| [1]姜永明,李炯明,徐鸿毅,等.输尿管长段撕脱伤的处理[J].中华泌尿外科杂志,2008,29(6):408-410.
[2]Neo EN, Zulkifli Z, Sritharan S, et al. Renal autotransplantation after an latrogenic left ureteric injury. Med J Malaysia. 2007;62(2):164-165.
[3]Gowda BD, Goldsmith P, Ahmad N. Boari flap vesicocalycostomy: a salvage drainage procedure for complete ureteric stricture and pyelocalyceal fistula. Clin Transplant. 2009;23(1):129-131.
[4]Lazica DA, Ubrig B, Brandt AS, et al. Ureteral substitution with reconfigured colon: long-term followup. J Urol. 2012;187(2): 542-548.
[5]Roth CC, Mondalek FG, Kibar Y, et al. Bladder regeneration in a canine model using hyaluronic acid-poly (lactic-co-glycolic-acid) nanoparticle modified porcine small intestinal submucosa. BJU Int. 2011;108(1):148-155.
[6]王德娟,李茂胤,潘文威,等.兔脂肪间充质干细胞结合聚乳酸纤维膜修复尿道缺损[J].中华实验外科杂志,2014,31(6):1217- 1219, 封3.
[7]谢敏凯,宋鲁杰,汪继洪,等.静电纺丝素蛋白材料复合尿路上皮细胞修复尿道的实验研究[J].中华泌尿外科杂志,2014,35(8): 629-634.
[8]张亚,周云,贾立山,等.多孔丝素复合脂肪间充质干细胞支架修复兔尿道缺损能促进血管的形成[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(47):8777-8781.
[9]Corcos J, Loutochin O, Campeau L, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cell therapy for external urethral sphincter restoration in a rat model of stress urinary incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn. 2011;30(3):447-455.
[10]Orabi H, AbouShwareb T, Zhang Y, et al. Cell-seeded tubularized scaffolds for reconstruction of long urethral defects: a preclinical study. Eur Urol. 2013;63(3):531-538.
[11]廖文彪,宋超,杨嗣星,等. 组织工程复合物进行兔尿流改道[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2013,17(2):196-200.
[12]Shalhav AL, Elbahnasy AM, Bercowsky E, et al. Laparoscopic replacement of urinary tract segments using biodegradable materials in a large-animal model. J Endourol. 1999;13(4): 241-244.
[13]Alescio T, Di Michele M. Relationship of epithelial growth to mitotic rate in mouse embryonic lung developing in vitro. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1968;19(2):227-237.
[14]Harris RG, Herzog EL, Bruscia EM, et al. Lack of a fusion requirement for development of bone marrow-derived epithelia. Science. 2004;305(5680):90-93.
[15]Anumanthan G, Makari JH, Honea L, et al. Directed differentiation of bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells into bladder urothelium. J Urol. 2008;180(4 Suppl): 1778-1783.
[16]Tian H, Bharadwaj S, Liu Y, et al. Differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into bladder cells: potential for urological tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(5):1769-1779.
[17]熊云鹤,杨嗣星,孟令超,等.兔骨髓间充质干细胞向尿路上皮分化后构建膀胱组织工程化移植物[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(32):5097-5102.
[18]Pariente JL, Kim BS, Atala A. In vitro biocompatibility assessment of naturally derived and synthetic biomaterials using normal human urothelial cells. J Biomed Mater Res. 2001;55(1):33-39.
[19]Pariente JL, Kim BS, Atala A. In vitro biocompatibility evaluation of naturally derived and synthetic biomaterials using normal human bladder smooth muscle cells. J Urol. 2002;167(4):1867-1871.
[20]Mauney JR, Cannon GM, Lovett ML, et al. Evaluation of gel spun silk-based biomaterials in a murine model of bladder augmentation. Biomaterials. 2011;32(3):808-818.
[21]Eberli D, Freitas Filho L, Atala A, et al. Composite scaffolds for the engineering of hollow organs and tissues. Methods. 2009;47(2):109-115.
[22]Lawrence BJ, Maase EL, Lin HK, et al. Multilayer composite scaffolds with mechanical properties similar to small intestinal submucosa. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2009;88(3):634-643.
[23]Chun SY, Lim GJ, Kwon TG, et al. Identification and characterization of bioactive factors in bladder submucosa matrix. Biomaterials. 2007;28(29):4251-4256.
[24]Farhat WA, Chen J, Haig J, et al. Porcine bladder acellular matrix (ACM): protein expression, mechanical properties. Biomed Mater. 2008;3(2):025015.
[25]Rosario DJ, Reilly GC, Ali Salah E, et al. Decellularization and sterilization of porcine urinary bladder matrix for tissue engineering in the lower urinary tract. Regen Med. 2008; 3(2):145-156.
[26]Davis NF, Callanan A, McGuire BB, et al. Evaluation of viability and proliferative activity of human urothelial cells cultured onto xenogenic tissue-engineered extracellular matrices. Urology. 2011;77(4):1007.e1-7. |
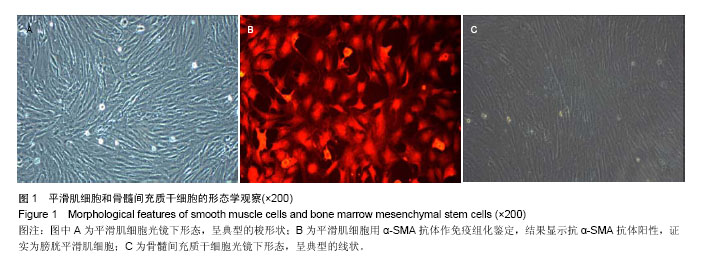
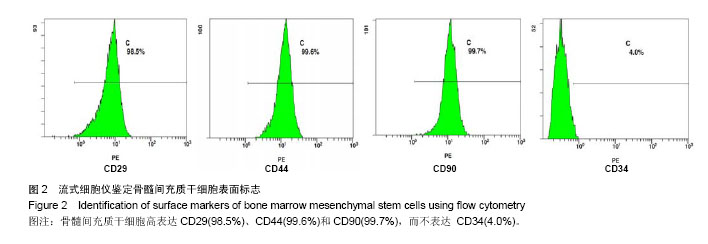
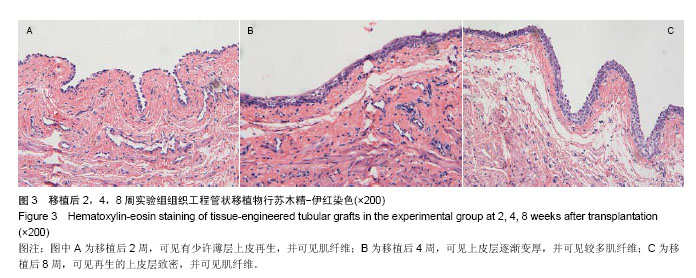
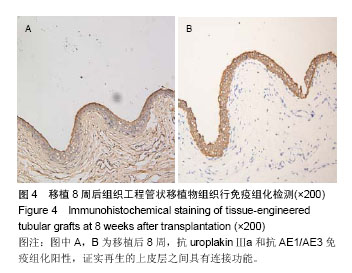
.jpg)