中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (29): 4728-4734.doi: 10.12307/2021.176
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
缺氧诱导因子1α与瘢痕疙瘩肿瘤特性及其放疗抵抗
黄晶晶1,蒋 英2,于静萍3
- 1大连医科大学,辽宁省大连市 116044; 南京医科大学附属常州第二人民医院,2皮肤科,3放疗科,江苏省常州市 213003
-
收稿日期:2020-11-09修回日期:2020-11-17接受日期:2021-01-07出版日期:2021-10-18发布日期:2021-07-22 -
通讯作者:于静萍,南京医科大学附属常州第二人民医院放疗科,江苏省常州市 213003 -
作者简介:黄晶晶,女,1993年生,湖南省石门县人,土家族,大连医科大学在读硕士,医师,主要从事皮肤肿瘤研究。 -
基金资助:江苏省“333 工程”第二层次人才科研资助项目 (BRA2019025),项目负责人:于静萍;常州市高层次卫生人才项目 (2016C2BJ007),项目负责人:于静萍
Research progress of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha in tumor-like characteristics of keloid and its radioresistance
Huang Jingjing1, Jiang Ying2, Yu Jingping3
- 1Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116044, Liaoning Province, China; 2Department of Dermatology, 3Department of Radiotherapy, Changzhou Second People’s Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Changzhou 213003, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2020-11-09Revised:2020-11-17Accepted:2021-01-07Online:2021-10-18Published:2021-07-22 -
Contact:Huang Jingjing, Master candidate, Physician, Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116044, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Huang Jingjing, Master candidate, Physician, Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116044, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:Jiangsu Provincial "333 Project" Second Level Talent Research Funding Project, No. BRA2019025 (to YJP); Changzhou Municipal High-level Health Talent Project, No. 2016C2BJ007 (to YJP)
摘要:
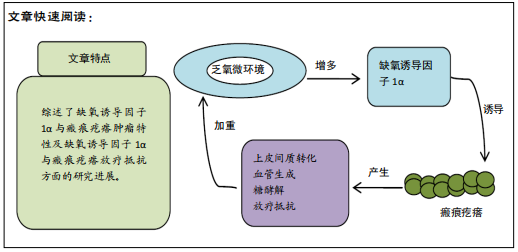
文题释义:
缺氧诱导因子1(hypoxia inducible factor-1,HIF-1):是乏氧微环境下介导缺氧应激反应和调节乏氧细胞生物学行为的核心因子[6],它由调节性亚基HIF-1α和结构性亚基HIF-1β组成,HIF-1α决定乏氧诱导因子1的活性,是乏氧反应的全局调控因子,受氧浓度的严格调控。
背景:瘢痕疙瘩是一种创伤后成纤维细胞大量增殖和胶原过度沉积的良性皮肤肿瘤。瘢痕疙瘩组织内血管闭塞、炎症和成纤维细胞的增殖及胶原分泌等高代谢行为均导致组织乏氧,组织乏氧在瘢痕疙瘩的发病和预后中起重要作用。
目的:就缺氧诱导因子1α在瘢痕疙瘩肿瘤特性中的研究进展作一综述。
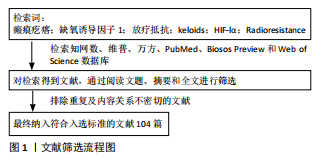
方法:检索知网数据库(CNKI)、维普数据库及万方数据平台,PubMed数据库、Biosos Preview数据库及Web of Science数据库从建库至2020年11月的相关文献,中英文检索词分别为“瘢痕疙瘩;缺氧诱导因子1;放疗抵抗”“keloids;HIF-lα;Radioresistance”。经过阅读文题、摘要和全文的逐步筛选,最终纳入104篇符合入选标准的文献。
结果与结论:乏氧微环境抑制缺氧诱导因子1α的降解,增多的缺氧诱导因子1α可诱导瘢痕疙瘩产生上皮间质转化、血管生成、糖酵解、放疗抵抗等类似于恶性肿瘤的生物学行为,而这些病理生理过程又加重组织乏氧,使得缺氧诱导因子1α呈指数增加,形成恶性循环。目前,瘢痕疙瘩的治疗仍以手术切除联合放疗为主。以缺氧诱导因子1α为靶点的治疗,如高压氧治疗治疗,可以显著改善瘢痕疙瘩组织的乏氧环境,促进伤口的愈合,逆转瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞的肿瘤特性,但目前关于高压氧治疗辅助手术联合放疗治疗瘢痕疙瘩的研究并不多,靶向瘢痕疙瘩缺氧诱导因子1α的临床治疗仍在探索中。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1798-4291 (黄晶晶)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
黄晶晶, 蒋 英, 于静萍. 缺氧诱导因子1α与瘢痕疙瘩肿瘤特性及其放疗抵抗[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(29): 4728-4734.
Huang Jingjing, Jiang Ying, Yu Jingping. Research progress of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha in tumor-like characteristics of keloid and its radioresistance[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(29): 4728-4734.
