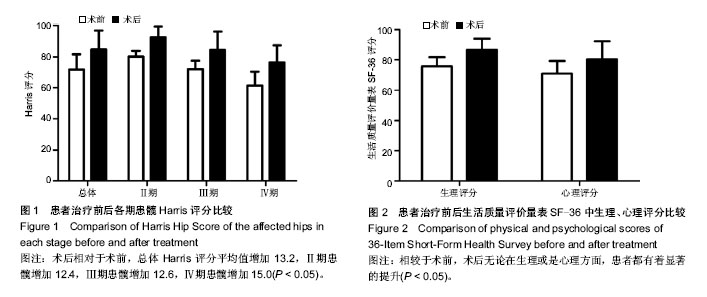
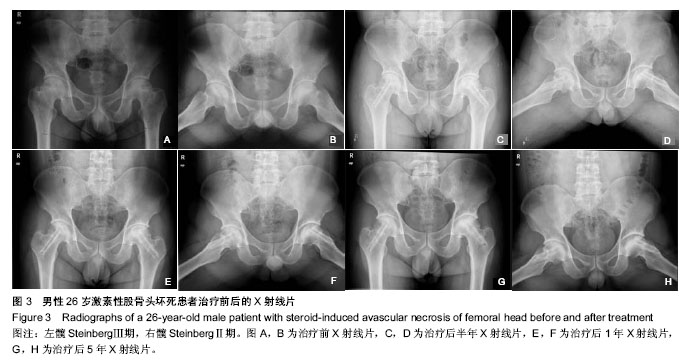
| [1] Babis GC, Sakellariou V, Parvizi J, et al. Osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Orthopedics. 2011;34(1): 39.
[2] Wei BF, Ge XH. Treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head with core decompression and bone grafting. Hip Int. 2011;21(2): 206-210.
[3] Wang XS, Zhuang QY, Weng XS, et al. Etiological and clinical analysis of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in Chinese patients. Chin Med J (Engl). 2013;126(2):290-295.
[4] Weinstein RS. Glucocorticoids, osteocytes, and skeletal fragility: the role of bone vascularity. Bone. 2010;46(3): 564-570.
[5] Griffith JF, Antonio GE, Kumta SM, et al. Osteonecrosis of hip and knee in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome treated with steroids. Radiology. 2005;235(1):168-175.
[6] Marston SB, Gillingham K, Bailey RF, et al. Osteonecrosis of the femoral head after solid organ transplantation: a prospective study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84-A(12): 2145-2151.
[7] 郑志辉,王少伟,李伟居,等.保髋治疗股骨头坏死的特异性量表[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2012,16 (35):6570-6575.
[8] Mont MA, Jones LC, Hungerford DS. Nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head: ten years later. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88(5):1117-1132.
[9] Korompilias AV, Lykissas MG, Beris AE, et al. Vascularised fibular graft in the management of femoral head osteonecrosis: twenty years later. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009;91(3):287-293.
[10] Steinberg ME, Hayken GD, Steinberg DR. A quantitative system for staging avascular necrosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995;77(1): 34-41.
[11] Zhang C, Zeng B, Xu Z, et al. Treatment of femoral head necrosis with free vascularized fibula grafting: a preliminary report. Microsurgery. 2005;25(4):305-309.
[12] Gao YS, Liu XL, Sheng JG, et al. Unilateral free vascularized fibula shared for the treatment of bilateral osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(3):531-536.
[13] Ware JE JR, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care. 1992;30(6):473-483.
[14] Yu J, Coons SJ, Draugalis JR, et al. Equivalence of Chinese and US-English versions of the SF-36 health survey. Qual Life Res. 2003;12(4): 449-457.
[15] Ohzono K, Saito M, Sugano N, et al. The fate of nontraumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head. A radiologic classification to formulate prognosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992;277:73-78.
[16] 毕鑫,李多玉,杨毅,等.不同人工骨材料复合骨髓间充质干细胞治疗早期股骨头坏死:争议与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(12): 1957-1962.
[17] 章乐成,尹宗生.骨髓间充质干细胞及其载体在股骨头坏死治疗中的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(3):440-445.
[18] Scully SP, Aaron RK, Urbaniak JR. Survival analysis of hips treated with core decompression or vascularized fibular grafting because of avascular necrosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998; 80(9):1270-1275.
[19] Dailiana ZH, Toth AP, Gunneson E, et al. Free vascularized fibular grafting following failed core decompression for femoral head osteonecrosis. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22(5): 679-688.
[20] Yoo MC, Chung DW, Hahn CS. Free vascularized fibula grafting for the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992;277:128-138.
[21] Judet H, Gilbert A. Long-term results of free vascularized fibular grafting for femoral head necrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;386:114-119.
[22] Berend KR, Gunneson EE, Urbaniak JR. Free vascularized fibular grafting for the treatment of postcollapse osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003; 85-A(6): 987-993.
[23] Gao YS, Chen SB, Jin DX, et al. Modified surgical techniques of free vascularized fibular grafting for treatment of the osteonecrosis of femoral head: Results from a series of 407 cases. Microsurgery. 2013.
[24] Takano-murakami R, Tokunaga K, Kondo N, et al. Glucocorticoid inhibits bone regeneration after osteonecrosis of the femoral head in aged female rats. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2009; 217(1):51-58.
[25] Zhao FC, Li ZR, Guo KJ. Clinical analysis of osteonecrosis of the femoral head induced by steroids. Orthop Surg.2012;4(1): 28-34.
[26] Li X, Jin L, Cui Q, et al. Steroid effects on osteogenesis through mesenchymal cell gene expression. Osteop Int. 2005; 16(1):101-108.
[27] Miyanishi K, Yamamoto T, Irisa T, et al. Bone marrow fat cell enlargement and a rise in intraosseous pressure in steroid-treated rabbits with osteonecrosis. Bone. 2002;30(1): 185-90.
[28] Tan G, Kang PD, Pei FX. Glucocorticoids affect the metabolism of bone marrow stromal cells and lead to osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a review. Chin Med J (Engl). 2012;125(1):134-139.
[29] Drescher W, Bunger MH, Weigert K, et al. Methylprednisolone enhances contraction of porcine femoral head epiphyseal arteries. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;423:112-117.
[30] Xu J, Zhang CQ, Zhang KG, et al. Modified Free Vascularized Fibular Grafting for the Treatment of Femoral Neck Nonunion. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24(4):230-235.
[31] Li M, Shen Y, Halloran BP, et al. Skeletal response to corticosteroid deficiency and excess in growing male rats. Bone. 1996;19(2):81-88.
[32] Wang Y, Ohtsuka-isoya M, Shao P, et al. Effects of methylprednisolone on bone formation and resorption in rats. Japan J Pharmacol. 2002;90(3):236-246.
[33] Cui Q, Wang GJ, Balian G. Steroid-induced adipogenesis in a pluripotential cell line from bone marrow. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997;79(7):1054-1063.
[34] Kerachian MA, Seguin C, Harvey EJ. Glucocorticoids in osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a new understanding of the mechanisms of action. J Ster Biochem Mol Biol. 2009; 114(3-5):121-128. |