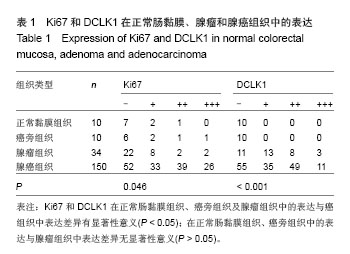
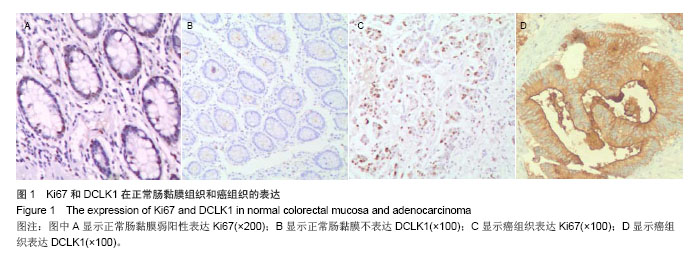
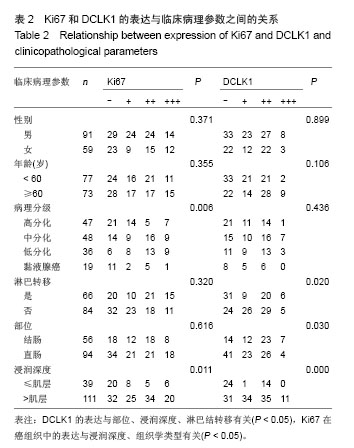
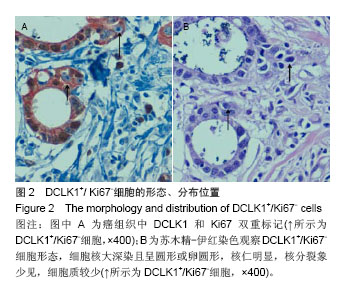
| [1]Lin PT, Gleeson JG, Corbo JC,et al.DCAMKL1 encodes a protein kinase with homology to doublecortin that regulates microtubule polymerization.J Neurosci. 2000;20(24): 9152-9161.
[2]Nakanishi Y, Seno H, Fukuoka A, et al. Dclk1 distinguishes between tumor and normal stem cells in the intestine. Nat Genet. 2013;45(1):98-103.
[3]张登才,刘斌,张丽华,等.一种简便实用的组织芯片制作方法[J]. 诊断病理学杂志,2013,20(11):722-724.
[4]Bonnet D, Dick JE. Human acute myeloid leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat Med. 1997;3(7):730-737.
[5]He S, Nakada D, Morrison SJ. Mechanisms of stem cell self-renewal. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2009;25:377-406.
[6]Simons BD, Clevers H. Strategies for homeostatic stem cell self-renewal in adult tissues. Cell. 2011;145(6):851-862.
[7]Lyashenko N, Winter M, Migliorini D, et al. Differential requirement for the dual functions of β-catenin in embryonic stem cell self-renewal and germ layer formation. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13(7):753-761.
[8]Clement V, Sanchez P, de Tribolet N, et al. HEDGEHOG-GLI1 signaling regulates human glioma growth, cancer stem cell self-renewal, and tumorigenicity. Curr Biol. 2007;17(2): 165-172.
[9]Rosen JM, Jordan CT. The increasing complexity of the cancer stem cell paradigm. Science. 2009;324(5935): 1670-1673.
[10]Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144(5):646-674.
[11]Merlos-Suárez A, Barriga FM, Jung P, et al. The intestinal stem cell signature identifies colorectal cancer stem cells and predicts disease relapse. Cell Stem Cell. 2011;8(5):511-524.
[12]Du L, Wang H, He L, et al. CD44 is of functional importance for colorectal cancer stem cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(21): 6751-6760.
[13]Barker N, van Es JH, Kuipers J, et al. Identification of stem cells in small intestine and colon by marker gene Lgr5. Nature. 2007;449(7165):1003-1007.
[14]Todaro M, Perez Alea M, Scopelliti A, et al. IL-4-mediated drug resistance in colon cancer stem cells. Cell Cycle. 2008; 7(3):309-313.
[15]Polley MY, Leung SC, McShane LM, et al. An international Ki67 reproducibility study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013;105(24): 1897-1906.
[16]Nielsen T, Polley M, Leung S, et al. An international Ki67 reproducibility study. Cancer Res. 2012;72(24 suppl):S4-6.
[17]韩军平,刘斌,杨艳丽,等.结直肠癌CD44+/ki-67-癌干细胞特征及其与临床病理关系[J].世界华人消化杂志,2011,19(34): 3483-3488.
[18]Gagliardi G, Bellows CF. DCLK1 expression in gastrointestinal stem cells and neoplasia. Journal of Cancer Therapeutics and Research. 2012;1:12.
[19]Sureban SM, May R, Lightfoot SA, et al. DCAMKL-1 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human pancreatic cells through a miR-200a-dependent mechanism. Cancer Res. 2011; 71(6):2328-2338.
[20]Sureban SM, May R, Ramalingam S, et al. Selective blockade of DCAMKL-1 results in tumor growth arrest by a Let-7a MicroRNA-dependent mechanism. Gastroenterology. 2009; 137(2):649-659.
[21]Sureban SM, May R, Mondalek FG, et al. Nanoparticle-based delivery of siDCAMKL-1 increases microRNA-144 and inhibits colorectal cancer tumor growth via a Notch-1 dependent mechanism. J Nanobiotechnology. 2011;9:40.
[22]Ali N, Allam H, May R, et al. Hepatitis C virus-induced cancer stem cell-like signatures in cell culture and murine tumor xenografts. J Virol. 2011;85(23):12292-1303.
[23]Tirino V, Desiderio V, Paino F, et al. Cancer stem cells in solid tumors: an overview and new approaches for their isolation and characterization. FASEB J. 2013;27(1):13-24.
[24]Dean M, Fojo T, Bates S. Tumour stem cells and drug resistance. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5(4):275-284.
[25]Vermeulen L, de Sousa e Melo F, Richel DJ, et al. The developing cancer stem-cell model: clinical challenges and opportunities. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13(2):e83-89. |