2.1.1 HIF-1α和瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞的功能 瘢痕疙瘩组织细胞增殖和细胞外基质合成过多导致氧气需求增加,然而组织的氧气供应往往是有限的,氧气的供需不平衡将导致组织乏氧[16]。HIF-1α在瘢痕疙瘩组织细胞增殖和胶原合成中扮演着重要的角色,乏氧时,HIF-1α与细胞核内p300和CREB结合蛋白 (CBP) 结合,激活靶基因胶原蛋白Ⅰ和Ⅲ的表达[17];当用HIF-1α抑制剂CAY10585和布洛芬作用于瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞时,瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞的增殖和胶原蛋白的表达水平显著减少,并且减少的程度与HIF-1α水平呈正相关[18-19]。HIF-1α还可通过与其他因子相互作用影响瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞的功能,如骨膜蛋白、转化生长因子β(transforming growth factor-β,TGF-β)。骨膜蛋白可被HIF-1信号通路诱导上调[20],而在瘢痕疙瘩中大量存在[21],是一种细胞外基质蛋白[22],可参与皮肤修复、纤维化、细胞增殖和细胞外基质重塑[23],骨膜蛋白敲除小鼠显示真皮厚度变薄[24];骨膜蛋白还可通过激活ERK1/2和黏着斑激酶(FAK)途径增加血管内皮生长因子和血管生成素1 的表达、促进瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞上皮间质转化和成纤维细胞的迁移等,通过重组人RNA 抑制骨膜蛋白的表达可降低低氧刺激瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞的增殖、胶原合成、迁移和侵袭[25]。HIF-1α可上调转化生长因子β的表达和激活TGF-β/SMAD信号通路[26-27],转化生长因子β位于19q13.1染色体上,其大部分生物学功能是通过结合转化生长因子β受体激活Smad途径来实现的,转化生长因子β是促进伤口纤维化愈合和细胞外基质沉积的主要细胞因子[28],成纤维细胞表达的转化生长因子β亦可增加HIF-1α的转录活性[29-30]。HIF-1α和多种细胞因子协同作用介导瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞的功能,揭示了瘢痕疙瘩的发病是由复杂的分子网络调控的,当抑制 HIF-1α的表达,瘢痕疙瘩组织细胞的增殖、迁徙和侵入等功能被抑制,从一定程度上说明HIF-1α是瘢痕疙瘩浸润性生长的关键因子[31]。
2.1.2 HIF-1α和上皮间质转化 上皮间质转化是一个上皮细胞丧失细胞极性和细胞间的连接,由成熟的上皮细胞转变为间质细胞、获得间质细胞形态和功能的过程。在这个过程中,上皮细胞标志物E-钙黏蛋白、细胞角蛋白和埃兹蛋白表达下降,成纤维细胞的标志物α-平滑肌动蛋白、弹性蛋白、N-钙黏蛋白表达上升,上皮细胞经过细胞骨架的改变、分子重排等获得迁移和侵袭的能力[32]。上皮间质转化主要参与了器官的纤维化、伤口的愈合以及肿瘤转移的启动等[32]。SUN 等[33]发现 HIF-1α可诱导肾小管上皮细胞发生上皮间质转化,导致肾纤维化。HIF-1α在瘢痕疙瘩角质形成细胞、成纤维细胞的上皮间质转化中发挥重要作用,HIF-1α可诱导瘢痕疙瘩角质形成细胞发生上皮间质转化,使其获得成纤维细胞的生物学特征,细胞间连接明显减少,瘢痕疙瘩组织细胞更易向周围侵袭生长[34],而沉默HIF-1α的表达可逆转瘢痕疙瘩角质形成细胞的上皮间质转化现象[35]。HIF-1α也参与瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞的上皮间质转化,HIF-1α通过TGF-β1/Smad3途径使瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞具有肌成纤维细胞的形态和功能,成纤维细胞向肌成纤维细胞的转化是伤口愈合的关键,肌成纤维细胞主要通过显著增强伤口收缩和细胞外基质合成来促进组织修复。然而,持续增加的肌成纤维细胞可导致瘢痕疙瘩的形成[35]。LEI等[6,30]发现二甲双胍可显著抑制HIF-1α的表达,并通过HIF-1α/PKM2信号通路抑制瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞上皮间质转化[36]。上皮间质转化相关的钙黏蛋白转换是形态改变和其他胚胎发育的主要调节因子[37]。 HIF-1α与上皮间质转化间关系的最新研究进展为认识瘢痕疙瘩生物学特性提供新的视野,为临床防治瘢痕疙瘩浸润性生长治疗手段提供理论基础。
2.1.3 HIF-1α和代谢转变 瘢痕疙瘩是一种纤维增生性皮肤病,具有类似于肿瘤对糖酵解的依赖性 (Warburg效应)。Warburg效应在肿瘤的恶变、细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭方面起重要作用[38-43]。肿瘤产生ATP的方式由氧化磷酸化转变成糖酵解被认为是由HIF-1α激活糖酵解酶导致的[44]。瘢痕疙瘩也存在Warburg效应,瘢痕疙瘩的Warburg效应主要与代谢重编程、糖酵解酶表达上调和线粒体功能障碍有关[45-47], 瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞中己糖激酶、甘油醛-3-磷酸脱氢酶和乳酸脱氢酶等糖酵解酶的活性显著高于正常成纤维细胞,当抑制这些酶的活性时,瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞中ATP的生物合成速率显著降低,表明瘢痕疙瘩产生能量的方式依赖于糖酵解;瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞中活性氧的生成速率较低,这与瘢痕疙瘩的代谢从线粒体氧化磷酸化转变细胞质的无氧糖酵解有关。乳酸是细胞无氧糖酵解的产物,可作为组织乏氧的间接指标。瘢痕疙瘩的乳酸浓度高于正常皮肤或正常瘢痕,在正常瘢痕组织中,随着创伤后时间的延长,乳酸含量逐渐降低,而在瘢痕疙瘩组织中的乳酸含量则长期维持在较高水平[48]。提示瘢痕疙瘩内存在持续的无氧糖酵解作用。瘢痕疙瘩乏氧区成纤维细胞糖酵解标记物的上调是细胞的一种生存机制,乳酸通过代谢偶联被挤压到边缘区的成纤维细胞可能是瘢痕疙瘩侵袭性生长的原因之一[49]。这些研究揭示了由HIF-1α诱导的代谢开关,该开关将葡萄糖代谢物从线粒体转移到细胞质中,以维持ATP的产生并防止有毒活性氧的产生,从而保护细胞免受乏氧诱导的凋亡[50]。
2.1.4 HIF-1α和自噬 自噬的主要作用是清除和降解细胞内受损的细胞结构、衰老的细胞器以及不再需要的生物大分子 (如错误折叠蛋白)等,为细胞的重建、再生和修复提供原料,实现细胞内物质的再循环和再利用,在肿瘤的缺氧区,自噬被激活的现象被认为是肿瘤存活的必需[51]。自噬可以帮助肿瘤细胞对抗HIF-1α和营养因子匮乏等不良的生长环境,从而促进肿瘤的发生发展。瘢痕疙瘩分为乏氧中心区和常氧边缘区,两部位因氧浓度不同而表现出的生理功能有所差异,低氧作为常见的应激因素而导致自噬水平变化[52],相较于瘢痕疙瘩常氧边缘区,HIF-1α高表达的乏氧中心区成纤维细胞自噬水平更高,这可以从高表达的自噬蛋白LC3和泛组织蛋白酶得到印证[49]。随着年龄、氧化等因素的作用,UPP降解蛋白质的功能减弱,组织内异常蛋白增多,导致多种疾病的发生发展[53]。在近期对神经元细胞的研究中发现,当UPP功能受损时,细胞内另一条主要的蛋白质降解的途径——自噬作用的活性将增强[54-55]。人体的老化对应着组织的老化,鲍卫汉等[56]通过病理观察发现,瘢痕疙瘩组织分为中央老化区、增生区和边缘浸润区,每个部位均表现出不同的组织学特征,瘢痕疙瘩中心老化区因乏氧导致UPP受抑制,自噬活性增加[49]。自噬具有双重作用:适度有效的自噬能够清除肿瘤细胞,维持机体稳态;而受损的自噬导致细胞生存能力降低,不能及时清除细胞内错误折叠蛋白,加重细胞内质网应激反应,加快癌症发展进程。自噬的双重作用对研究瘢痕疙瘩的自噬机制有借鉴意义,但目前关于自噬在瘢痕疙瘩的作用存在争议,自噬在瘢痕疙瘩中作用的度也待进一步发现,充分了解瘢痕疙瘩自噬活性状况,在自噬发生的合适阶段和部位给予合适治疗具有潜在的临床实践意义和药物开发意义。
2.1.5 HIF-1α与血管生成 瘢痕疙瘩的血流量和组织氧供并不成正比。随着技术的进步,TIMAR-BANU等[57]用激光多普勒血流计分析发现,瘢痕疙瘩的血流量比正常皮肤多。Liu等[58]用激光扫描技术发现瘢痕疙瘩组织周围邻近皮肤的血流量大于正常皮肤组织的血流量。供血是否充足与组织代谢状态密切相关,不能简单地用血管密度、血流量等指标来评价,尽管瘢痕疙瘩组织中血管密度增加,血流量增加,但瘢痕疙瘩组织仍呈乏氧状态,这是由氧供应不足引起的,氧气供应不足可由血管氧供不足和组织氧耗增加引起。一方面,血管氧供不足跟瘢痕疙瘩组织内血管闭塞、血液中氧向组织弥散受阻有关;血管闭塞可由多种因素引起,内皮细胞大量增殖和功能障碍加剧血管闭塞和组织乏氧[1],再者成纤维细胞过度增殖和细胞外基质大量沉积压迫血管,可导致血管扭曲和狭窄[59]。一项研究表明,病理性瘢痕中的血管口径较大,即使组织中的血流增加,实际上血液供应的氧气并没有到达管周组织[60];而通过血管壁的无效氧气交换仍然可能导致乏氧。另一方面,由于瘢痕疙瘩组织耗氧增加,导致组织供氧相对不足,因此瘢痕疙瘩内部环境仍处于相对乏氧状态[60]。在乏氧状态下,HIF-1α进入细胞核,与乏氧反应元件结合,并调节其下游因子如血管内皮生长因子的转录和表达[61]。血管内皮生长因子是目前已知活性最强的血管生成因子,其在瘢痕疙瘩组织中高表达可促进血管内皮细胞分裂增殖和趋化,进而引起血管异常增生,不成熟的血管渗透性增加,血管周围组织发生水肿,导致瘢痕疙瘩呈现出炎症状态[62-67]。张哲等[68]发现乏氧刺激增加瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞的促血管形成因子血管内皮生长因子、血管生成素1和periostin的合成分泌,其条件培养基显著增加血管内皮细胞的血管形成能力。这些细胞因子之间也存在着协同性,例如,转化生长因子β可以与HIF-1α在转录水平上协同调节血管内皮生长因子基因的表达,HIF-1α也可通过激活 TGF-β/Smad 信号通路诱导和刺激血管内皮生长因子的表达,从而导致异常血管增生,促进瘢痕疙瘩的形成[6]。既往观点认为,正常皮肤创面的愈合需要大量新生毛细血管,以恢复足够的氧供,并提供营养支持,而目前发现,适当减少创面毛细血管的生成,促进毛细血管结构和功能成熟,增加创面有效血流灌注和氧供才可能有效防止瘢痕疙瘩的形成或治疗后复发[69]。经典的靶向血管内皮生长因子或其上游分子HIF-1α的抗血管生成治疗或许会成为瘢痕疙瘩有效的治疗手段[67-70]。
