| [1]Williams D.The golden anniversary of titanium biomaterials.Med Device Technol. 2001;12(7):8-11.
[2]Ferguson SJ,Langhoff JD,Voelter K,et al.Biomechanical comparison of different surface modifications for dental implants.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2008;23(6): 1037-1046.
[3]Vadillo-Rodriguez V,Bruque JM,Gallardo-Moreno AM,et al.Surface-dependent mechanical stability of adsorbed human plasma fibronectin on Ti6Al4V: domain unfolding and stepwise unraveling of single compact molecules. Langmuir : the ACS journal of surfaces and colloids.2013;29(27): 8554-8560.
[4]Zhao Y,Wong SM,Wong HM,et al.Effects of carbon and nitrogen plasma immersion ion implantation on in vitro and in vivo biocompatibility of titanium alloy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5(4):1510-1516.
[5]Fischer U,Hempel U,Becker D,et al.Transforming growth factor beta1 immobilized adsorptively on Ti6Al4V and collagen type I coated Ti6Al4V maintains its biological activity. Biomaterials.2003;24(15):2631-2641.
[6]Leventhal GS.Titanium, a metal for surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1951;33-a(2):473-474.
[7]De Nardo L,Raffaini G,Ebramzadeh E,et al.Titanium oxide modeling and design for innovative biomedical surfaces: a concise review.Int J Artif Organs.2012;35(9):629-641.
[8]Murr LE,Quinones SA,Gaytan SM,et al.Microstructure and mechanical behavior of Ti-6Al-4V produced by rapid-layer manufacturing, for biomedical applications. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2009;2(1):20-32.
[9]Minagar S,Wang J,Berndt CC,et al. Cell response of anodized nanotubes on titanium and titanium alloys.J Biomed Mater Res A.2013;101(9):2726-2739.
[10]Abdel-Hady Gepreel M,Niinomi M.Biocompatibility of Ti-alloys for long-term implantation.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2013; 20:407-415.
[11]Vanderleyden E,Mullens S,Luyten J,et al.Implantable (bio)polymer coated titanium scaffolds: a review.Curr Pharm Des.2012;18(18):2576-2590.
[12]Saharudin KA,Sreekantan S,Abd Aziz SN,et al.Surface modification and bioactivity of anodic Ti6Al4V alloy.J Nanosci Nanotechnol.2013;13(3):1696-1705.
[13]Niinomi M,Nakai M,Hieda J.Development of new metallic alloys for biomedical applications. Acta Biomaterialia. 2012; 8(11):3888-3903.
[14]Hanawa T.A comprehensive review of techniques for biofunctionalization of titanium.J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2011;41(6):263-272.
[15]Nakai M,Niinomi M,Akahori T,et al.Development of biomedical porous titanium filled with medical polymer by in-situ polymerization of monomer solution infiltrated into pores.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2010;3(1):41-50.
[16]Yilmazer H,Niinomi M,Nakai M,et al.Heterogeneous structure and mechanical hardness of biomedical beta-type Ti-29Nb-13Ta-4.6Zr subjected to high-pressure torsion.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2012;10:235-245.
[17]Niinomi M,Nakai M,Akahori T.Frictional wear characteristics of biomedical Ti-29Nb-13Ta-4.6Zr alloy with various microstructures in air and simulated body fluid. Biomed Mater. 2007;2(3):S167-174.
[18]Nakai M,Niinomi M,Ishii D.Mechanical and biodegradable properties of porous titanium filled with poly-L-lactic acid by modified in situ polymerization technique. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2011;4(7):1206-1218.
[19]Tanaka Y,Matsuo Y,Komiya T,et al.Characterization of the spatial immobilization manner of poly(ethylene glycol) to a titanium surface with immersion and electrodeposition and its effects on platelet adhesion.J Biomed Mater Res A.2010; 92(1):350-358.
[20]Nowicka J,Bartoszewicz M,Gosciniak G.[Effect of selected properties of Staphylococcus epidermidis to biofilm formation on orthopedic implants]. Med Dosw Mikrobiol. 2012;64(3): 189-196.
[21]Ji J,Zhang W. Bacterial behaviors on polymer surfaces with organic and inorganic antimicrobial compounds.J Biomed Mater Res A.2009;88(2):448-453.
[22]Raulio M,Jarn M,Ahola J,et al. Microbe repelling coated stainless steel analysed by field emission scanning electron microscopy and physicochemical methods.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol.2008;35(7):751-760.
[23]Okada A,Nikaido T,Ikeda M,et al.Inhibition of biofilm formation using newly developed coating materials with self-cleaning properties. Dent Mater J. 2008;27(4):565-572.
[24]Huan Z,Fratila-Apachitei LE,Apachitei I,et al. Porous TiO? surface formed on nickel-titanium alloy by plasma electrolytic oxidation: a prospective polymer-free reservoir for drug eluting stent applications.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2013;101(5):700-708.
[25]Antoci V Jr,Adams CS,Hickok NJ,et al.Vancomycin bound to Ti rods reduces periprosthetic infection: preliminary study.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2007;461:88-95.
[26]Neogi DS,Yadav CS,Khan SA,et al.In vivo efficacy of antimicrobial-coated devices. J Bone Joint Surg.2008; 90(8): 1785; author reply 1785-1786.
[27]An YH,Stuart GW,McDowell SJ,et al. Prevention of bacterial adherence to implant surfaces with a crosslinked albumin coating in vitro.J Orthop Res.1996;14(5):846-849.
[28]Arciola CR,Radin L,Alvergna P,et al.Heparin surface treatment of poly(methylmethacrylate) alters adhesion of a Staphylococcus aureus strain: utility of bacterial fatty acid analysis.Biomaterials.1993;14(15):1161-1164.
