenerative pathways in obesity, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017;1863(5):1037-1045.
[14] SIVANANDAM TM, THAKUR MK. Traumatic brain injury: a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2012;36(5):1376-1381.
[15] HUNTER R, OJHA U, BHURTEL S, et al. Lipopolysaccharide-induced functional and structural injury of the mitochondria in the nigrostriatal pathway. Neurosci Res. 2017;114:62-69.
[16] GARABADU D, AGRAWAL N, SHARMA A, et al. Mitochondrial metabolism: a common link between neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Behav Pharmacol. 2019;30(8):642-652.
[17] PERRY VH, TEELING J. Microglia and macrophages of the central nervous system: the contribution of microglia priming and systemic inflammation to chronic neurodegeneration. Semin Immunopathol. 2013;35(5):601-612.
[18] ROSENBERG PB. Clinical aspects of inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2005;17(6):503-514.
[19] 刘娜,郑玉敏,罗晓光,等.转位蛋白与神经系统变性疾病[J].中华神经科杂志,2016,49(11):887-891.
[20] LAVISSE S, GUILLERMIER M, HÉRARD AS, et al. Reactive astrocytes overexpress TSPO and are detected by TSPO positron emission tomography imaging. J Neurosci. 2012;32(32):10809-10818.
[21] SARLUS H, HENEKA M. Microglia in Alzheimer’s disease. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(9):3240-3249.
[22] YE X, ZHOU WJ, ZHANG J. Association of CSF CD40 levels and synaptic degeneration across the Alzheimer’s disease spectrum. Neurosci Lett. 2019;694:41-45.
[23] SUBRAMANIYAN S, TERRANDO N. Neuroinflammation and Perioperative Neurocognitive Disorders. Anesth Analg. 2019;128(4):781-788.
[24] SUBHRAMANYAM CS, WANG C, HU Q, et al. Microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019;94:112-120.
[25] HICKMAN S, IZZY S, SEN P, et al. Microglia in neurodegeneration. Nat Neurosci. 2018;21(10):1359-1369.
[26] 邓佳丽.小胶质细胞活化抑制与中枢炎症反应关系的研究进展[J].临床与病理杂志,2020,40(5):1286-1290.
[27] SHABAB T, KHANABDALI R, MOGHADAMTOUSI SZ, et al. Neuroinflammation pathways: a general review. Int J Neurosci. 2017; 127(7):624-633
[28] SCHUITEMAKER A, VAN DER DOEF TF, BOELLAARD R, et al. Microglial activation in healthy aging. Neurobiol Aging. 2012;33(6):1067-1072.
[29] YIN Z, RAJ D, SAIEPOUR N, et al. Immune hyperreactivity of Aβ plaque-associated microglia in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2017;55:115-122.
[30] ARRANZ AM, DE STROOPER B. The role of astroglia in Alzheimer’s disease: pathophysiology and clinical implications. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(4):406-414.
[31] KAUR D, SHARMA V, DESHMUKH R. Activation of microglia and astrocytes: a roadway to neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Inflammopharmacology. 2019;27(4):663-677.
[32] MCGEER EG, MCGEER PL. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment: a field in its infancy. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;19(1):355-361.
[33] GONZÁLEZ-REYES RE, NAVA-MESA MO, VARGAS-SÁNCHEZ K, et al. Involvement of astrocytes in Alzheimer’s disease from a neuroinflammatory and oxidative stress perspective. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017;10:427.
[34] LIN L, ZHENG LJ, ZHANG LJ. Neuroinflammation,Gut Microbiome,and Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55(11):8243-8250.
[35] FURMAN JL, SAMA DM, GANT JC, et al. Targeting astrocytes ameliorates neurologic changes in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci. 2012;32(46):16129-16140.
[36] AGGARWAL BB. Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3(9):745-756.
[37] MCCOY MK, TANSEY MG. TNF signaling inhibition in the CNS: implications for normal brain function and neurodegenerative disease. J Neuroinflammation. 2008;5:45.
[38] STELLWAGEN D, BEATTIE EC, SEO JY, et al. Differential regulation of AMPA receptor and GABA receptor trafficking by tumor necrosis factor-alpha . J Neurosci. 2005;25(12):3219-3228.
[39] SANTOS SD, CARVALHO AL, CALDEIRA MV, et al. Regulation of AMPA receptors and synaptic plasticity. Neuroscience. 2009;158(1):105-125.