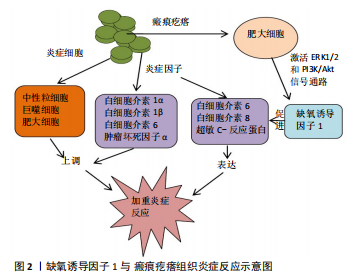
2.1.6 HIF-1α与炎症 有学者认为瘢痕疙瘩是一种网状真皮慢性炎症性疾病,炎症细胞如中性粒细胞、巨噬细胞和肥大细胞和炎症因子如白细胞介素1α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α在瘢痕疙瘩组织中均上调[71]。SIMONART等[72]发现,抑菌剂量的四环素可通过抗炎作用防止痤疮形成瘢痕疙瘩。瘢痕疙瘩组织中浸润的肥大细胞可通过激活ERK1/2和PI3K/Akt信号通路促进HIF-1α的表达[73];而HIF-1α也能促进炎症因子白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8、超敏C-反应蛋白的表达,加重瘢痕疙瘩组织炎症反应的严重程度[74-76](图2)。HIF-1α还可通过TLR途径介导炎症反应,炎症细胞上的TLR被激活后,启动损伤相关分子模式(DAMP),并介导炎症递质转化生长因子β、白细胞介素13、白细胞介素4的释放,从而导致转化生长因子β信号通路的持续激活,组织过度纤维化[77]。雷睿[78]发现HIF-1α可增加TLR-4的表达,并通过TLR-MyD88-NF-?B信号通路增加炎症因子白细胞介素6的表达, 而白细胞介素6是瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞增殖和胶原分泌的关键因子。HIF-1α表达的增加可导致瘢痕疙瘩组织的血管生成、炎症反应、上皮-间质转化等。这些高代谢的生物学行为进一步加剧组织的乏氧,使瘢痕疙瘩不那么像瘢痕,而更像是一种具有恶性肿瘤倾向的慢性炎症性疾病[4]。
2.2 HIF-1α与瘢痕疙瘩的放疗抵抗 瘢痕疙瘩通常被认为是一种良性增生性皮肤肿瘤,它在乏氧微环境中浸润性生长,并表现出与肿瘤相似的特征,包括不受控制的增殖、迁移和侵袭。HIF-1α可诱导瘢痕疙瘩细胞增殖和血管生成,赋予瘢痕疙瘩生长优势和对细胞凋亡的抵抗力,并有助于瘢痕疙瘩对治疗的抵抗。
瘢痕疙瘩的治疗主要包括皮损内糖皮质激素注射、冷冻治疗、手术联合放疗等,大多数学者认为手术联合放疗是瘢痕疙瘩有效的治疗方案之一[79-80]。SHEN等[81]报道用电子线对568例患者的834处瘢痕疙瘩进行放疗,局控率可达88.25%(736/834)。RAGOOWANSI等[82]认为大多数瘢痕疙瘩可以通过手术联合放疗来控制,其1年复发率为9%,5年复发率为16%。电离辐射可以穿透组织,导致多种形式的细胞死亡,包括坏死、凋亡、自噬、衰老和有丝分裂抑制等。电离辐射在诱导细胞死亡的同时也激活了放疗抵抗相关信号通路来逃避或消除危险,以适应细胞外环境。其中,HIF-1α通路是研究最广泛的途径之一[83]。HIF-1α可诱导DNA双链修复酶表达增加,从而修复放疗引起的DNA损伤,使细胞免于放疗诱导的凋亡,使瘢痕疙瘩对放疗产生抵抗[84]。因此,靶向HIF-1α的治疗对提高瘢痕疙瘩的放疗效果至关重要。
2.2.1 2-甲氧基雌二醇(2-methoxyestradiol,2ME2) 2ME2是体内雌二醇生理代谢产物,具有抗肿瘤的作用,可通过抑制细胞增生[85]、抑制微管功能和下调HIF-1α介导的血管生成[86],诱导细胞凋亡等拮抗多种肿瘤的生长[87],包括肺癌、乳腺癌、肝癌、前列腺癌、胃癌等多种肿瘤。2ME2的促细胞凋亡活性是针对活跃增殖的细胞,如肿瘤与活化的内皮细胞,对正常上皮细胞及静止期的内皮细胞无明显促凋亡效应[88]。 2ME2不仅对肿瘤细胞有较好的抗增殖作用,对一些非肿瘤细胞也具有抗增殖的效果,如人皮肤纤维母细胞、内皮细胞等[89]。LONG等[90]发现 2ME2能有效抑制瘢痕疙瘩HIF-1α蛋白的表达,提高瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞对放疗的敏感性,促进瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞的凋亡,为瘢痕疙瘩的无创治疗提供了可能。2ME2也可呈剂量依赖效应的抑制HIF-1α下游重要因子血管内皮生长因子的表达及其活性,从而抑制血管生成。血管内皮生长因子、HIF-1α均是产生放疗抵抗的关键分子,基于 2ME2易获得性,2ME2可能成为瘢痕疙瘩无创治疗的靶向HIF-1α的药物[91]。
2.2.2 槲皮素 槲皮素是一种黄酮类化合物,大量存在于水果和绿色蔬菜中。槲皮素也被确定为药用植物的活性成分,具有多种生物学效应,包括抗氧化、抗炎、抗癌等,在细胞和分子水平上,可诱导凋亡、抑制蛋白激酶C和血管生成等。槲皮素具有显著的抗纤维化作用,可通过阻断TGF-β/Smad[43]、胰岛素样生长因子信号通路,从而抑制成纤维细胞增殖和胶原合成以及细胞挛缩等。槲皮素可呈剂量依赖性的抑制细胞中HIF-1α和血管内皮生长因子的表达,其机制与抑制核内HIF-1α下游细胞感应元件的活化和直接抑制HIF-1α蛋白的合成有关[42]。PI3K/Akt信号通路高度参与HIF-1α诱导的细胞增殖、血管生成、放疗抵抗等,并已被认为是一种致癌途径[92-93]。槲皮素可抑制PI3K/Akt信号通路介导的瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞增殖,并导致细胞周期停滞和凋亡[94]。中国学者SI等[95]发现槲皮素干预可明显降低瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞中HIF-1α的表达,减少细胞的放疗抵抗,促进瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞凋亡,且槲皮素对放疗增敏作用依赖于PI3K/Akt途径的抑制。一方面,槲皮素本身对瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞的功能具有抑制作用;另一方面,槲皮素还可增加瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞的放疗敏感性来增加放疗诱导的凋亡。无论是作为单一药物治疗还是与放射联合用治疗瘢痕疙瘩,槲皮素均可能成为一种安全有效的治疗手段[96]。
2.2.3 高压氧治疗 高压氧治疗是指在高于1个大气压的压力室内呼吸纯氧,是增加组织中氧分压的有效方法,可改善局部血液循环,促进伤口愈合,减轻炎症反应,逆转上皮间质转化等[97-99],被广泛用于治疗难治性伤口和神经系统疾病。高压氧治疗可增加组织氧合[100]、减少HIF-1α、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β及血管内皮生长因子的表达[101]。氧利用率对其组织细胞的生理功能和治疗反应性至关重要,高氧环境通过下调HIF-1α和血管内皮生长因子的表达使乏氧细胞对电离辐射敏感[102]。多项研究显示出高压氧治疗在改善HIF-1α介导的治疗抵抗中的优越性,SONG等[103]用高压氧辅助手术和放疗治疗瘢痕疙瘩,发现高压氧治疗可显著改善瘢痕疙瘩组织的乏氧微环境,提高组织中的氧含量,减少放疗抵抗因子HIF-1α的表达,继而减轻HIF-1α诱导的炎症反应和放疗抵抗,使瘢痕疙瘩复发率由14.15%降至5.97%[38]。郭大志等[104]通过比较术后放疗联合2个疗程高压氧治疗与单纯术后放疗的疗效和安全性,发现两组患者治疗后温哥华瘢痕量表评分较治疗前均降低,但术后放疗联合高压氧组降低更明显;与单纯术后放疗组比,术后放疗联合高压氧组患者总有效率明显提高,12,18个月复发率明显降低。高压氧治疗还可减少HIF-1α、血管内皮生长因子、间质标志物波形蛋白和纤连蛋白的表达,增加上皮标志物E-钙黏蛋白、紧密连接蛋白1的表达,逆转瘢痕疙瘩组织细胞的上皮间质转化的生物学行为,这个作用可能是通过增加瘢痕疙瘩组织含氧量实现的,含氧丰富的环境减少了 HIF-1α和血管内皮生长因子表达,从而减少了瘢痕疙瘩的异常血管形成及炎症反应等[99]。高压氧可通过改善瘢痕组织的低氧环境、提高组织内氧分压和增加局部组织血供等机制促进瘢痕疙瘩愈合,作为术后放疗的辅助治疗,可增加放疗的敏感性、提高疗效,但仍需更多的临床研究来观察高压氧治疗辅助手术联合放疗治疗的有效性及不良反应,为瘢痕疙瘩的高压氧治疗的推广提供更多的循证学证据。