[29]Chandy T,Sharma CP.Chitosan--as a biomaterial. Biomater Artif Cells Artif Organs. 1990;18(1):1-24.
[30]Chandy T,Sharma CP.Chitosan matrix for oral sustained delivery of ampicillin. Biomaterials.1993;14(12):939-944.
[31]Wassall MA,Santin M,Isalberti C,et al.Adhesion of bacteria to stainless steel and silver-coated orthopedic external fixation pins.J Biomed Mater Res.1997;36(3):325-330.
[32]Dell'Acqua G,Giacometti A,Cirioni O,et al.Suppression of drug-resistant Staphylococcal Infections by the quorum-sensing inhibitor RNAIII-inhibiting peptide. J Infect Dis.2004;190(2):318-320.
[33]Lerebour G,Cupferman S,Bellon-Fontaine MN.Adhesion of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis to the Episkin reconstructed epidermis model and to an inert 304 stainless steel substrate.J Appl Microbiol.2004;97(1):7-16.
[34]Lafuma A,Quéré D.Superhydrophobic states. Nat Mater.2003; 2(7):457-460.
[35]Lewis K. Persister cells, dormancy and infectious disease. Nature reviews. Microbiology. Jan 2007;5(1):48-56.
[36]Bernhardt R,Scharnweber D,Muller B,et al.Comparison of microfocus- and synchrotron X-ray tomography for the analysis of osteointegration around Ti6Al4V implants.Eur Cell Mater.2004;7:42-51; discussion 51.
[37]Bernhardt R,Kuhlisch E,Schulz MC,et al.Comparison of bone-implant contact and bone-implant volume between 2D-histological sections and 3D-SRµCT slices.Eur Cell Mater.2012;23:237-247;discussion 247-248.
[38]Shalabi MM,Wolke JG,Cuijpers VM,et al.Evaluation of bone response to titanium-coated polymethyl methacrylate resin (PMMA) implants by X-ray tomography.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2007;18(10):2033-2039.
[39]Kiba H,Hayakawa T,Oba S,et al.Potential application of high-resolution microfocus X-ray techniques for observation of bone structure and bone-implant interface.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2003;18(2):279-285.
[40]Cancedda R,Cedola A,Giuliani A,et al.Bulk and interface investigations of scaffolds and tissue-engineered bones by X-ray microtomography and X-ray microdiffraction. Biomaterials. 2007;28(15):2505-2524. |
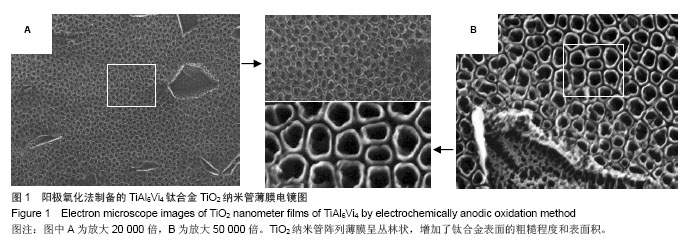

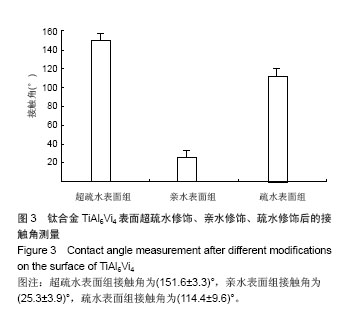
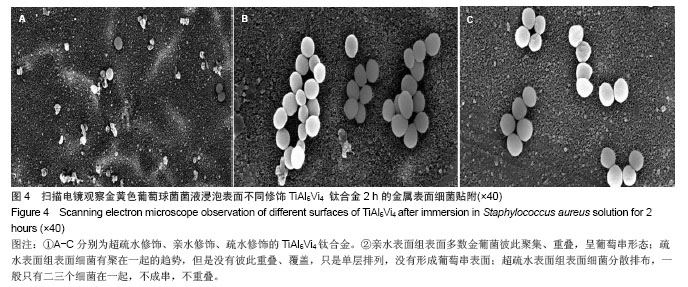
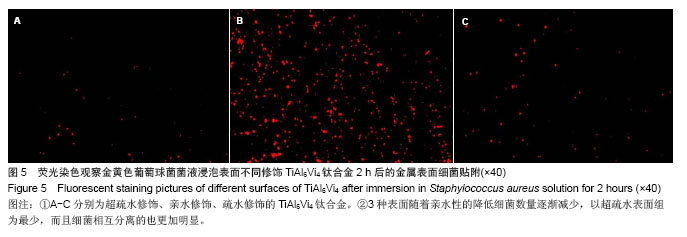
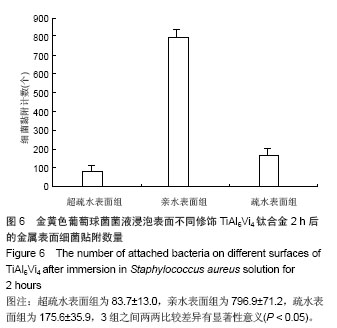
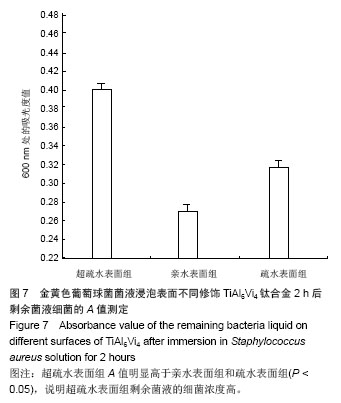
.jpg)