[40] RIAZI K, GALIC MA, KENTNER AC, et al. Microglia-dependent alteration of glutamatergic synaptic transmission and plasticity in the hippocampus during peripheral inflammation. J Neurosci. 2015;35(12): 4942-4952.
[41] SAFAVYNIA SA, GOLDSTEIN PA. The Role of Neuroinflammation in Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction:Moving From Hypothesis to Treatment. Front Psychiatry. 2019;9:752.
[42] CHOWDHURY S, SHEPHERD JD, OKUNO H, et al. Arc/Arg3.1 interacts with the endocytic machinery to regulate AMPA receptor trafficking. Neuron. 2006;52(3):445-459.
[43] LIU Y, ZHOU LJ, WANG J, et al. TNF-α Differentially Regulates Synaptic Plasticity in the Hippocampus and Spinal Cord by Microglia-Dependent Mechanisms after Peripheral Nerve Injury. J Neurosci. 2017;37(4): 871-881.
[44] SAXENA S, MAZE M. Impact on the brain of the inflammatory response to surgery. Presse Med. 2018;47(4 Pt 2):e73-e81.
[45] KANNEGANTI TD, LAMKANFI M, NUNEZ G. Intracellular NODlike receptors in host defense and disease. Immunity. 2007;27(4):549-559.
[46] HALLE A, HORNUNG V, PETZOLD GC, et al. The NALP3 inflammasome is involved in the innate immune response to amyloid-beta. Nat Immunol. 2008;9(8):857-865.
[47] LUČIŪNAITĖ A, MCMANUS RM, JANKUNEC M, et al. Soluble Aβ oligomers and protofibrils induce NLRP3 inflammasome activation in microglia. J Neurochem. 2020;155(6):650-661.
[48] HENEKA MT, KUMMER MP, STUTZ A, et al. NLRP3 is activated in Alzheimer’s disease and contributes to pathology in APP/PS1 mice. Nature. 2013;493(7434):674-678.
[49] LAMKANFI M. Emerging inflammasome effector mechanisms. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11(3):213-220.
[50] HENEKA MT, KUMMER MP, STUTZ A, et al. NLRP3 is activated in Alzheimer’s disease and contributes to pathology in APP/PS1 mice. Nature. 2013;493(7434):674-678.
[51] MITCHELL JP, CARMODY RJ. NF-κB and the Transcriptional Control of Inflammation. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2018;335:41-84.
[52] SRINIVASAN M, LAHIRI DK. Significance of NF-κB as a pivotal therapeutic target in the neurodegenerative pathologies of Alzheimer’s disease and multiple sclerosis. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2015;19(4):471-487.
[53] ZHANG Q, LENARDO MJ, BALTIMORE D. 30 Years of NF-κB: A Blossoming of Relevance to Human Pathobiology. Cell. 2017;168(1-2): 37-57.
[54] LI H, YOON JH, WON HJ, et al. Isotrifoliol inhibits pro-inflammatory mediators by suppression of TLR/NF-κB and TLR/MAPK signaling in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;45:110-119.
[55] SEO EJ, FISCHER N, EFFERTH T. Phytochemicals as inhibitors of NF-κB for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacol Res. 2018;129: 262-273.
[56] SAMIDURAI M, RAMASAMY VS, JO J. β-amyloid inhibits hippocampal LTP through TNFR/IKK/NF-κB pathway. Neurol Res. 2018;40(4):268-276.
[57] ZHAO Y, DENG H, LI K, et al. Trans-cinnamaldehyde improves neuroinflammation-mediated NMDA receptor dysfunction and memory deficits through blocking NF-κB pathway in presenilin1/2 conditional double knockout mice. Brain Behav Immun. 2019;82:45-62.
[58] CHAKRABARTI S, RIZVI M, PATHAK D, et al. Hypoxia influences CD40-CD40L mediated inflammation in endothelial and monocytic cells. Immunol Lett. 2009;122(2):170-184.
[59] YE X, ZHOU W, ZHANG J. For Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Association of CSF CD40 levels and synaptic degeneration across the Alzheimer’s disease spectrum. Neurosci Lett. 2019;694: 41-45.
[60] MICHELS M, DANIESLKI LG, VIEIRA A, et al. CD40-CD40 Ligand Pathway is a Major Component of Acute Neuroinflammation and Contributes to Long-term Cognitive Dysfunction after Sepsis. Mol Med. 2015;21(1):219-226.
[61] GIUNTA B, REZAI-ZADEH K, TAN J. Impact of the CD40-CD40L dyad in Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2010;9(2): 149-155.
(责任编辑:GD,ZN,TXY)
|