| [1] JUMPER N, PAUS R, BAYAT A. Functional histopathology of keloid disease.Histol Histopathol. 2015;30(9):1033-1057. [2] LEE JY, YANG CC, CHAO SC, et al. Histopathological differential diagnosis of keloid and hypertrophic scar. Am J Dermatopathol. 2004;26(5):379-384. [3] HOU Z, FAN F, LIU P. BTXA regulates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and autophagy of keloid fibroblasts via modulating miR-1587/miR-2392 targeted ZEB2. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(10):BSR20190679 [4] TAN S, KHUMALO N, BAYAT A. Understanding Keloid Pathobiology From a Quasi-Neoplastic Perspective: Less of a Scar and More of a Chronic Inflammatory Disease With Cancer-Like Tendencies. Front Immunol. 2019; 10(1664-3224(Electronic)):1810. [5] 陈亚红, 武晓莉.瘢痕疙瘩浸润性生长机制的研究进展[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2015,11(5):335-338. [6] LEI R, LI J, LIU F, et al. HIF-1alpha promotes the keloid development through the activation of TGF-beta/Smad and TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB pathways.Cell Cycle. 2019;18(23):3239-3250. [7] MEIJER TW, KAANDERS JH, SPAN PN, et al. Targeting hypoxia, HIF-1, and tumor glucose metabolism to improve radiotherapy efficacy. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(20):5585-5594. [8] HAN ZB, REN H, ZHAO H, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 alpha directly enhances the transcriptional activity of stem cell factor (SCF) in response to hypoxia and epidermal growth factor (EGF). Carcinogenesis. 2008;29(10):1853-1861. [9] CONDE E, ALEGRE L, BLANCO-SÁNCHEZ I, et al. Hypoxia inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1 alpha) is induced during reperfusion after renal ischemia and is critical for proximal tubule cell survival. PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33258. [10] MANCINI M, GARIBOLDI MB, TAIANA E, et al. Co-targeting the IGF system and HIF-1 inhibits migration and invasion by (triple-negative) breast cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 2014;110(12):2865-2873. [11] LEE JW, BAE SH, JEONG JW, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1)alpha: its protein stability and biological functions. Exp Mol Med. 2004;36(1):1-12. [12] SEMENZA GL. Defining the role of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in cancer biology and therapeutics. Oncogene. 2010;29(5):625-634. [13] ZHANG Q, TANG X, LU QY, et al. Resveratrol inhibits hypoxia-induced accumulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and VEGF expression in human tongue squamous cell carcinoma and hepatoma cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005;4(10):1465-1474. [14] WULANDARI E, JUSMAN SW, MOENADJAT Y, et al. Expressions of Collagen I and III in Hypoxic Keloid Tissue. Kobe J Med Sci. 2016;62(3):E58-69. [15] REZVANI HR, ALI N, NISSEN LJ, et al. HIF-1α in epidermis: oxygen sensing, cutaneous angiogenesis, cancer, and non-cancer disorders. J Invest Dermatol. 2011;131(9):1793-1805. [16] SEMENZA GL. HIF-1 and mechanisms of hypoxia sensing. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001;13(2):167-171. [17] SINGH S, MANDA SM, SIKDER D, et al. Calcineurin activates cytoglobin transcription in hypoxic myocytes. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(16):10409-10421. [18] KANG Y, ROH MR, RAJADURAI S, et al. Hypoxia and HIF-1α Regulate Collagen Production in Keloids. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140(11):2157-2165. [19] JUSMAN SWA, SARI DH, NINGSIH SS, et al. Role of Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1 Alpha (HIF-1α) in Cytoglobin Expression and Fibroblast Proliferation of Keloids. Kobe J Med Sci. 2019;65(1):E10-E18. [20] ZHANG Z, NIE F, KANG C, et al. Increased periostin expression affects the proliferation, collagen synthesis, migration and invasion of keloid fibroblasts under hypoxic conditions. Int J Mol Med. 2014;34(1):253-261. [21] JACKSON-BOETERS L, WEN W, HAMILTON DW. Periostin localizes to cells in normal skin, but is associated with the extracellular matrix during wound repair. J Cell Commun Signal. 2009;3(2):125-133. [22] HAMILTON DW. Functional role of periostin in development and wound repair: implications for connective tissue disease. J Cell Commun Signal. 2008;2(1-2):9-17. [23] ZHOU HM, WANG J, ELLIOTT C, et al. Spatiotemporal expression of periostin during skin development and incisional wound healing: lessons for human fibrotic scar formation. J Cell Commun Signal. 