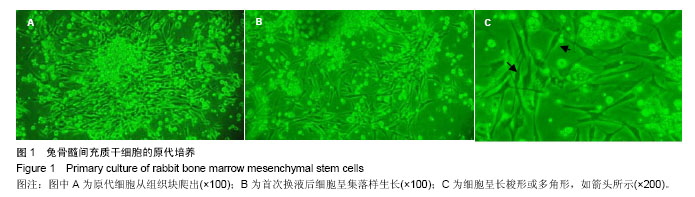
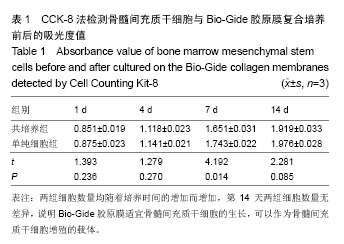
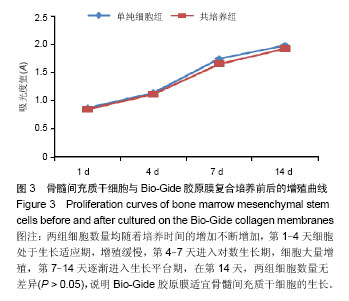
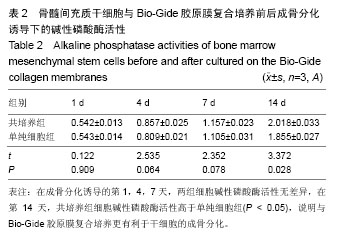
| [1] Nyman S,Lindhe J,Karring T,et al.New attachment following surgical treatment of human periodontal disease.J Clin Periodontol.1982;9(4):290-296.
[2] Gottlow J,Nyman S,Karring T,et al.New attachment formation as the result of controlled tissue regeneration.J Clin Periodontol.1984;11(8):494-503.
[3] 陈发明,金岩,吴织芬.生长因子复合生物膜引导牙周组织再生[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2004,14(10):559-561.
[4] Beresford JN.Osteogenic stem cells and the stromal system of bone and marrow. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;(240): 270-280.
[5] Takeuchi Y,Nakayama K,Matsunoto T.Differentiation and cell surface expression of transforming growth factor-beta receptors are regulated by interaction with matrix collagen in murine osteoblastic cells.J Boil Chem.1996;27(7): 3938-3944.
[6] Behring J,Junker R,Frank X,et al.Toward guided tissue and bone regeneration: Morphology, attachment, proliferation, and migration of cells cultured on collagen barrier membranes: A systematic review.Odontology.2008;96(1):1-11.
[7] Tonetti MS,Cortellini P,Lang NP,et al.Clinical outcomes following treatment of human intrabony defects with GTR/bone replacement material or access flap alone. A multicenter randomized controlled clinical trial.J Clin Periodontol. 2004;31(9):770-776.
[8] Schwarz F,Bieling K,Latz T,et al.Healing of intrabony peri-implantitis defects following application of a nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite(Ostim) or a bovine-derived xenograft(Bio-Oss) in combination with a collagen membrane(Bio-Gide). A case Series.J Clin Periodontol. 2006; 33(7):491-499.
[9] Sculean A,Schwarz F,Chiantella GC,et al.Five-year results of a prospective,randomized, controlled study evaluating treatment of intra-bony defects with a natural bone mineral and GTR. J Clin Periodontol. 2007;34(1):72-77.
[10] Liu Q,Humpe A,Kletsas D,et al.Proliferation assessment of primary human mesenchymal stem cells on collagen membranes for guided bone regeneration.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2011;26(5):1004-1010.
[11] 宋莉,曲丰江,汪泱,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞体外培养及与Bio-Gide胶原膜复合培养的实验研究[J].江西医学院学报, 2009, 49(5):15-18.
[12] 马超,张丁,李平,等.成骨细胞在两种胶原支架材料上的生长特征[J].中国医学科学院学报,2011,33(5):538-542.
[13] Nevins ML,Camelo M,Lynch SE,et al.Evaluation of periodontal regeneration following grafting intrabony defects with bio-oss collagen: a human histologic report.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent.2003;23(1):9-17.
[14] Rothamel D,Schwarz F,Fienitz T,et al.Biocompatibility and biodegradation of a nativeporcine pericardium membrane: results of in vitro and in vivo examinations.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2012;27(1):146-154.
[15] Caneva M,Botticelli D,Salata LA,et al.Collagen membranes at immediate implants: a histomorphometric study in dogs.Clin Oral Implants Res.2010;21(9):891-897.
[16] 谢江涛,刘世清.骨髓基质细胞促进引导性骨再生的研究[J].中华试验外科杂志,2007,24(11):1417-1418.
[17] Zubery Y,Goldlust A,Alves A,et al.Ossification of a novel cross-linked porcine collagen barrier in guided bone regeneration in dogs. J Periodontol.2007;78(1):112-121.
[18] 王建,胡秀莲,林野.Bio-oss和Bio-oss骨胶原保持牙槽骨量的临床研究[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2009,23(1):4-6.
[19] 柏树令,顾晓松,张传森.组织工程学教程[M].北京:人民军医出版社,2009:86-88.