2010;4(2):99-107. [24] NORRIS RA, DAMON B, MIRONOV V, et al. Periostin regulates collagen fibrillogenesis and the biomechanical properties of connective tissues. J Cell Biochem. 2007;101(3):695-711. [25] RUAN K, BAO S, OUYANG G. The multifaceted role of periostin in tumorigenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009;66(14):2219-2230. [26] MASOUD GN, LI W. HIF-1α pathway: role, regulation and intervention for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015;5(5):3783-3789. [27] LIN X, WANG Y, JIANG Y, et al. Sumoylation enhances the activity of the TGF-β/SMAD and HIF-1 signaling pathways in keloids. Life Sci. 2020;255: 117859. [28] NANGOLE FW, AGAK GW. Keloid pathophysiology: fibroblast or inflammatory disorders?.JPRAS Open. 2019;22(2352-5878 (Print)):44-54. [29] HERR B, ZHOU J, WERNO C, et al. The supernatant of apoptotic cells causes transcriptional activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in macrophages via sphingosine-1-phosphate and transforming growth factor-beta. Blood. 2009;114(10):2140-2148. [30] LEI R, ZHANG S, WANG Y, et al. Metformin Inhibits Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition of Keloid Fibroblasts via the HIF-1α/PKM2 Signaling Pathway. Int J Med Sci. 2019;16(7):960-966. [31] SYED F, BAYAT A. Notch signaling pathway in keloid disease: enhanced fibroblast activity in a Jagged-1 peptide-dependent manner in lesional vs. extralesional fibroblasts. Wound Repair Regen. 2012;20(5):688-706. [32] OMBRATO L, MALANCHI I. The EMT universe: space between cancer cell dissemination and metastasis initiation. Crit Rev Oncog. 2014;19(5):349-361. [33] SUN S, NING X, ZHANG Y, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha induces Twist expression in tubular epithelial cells subjected to hypoxia, leading to epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Kidney Int. 2009;75(12):1278-1287. [34] 马晓阳. 低氧/HIF-1α诱导瘢痕疙瘩角化上皮细胞发生EMT及其对侵袭能力影响的相关研究[D].北京:北京协和医学院;中国医学科学院;清华大学医学部;北京协和医学院中国医学科学院,2015. [35] ZHAO B, GUAN H, LIU JQ, et al. Hypoxia drives the transition of human dermal fibroblasts to a myofibroblast-like phenotype via the TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2017;39(1):153-159. [36] O’CONNELL MP, WEERARATNA AT. Change is in the air: the hypoxic induction of phenotype switching in melanoma. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133(10): 2316-2317. [37] YANG MH, WU KJ. TWIST activation by hypoxia inducible factor-1 (HIF-1): implications in metastasis and development. Cell Cycle. 2008;7(14):2090-2096. [38] LÓPEZ-LÁZARO M. The warburg effect: why and how do cancer cells activate glycolysis in the presence of oxygen?. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2008; 8(3):305-312. [39] JAIN M, NILSSON R, SHARMA S, et al. Metabolite profiling identifies a key role for glycine in rapid cancer cell proliferation. Science. 2012;336(6084): 1040-1044. [40] XIE H, HANAI J, REN JG, et al. Targeting lactate dehydrogenase--a inhibits tumorigenesis and tumor progression in mouse models of lung cancer and impacts tumor-initiating cells. Cell Metab. 2014;19(5):795-809. [41] SCHULZE A, HARRIS AL. How cancer metabolism is tuned for proliferation and vulnerable to disruption. Nature. 2012;491(7424):364-373. [42] PORPORATO PE, PAYEN VL, PÉREZ-ESCUREDO J, et al. A mitochondrial switch promotes tumor metastasis. Cell Rep. 2014;8(3):754-766. [43] VANDER HEIDEN MG, CANTLEY LC, THOMPSON CB. Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science. 2009;324(5930):1029-1033. [44] SEMENZA GL. Regulation of mammalian O2 homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1999;15:551-578. [45] MARI W, ALSABRI SG, TABAL N, et al. Novel Insights on Understanding of Keloid Scar: Article Review. J Am Coll Clin Wound Spec. 2016;7(1-3):1-7. [46] VINCENT AS, PHAN TT, MUKHOPADHYAY A, et al. Human skin keloid fibroblasts display bioenergetics of cancer cells. J Invest Dermatol. 2008; 128(3):702-709. [47] SEMENZA GL, ROTH PH, FANG HM, et al. Transcriptional regulation of genes encoding glycolytic enzymes by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem. 1994;269(38):23757-23763. [48] UEDA K, YASUDA Y, FURUYA E, et al. Inadequate blood supply persists in keloids. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg. 2004;38(5):267-271. [49] OKUNO R, ITO Y, EID N, et al. Upregulation of autophagy and glycolysis markers in keloid hypoxic-zone fibroblasts: Morphological characteristics and implications. Histol Histopathol. 2018;33(10):1075-1087. [50] BIN C, DONGNING Y, ZELIAN Q, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunctions of keloid fibroblasts and it’s effects on cell metabolic functions. Chin J Plast Surg. 2016;32(5):359-364. [51] DEGENHARDT K, MATHEW R, BEAUDOIN B, et al. Autophagy promotes tumor cell survival and restricts necrosis, inflammation, and tumorigenesis.Cancer Cell. 2006;10(1):51-64. [52] COSIN-ROGER J, SIMMEN S, MELHEM H, et al. Hypoxia ameliorates intestinal inflammation through NLRP3/mTOR downregulation and autophagy activation. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):98. [53] WIRTH MG, RUSSELL-EGGITT IM, CRAIG JE, et al. Aetiology of congenital and paediatric cataract in an Australian population. Br J Ophthalmol. 2002; 86(7):782-786. [54] SOLANO RM, CASAREJOS M J, GÓMEZ A, et al.Parkin null cortical neuronal/glial cultures are resistant to amyloid-β1-42 toxicity: a role for autophagy?. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;32(1):57-76. [55] TAYLOR JM, BRODY KM, LOCKHART PJ. Parkin co-regulated gene is involved in aggresome formation and autophagy in response to proteasomal impairment. Exp Cell Res. 2012;318(16):2059-2070. [56] 鲍卫汉,王传民,朱洪荫 .瘢痕疙瘩不同部位组织形态研究[J].中华整形烧伤外科杂志,1995,11(5):368-370. [57] TIMAR-BANU O, BEAUREGARD H, TOUSIGNANT J, et al. Development of noninvasive and quantitative methodologies for the assessment of chronic ulcers and scars in humans. Wound Repair Regen. 2001;9(2):123-132. [58] LIU Q, WANG X, JIA Y, et al. Increased blood flow in keloids and adjacent skin revealed by laser speckle contrast imaging. Lasers Surg Med. 2016;48(4): 360-364. [59] WOLFRAM D, TZANKOV A, PÜLZL P, et al. Hypertrophic scars and keloids--a review of their pathophysiology, risk factors, and therapeutic management.Dermatol Surg. 2009;35(2):171-181. [60] KUROKAWA N, UEDA K, TSUJI M. Study of microvascular structure in keloid and hypertrophic scars: density of microvessels and the efficacy of three-dimensional vascular imaging. J Plast Surg Hand Surg. 2010;44(6):272-277. [61] ZHENG J, SONG F, LU SL, et al. Dynamic hypoxia in scar tissue during human hypertrophic scar progression. Dermatol Surg. 2014;40(5):511-518. [62] NAGY JA, BENJAMIN L, ZENG H, et al. Vascular permeability, vascular hyperpermeability and angiogenesis. Angiogenesis. 2008;11(2):109-119. [63] DVORAK HF, DETMAR M, CLAFFEY KP, et al. Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor: an important mediator of angiogenesis in malignancy and inflammation. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1995;107(1-3): 233-235. [64] STEINBRECH DS, MEHRARA BJ, CHAU D, et al. Hypoxia upregulates VEGF production in keloid fibroblasts. Ann Plast Surg. 1999;42(5):514-519; discussion 519-520. [65] NISSEN NN, POLVERINI PJ, KOCH AE, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor mediates angiogenic activity during the proliferative phase of wound healing. Am J Pathol. 1998;152(6):1445-1452. [66] BROWN L F, YEO K T, BERSE B, et al. Expression of vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) by epidermal keratinocytes during wound healing. J Exp Med. 1992;176(5):1375-1379. [67] DIPIETRO LA. Angiogenesis and wound repair: when enough is enough.J Leukoc Biol. 2016;100(5):979-984. [68] 张哲, 康春福, 陈斌, 等.缺氧状态下瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞条件培养基对血管形成能力的影响[J].中华整形外科杂志,2014,30(4):283-288. [69] 朱君佑, 祁少海.血管生成的调节在瘢痕形成过程中的作用[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2019,14(4):303-306. [70] GIRA AK, BROWN LF, WASHINGTON CV, et al. Keloids demonstrate high-level epidermal expression of vascular endothelial growth factor. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50(6):850-853. [71] OGAWA R. Keloid and Hypertrophic Scars Are the Result of Chronic Inflammation in the Reticular Dermis. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(3):606. [72] SIMONART T, DRAMAIX M, DE MAERTELAER V. Efficacy of tetracyclines in the treatment of acne vulgaris: a review. Br J Dermatol. 2008;158(2):208-216. [73] ZHANG Q, OH CK, MESSADI DV, et al. Hypoxia-induced HIF-1 alpha accumulation is augmented in a co-culture of keloid fibroblasts and human mast cells: involvement of ERK1/2 and PI-3K/Akt. Exp Cell Res. 2006;312(2): 145-155. [74] 叶飞轮.