[20] Maeda S,Fujitomo T,Okabe T,et al.Shrinkage-free preparation of scaffold-free cartilage-like disk-shaped cell sheet using human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.J Biosci Bioeng. 2011;111(4):489-492.
[21] Zhou W,Han C,Song Y,et al.The performance of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell--implant complexes prepared by cell sheet engineering techniques. Biomaterials. 2010;31(12): 3212-3221.
[22] 荆恒,陈欣,李宁毅.细胞片层技术的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2010,37(1):71-73.
[23] 王玲玲,李宁毅,樊功为,等.犬骨髓基质细胞片层在构建组织工程骨中的作用[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2011,9(2):96-100.
[24] Trabulsi M,Oh TJ,Eber R,et al.Effect of enamel matrix derivative on collagen guided tissue regeneration-based root coverage procedure.J Periodontol.2004;75(11):1446-1457.
[25] Schwarz F,Rothamel D,Herten M,et al.Angiogenesis pattern of native and cross-linked collagen membranes: an immunohistochemical study in the rat. Clin Oral lmplants Res.2006;17(4):403-409.
[26] Temenoff JS,Mikos AG.Review: tissue engineering for regeneration of articular cartilage. Biomaterials. 2000;21(5): 431-440.
[27] 张铭杰,张庆文,何伟,等.成人骨髓间充质干细胞体外培养、鉴定与成骨诱导[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(45):7947-7953.
[28] Nguyen MN,Lebarbe T,Zouani OF,et al.Impact of RGD nanopatterns grafted onto titanium on osteoblastic cell adhesion. Biomacromolecules.2012;13(3):896-904.
[29] Takata T,Wang HL,Miyauchi M.Migration of osteoblastic cells on various guided bone regeneration membranes.Clin Oral Impants Res.2001;12(4):332-338.
[30] Nur-E-Kamal A,Ahmed I,Kamal J,et al.Three-dimensional nanofibrillar surfaces promote self-renewal in mouse embryonic stem cells.Stem Cells.2006;24(2):426-433.
[31] Chung CH,Golub EE,Forbe E,et al.Mechanism of action of beta-glycerophosphate on bone cell mineralization.Calaif Tissue Int.1992;51(4):305-311.
[32] Bruder SP,Jaiswal N,Haynesworth SE.Growth kinetics, self-renewal, and the osteogenic potential of purified human mesenchymal stem cells during extensive subcultivation and following cryopreservation.J Cell Biochem. 1997;64(2): 278-294.
[33] Tabata Y.Tissue regeneration based on tissue engineering technology. Congenit Anom(Kyoto).2004;44(3):111-124.
[34] Herbertson A,Aubin JE.Cell sorting enriches osteogenic populations in rat bone marrow stromal cell culture. Bone.1997;21(6):491-500.
[35] Li X,Jin L,Cui Q,et al.Steroid effects on osteogenesis through mesenchymal cell gene expression.Osteoporos Int.2005;16(1):101-108.
[36] 谷子芽,翟强,吕秋峰,等.地塞米松诱导牙周膜干细胞的定向成骨分化及凋亡[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(40):7090-7095.
[37] 邹慧儒,张兰成,秦宗长,等.地塞米松对人牙髓细胞增殖分化影响的研究[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2012,8(1):8-13.
[38] Hidalgo-Bastida LA,Cartmell SH.Mesenchymal stem cells, osteoblasts and extracellular matrix proteins: enhancing cell adhesion and differentiation for bone tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part B Rev.2010;16(4):405-412.
[39] Wada K,Mizuno M,Komori T,et al.Extracellular inorganic phosphate regulates gibbon ape leukemia virus receptor-2/phosphate transporter mRNA expression in rat bone marrow stromal cells.J Cell Physiol.2004;198(1):40-47.
[40] Linsley C,Wu B,Tawil B.The effect of fibrinogen, collagen type I, and fibronectin on mesenchymal stem cell growth and differentiation into osteoblasts. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013; 19(11-12):1416-1423.
[41] Taguchi Y,Amizuka N,Nakadate M,et al. A histological evaluation for guided bone regeneration induced by a collagenous membrane.Biomaterials.2005;26(31): 6158-6166.
[42] Mackie EJ.Osteoblasts:novel roles in orchestration of skeletal architecture. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.2003;35(9):1301-1305.
[43] Anselme K.Osteoblast adhesion on biomaterials. Biomaterials. 2000;21(7):667-681.
[44] Suzawa M,Takeuchi Y,Fukumoto S,et al.Extracellular Matrix-associated bone morphogenetic proteins are essential for differentiation of murine osteoblastic cells in vitro. Endocrinology. 1999;140(5):2125-2133.
[45] Hsu FY,Chueh SC,Wang YJ.Microspheres of hydroxyapatite/ reconstituted collagen as supports for osteoblast cell growth. Biomaterials.1999;20(20):1931-1936.
[46] Borkenhagen M,Clemence JF,Sigrist H,et al. Three-dimensional extracellular matrix engineering in the nervous system.J Biomed Mater Res.1998;40:392-400. |