瘢痕疙瘩中HIF-1α的表达及其与血管新生、炎症反应及细胞凋亡的相关性研究[J].海南医学院学报,2017,23(17):2442-2444,2448. [75] 张明子, 王晨羽, 管恩玲, 等.不同类型瘢痕中HIF-1α的表达及其炎性因子的相关性分析[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2017,28(6):324-327. [76] 李丽, 王林.正常皮肤与病理性瘢痕组织中HIF-1α和促炎细胞因子水平比较及两者 相关性研究[J].中国美容医学,2019,28(4):71-73. [77] FICHTNER-FEIGL S, STROBER W, KAWAKAMI K, et al. IL-13 signaling through the IL-13alpha2 receptor is involved in induction of TGF-beta1 production and fibrosis. Nat Med. 2006;12(1):99-106. [78] 雷睿. 缺氧诱导因子-1α及其相关信号通路促进瘢痕疙瘩形成的作用机制研究[D]. 杭州:浙江大学,2017. [79] ARNO A I, GAUGLITZ GG, BARRET JP, et al. Up-to-date approach to manage keloids and hypertrophic scars: a useful guide. Burns. 2014;40(7):1255-1266. [80] SIOTOS C, UZOSIKE AC, HONG H, et al. Keloid Excision and Adjuvant Treatments: A Network Meta-analysis. Ann Plast Surg. 2019;83(2):154-162. [81] SHEN J, LIAN X, SUN Y, et al. Hypofractionated electron-beam radiation therapy for keloids: retrospective study of 568 cases with 834 lesions. J Radiat Res. 2015;56(5):811-817. [82] RAGOOWANSI R, CORNES PG, MOSS AL, et al. Treatment of keloids by surgical excision and immediate postoperative single-fraction radiotherapy.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003;111(6):1853-1859. [83] MANKOWSKI P, KANEVSKY J, TOMLINSON J, et al. Optimizing Radiotherapy for Keloids: A Meta-Analysis Systematic Review Comparing Recurrence Rates Between Different Radiation Modalities. Ann Plast Surg. 2017;78(4):403-411. [84] HARRIS AL. Hypoxia--a key regulatory factor in tumour growth.Nature reviews. Cancer. 2002;2(1):38-47. [85] PRIBLUDA VS, GUBISH ER JR, LAVALLEE TM, et al. 2-Methoxyestradiol: an endogenous antiangiogenic and antiproliferative drug candidate.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2000;19(1-2):173-179. [86] MABJEESH NJ, ESCUIN D, LAVALLEE TM, et al. 2ME2 inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis by disrupting microtubules and dysregulating HIF. Cancer Cell. 2003;3(4):363-375. [87] KUMAR AP, GARCIA GE, SLAGA TJ. 2-methoxyestradiol blocks cell-cycle progression at G(2)/M phase and inhibits growth of human prostate cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 2001;31(3):111-124. [88] FOTSIS T, ZHANG Y, PEPPER MS, et al. The endogenous oestrogen metabolite 2-methoxyoestradiol inhibits angiogenesis and suppresses tumour growth.Nature. 1994;368(6468):237-239. [89] SWEENEY C, LIU G, YIANNOUTSOS C, et al. A phase II multicenter, randomized, double-blind, safety trial assessing the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and efficacy of oral 2-methoxyestradiol capsules in hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(18):6625-6633. [90] LONG F, SI L, LONG X, et al. 2ME2 increase radiation-induced apoptosis of keloid fibroblasts by targeting HIF-1α in vitro. Australas J Dermatol. 2016; 57(2):e32-8. [91] 龙飞. 2-甲氧基雌二醇对瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞放疗凋亡及乏氧诱导因子-1表达影响的研究[D]. 北京:北京协和医学院;中国医学科学院;清华大学医学部;北京协和医学院中国医学科学院,2015. [92] BRAN GM, GOESSLER UR, HORMANN K, et al. Keloids: current concepts of pathogenesis (review). Int J Mol Med. 2009;24(3):283-293. [93] ESFAHANIAN N, SHAKIBA Y, NIKBIN B, et al. Effect of metformin on the proliferation, migration, and MMP-2 and -9 expression of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Mol Med Rep. 2012;5(4):1068-1074. [94] KM D, MK NR. The impact of quercetin on wound healing relates to changes in αV and β1 integrin expression.Experimental biology and medicine (Maywood, N.J.). 2017;242(14):1424-1431. [95] SI LB, ZHANG MZ, HAN Q, et al. Sensitization of keloid fibroblasts by quercetin through the PI3K/Akt pathway is dependent on regulation of HIF-1alpha. Am J Transl Res. 2018;10(12):4223-4234. [96] UNAHABHOKHA T, SUCONTPHUNT A, NIMMANNIT U, et al. Molecular signalings in keloid disease and current therapeutic approaches from natural based compounds. Pharm Biol. 2015;53(3):457-463. [97] DEMIRTAŞ A, AZBOY I, BULUT M, et al. The effect of hyperbaric oxygen therapy on fracture healing in nicotinized rats. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2014;20(3):161-166. [98] ZHANG T, GONG W, LI Z, et al. Efficacy of hyperbaric oxygen on survival of random pattern skin flap in diabetic rats. Undersea Hyperb Med. 2007; 34(5):335-339. [99] ZHANG M, LIU S, GUAN E, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy can ameliorate the EMT phenomenon in keloid tissue. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(29): e11529. [100] FIFE CE, HOPF H. Discussion. Hyperbaric oxygen: its mechanisms and efficacy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;127 Suppl 1:142s-143s. [101] LU Z, MA J, LIU B, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy sensitizes nimustine treatment for glioma in mice. Cancer Med. 2016;5(11):3147-3155. [102] DONG D, FU Y, CHEN F, et al. Hyperoxia sensitizes hypoxic HeLa cells to ionizing radiation by downregulating HIF‑1α and VEGF expression. Mol Med Rep. 2021;23(1):1. [103] SONG KX, LIU S, ZHANG MZ, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy improves the effect of keloid surgery and radiotherapy by reducing the recurrence rate. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2018;19(11):853-862. [104] 郭大志, 史巍, 张敦晓, 等.术后放疗联合高压氧治疗瘢痕疙瘩的疗效和安全性[J].中华医学美学美容杂志,2019,25(3):234-237. (责任编辑:WZH,ZN,SX) |
| [1] | 蒲 锐, 陈子扬, 袁凌燕. 不同细胞来源外泌体保护心脏的特点与效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | 张 超, 吕 欣. 髋臼骨折固定后的异位骨化:危险因素、预防及其治疗进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [3] | 周继辉, 李新志, 周 游, 黄 卫, 陈文瑶. 髌骨骨折修复内植物选择的多重问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [4] | 王德斌, 毕郑刚. 尺骨鹰嘴骨折-脱位解剖力学、损伤特点、固定修复及3D技术应用的相关问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [5] | 姬志祥, 蓝常贡. 尿酸盐转运蛋白在痛风中的多态性和治疗相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1290-1298. |
| [6] | 袁 美, 张新新, 郭祎莎, 毕 霞. 循环microRNA在血管性认知障碍诊断中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [7] | 侯婧瑛, 于萌蕾, 郭天柱, 龙会宝, 吴 浩. 缺氧预处理激活HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞生存和血管再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [8] | 汪显耀, 关亚琳, 刘忠山. 提高间充质干细胞治疗难愈性创面的策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [9] | 万 然, 史 旭, 刘京松, 王岩松. 间充质干细胞分泌组治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [10] | 廖成成, 安家兴, 谭张雪, 王 倩, 刘建国. 口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的治疗靶点及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [11] | 赵 敏, 冯柳祥, 陈 垚, 顾 霞, 王平义, 李一梅, 李文华. 低氧环境下外泌体可作为疾病的标志物[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [12] | 谢文佳, 夏天娇, 周卿云, 刘羽佳, 顾小萍. 小胶质细胞介导神经元损伤在神经退行性疾病中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [13] | 李珊珊, 郭笑霄, 尤 冉, 杨秀芬, 赵 露, 陈 曦, 王艳玲. 感光细胞替代治疗视网膜变性疾病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [14] | 焦 慧, 张一宁, 宋雨晴, 林 宇, 王秀丽. 乳腺癌类器官研究进展及临床应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [15] | 王诗琦, 张金生. 中医药调控缺血缺氧微环境对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖、分化及衰老的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
瘢痕疙瘩呈向周围浸润性生长的模式,生长过程中逐渐向周围正常皮肤蔓延,并将其转变为瘢痕疙瘩的病灶组织[5]。瘢痕疙瘩具有浸润性生长的肿瘤特性,这与其微环境介导的细胞增殖、转移、代谢有关,瘢痕疙瘩被认为有类似于肿瘤的乏氧微环境。缺氧诱导因子1(hypoxia inducible factor-1,HIF-1)是乏氧微环境下介导缺氧应激反应和调节乏氧细胞生物学行为的核心因子[6],它由调节性亚基HIF-1α和结构性亚基HIF-1β组成,HIF-1α决定乏氧诱导因子1的活性,是乏氧反应的全局调控因子,受氧浓度的严格调控,其在常氧条件下极不稳定,可通过泛素蛋白酶途径(ubiquitin-proteasome pathway,UPP)快速降解[7]。乏氧时,HIF-1α的UPP被抑制,导致组织中HIF-1α呈指数增加[8],HIF-1α的积累促进其与HIF-1β的结合,形成活性二聚体,这些二聚体被认为是涉及血管生成、细胞增殖、转移、代谢等100多个基因的转录因子[9-10],引起细胞对乏氧的适应性反应[11]。乏氧微环境在肿瘤发生发展过程中发挥着重要作用,包括头颈肿瘤在内的多种肿瘤细胞在乏氧环境下会产生一系列病理生理改变,如能量代谢转变、血管生成、细胞增殖、分化和侵袭转移等[12];HIF-1α也是评估预后、死亡风险或治疗效果的潜在标志物[13]。与肿瘤类似,瘢痕疙瘩也存在乏氧微环境,瘢痕疙瘩的乏氧微环境是由大量异常闭塞的血管造成的,此外,组织损伤引起的炎症或修复过程中的高代谢状态也会增加氧耗,加重组织缺氧[14]。REZVANI等[15]从组织学水平证实,HIF-1α在瘢痕疙瘩中高表达,而在正常皮肤没有发现HIF-1α的存在,高表达的HIF-1α使瘢痕疙瘩组织细胞具有肿瘤细胞相关表型。文章就HIF-1α在瘢痕疙瘩肿瘤特性中的研究进展作一综述。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
1.2 文献筛选标准
纳入标准:①HIF-1α与瘢痕疙瘩肿瘤特性相关的研究;②HIF-1α与瘢痕疙瘩放疗抵抗的相关研究。
排除标准:①重复及年代久远的文献;②与文章探讨内容关系不密切的文献。
1.3 质量评估 对上述关键词分别检索和组合检索得到的文献,通过阅读文题、摘要进行初筛,经过对全文的泛读或精读再次筛选,最终纳入的104篇文献均符合入选标准。文献筛选流程图见图1。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程

文题释义:#br# 缺氧诱导因子1(hypoxia inducible factor-1,HIF-1):是乏氧微环境下介导缺氧应激反应和调节乏氧细胞生物学行为的核心因子[6],它由调节性亚基HIF-1α和结构性亚基HIF-1β组成,HIF-1α决定乏氧诱导因子1的活性,是乏氧反应的全局调控因子,受氧浓度的严格调控。
#br#
瘢痕疙瘩是继发于皮肤外伤或自发形成表现过度生长的病理性瘢痕组织,瘢痕高出皮肤表面,质硬韧,呈结节状、条索状或片状,临床上表现为过度生长,侵犯临近组织,并且患者发病后呈瘤样增生,导致机体功能障碍,影响患者健康。缺氧诱导因子1α和多种细胞因子协同作用介导瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞的功能,揭示了瘢痕疙瘩的发病是由复杂的分子网络调控的,当抑制 缺氧诱导因子1α的表达,瘢痕疙瘩组织细胞的增殖、迁徙和侵入等功能被抑制,从一定程度上说明缺氧诱导因子1α是瘢痕疙瘩浸润性生长的关键因子。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||