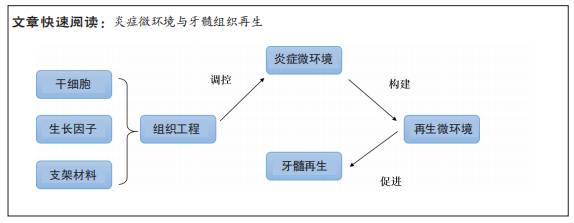
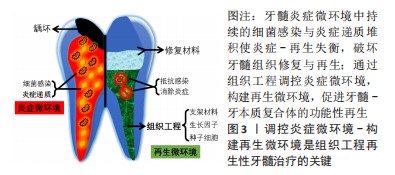
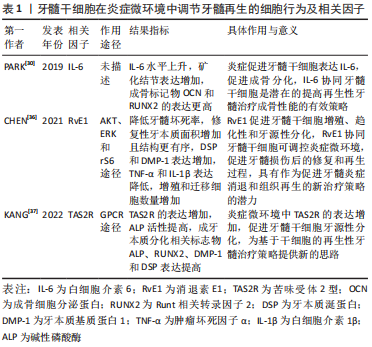
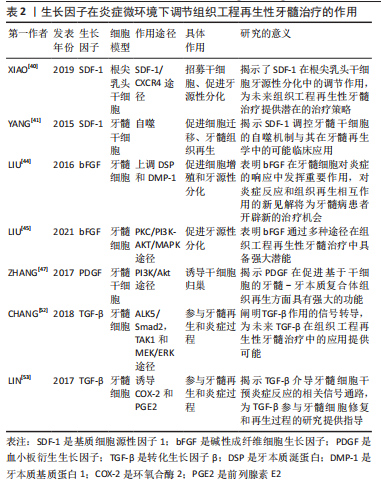
[1] MOROTOMI T, WASHIO A, KITAMURA C. Current and future options for dental pulp therapy. Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 2019;55(1):5-11.
[2] 吴补领,罗奕菲,徐稳安,等.恒牙牙髓炎的活髓保存治疗[J].口腔疾病防治,2021, 29(7):433-441.
[3] MERGONI G, GANIM M, LODI G, et al. Single versus multiple visits for endodontic treatment of permanent teeth. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022;12(12):CD005296.
[4] WEI X, YANG M, YUE L, et al. Expert consensus on regenerative endodontic procedures. Int J Oral Sci. 2022;14(1):55.
[5] 王雪纯,毕静, 陈旭.微环境对牙髓再生影响的研究进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志, 2021,14(3):347-350.
[6] RECHENBERG DK, GALICIA JC, PETERS OA. Biological markers for pulpal inflammation: a systematic review. PLoS One. 2016;11(11):e0167289.
[7] LIU C, XIONG H, CHEN K, et al. Long-term exposure to pro-inflammatory cytokines inhibits the osteogenic/dentinogenic differentiation of stem cells from the apical papilla. Int Endod J. 2016;49(10):950-959.
[8] GOLDBERG M, NJEH A, UZUNOGLU E. Is pulp inflammation a prerequisite for pulp healing and regeneration? Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:347649.
[9] ZAKY SH, SHEHABELDIN M, RAY H, et al. The role of inflammation modulation in dental pulp regeneration. Eur Cell Mater. 2021;41:184-193.
[10] BERGMANN M, JEANNEAU C, GIRAUD T, et al. Complement activation links inflammation to dental tissue regeneration. Clin Oral Investig. 2020;24(12):4185-4196.
[11] IRFAN M, KIM JH, MARZBAN H, et al. The role of complement C5a receptor in DPSC odontoblastic differentiation and in vivo reparative dentin formation. Int J Oral Sci. 2022;14(1):7.
[12] ZHONG TY, ZHANG ZC, GAO YN, et al. Loss of Wnt4 expression inhibits the odontogenic potential of dental pulp stem cells through JNK signaling in pulpitis. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(3):1819-1826.
[13] INOSTROZA C, VEGA-LETTER AM, BRIZUELA C, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from human inflamed dental pulp exhibit impaired immunomodulatory capacity in vitro. J Endod. 2020;46(8):1091-1098.e2.
[14] HENDERSON NC, RIEDER F, WYNN TA. Fibrosis: from mechanisms to medicines. Nature. 2020;587(7835):555-566.
[15] GIRAUD T, JEANNEAU C, ROMBOUTS C, et al. Pulp capping materials modulate the balance between inflammation and regeneration. Dent Mater Off Publ Acad Dent Mater. 2019;35(1):24-35.
[16] LIANG C, LIAO L, TIAN W. Stem cell-based dental pulp regeneration: insights from signaling pathways. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021;17(4):1251-1263.
[17] SUI B, CHEN C, KOU X, et al. Pulp stem cell-mediated functional pulp regeneration. J Dent Res. 2019;98(1):27-35.
[18] SHEKATKAR MR, KHEUR SM, KHARAT AH, et al. Assessment of angiogenic potential of mesenchymal stem cells derived conditioned medium from various oral sources. J Clin Transl Res. 2022;8(4):323-338.
[19] PULYODAN MK, PARAMEL MOHAN S, VALSAN D, et al. Regenerative endodontics: a paradigm shift in clinical endodontics. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2020;12(Suppl 1):S20-S26.
[20] LIN LM, HUANG GTJ, SIGURDSSON A, et al. Clinical cell-based versus cell-free regenerative endodontics: clarification of concept and term. Int Endod J. 2021;54(6): 887-901.
[21] ALTAII M, RICHARDS L, ROSSI-FEDELE G. Histological assessment of regenerative endodontic treatment in animal studies with different scaffolds: a systematic review. Dent Traumatol Off Publ Int Assoc Dent Traumatol. 2017;33(4):235-244.
[22] AHMED GM, ABOUAUF EA, ABUBAKR N, et al. Cell-based transplantation versus cell homing approaches for pulp-dentin complex regeneration. Stem Cells Int. 2021;2021:1-23.
[23] KIM SG. A cell-based approach to dental pulp regeneration using mesenchymal stem cells: a scoping review. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(9):4357.
[24] XIE Z, SHEN Z, ZHAN P, et al. Functional dental pulp regeneration: basic research and clinical translation. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(16):8991.
[25] RAVINDRAN S, HUANG CC, GEORGE A. Extracellular matrix of dental pulp stem cells: applications in pulp tissue engineering using somatic MSCs. Front Physiol. 2014;4:395.
[26] CHEN Y, MA Y, YANG X, et al. The application of pulp tissue derived-exosomes in pulp regeneration: a novel cell-homing approach. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022;17:465-476.
[27] HUANG X, LI Z, LIU A, et al. Microenvironment influences odontogenic mesenchymal stem cells mediated dental pulp regeneration. Front Physiol. 2021;12:656588.
[28] XUAN K, LI B, GUO H, et al. Deciduous autologous tooth stem cells regenerate dental pulp after implantation into injured teeth. Sci Transl Med. 2018;10(455):eaaf3227.
[29] HONG H, CHEN X, LI K, et al. Dental follicle stem cells rescue the regenerative capacity of inflamed rat dental pulp through a paracrine pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020; 11(1):333.
[30] PARK YT, LEE SM, KOU X, et al. The role of interleukin 6 in osteogenic and neurogenic differentiation potentials of dental pulp stem cells. J Endod. 2019;45(11):1342-1348.
[31] THANKAM FG, WILSON VED, RADWAN MM, et al. Involvement of ischemia-driven 5-lipoxygenase-resolvin-E1-chemokine like receptor-1 axis in the resolution of post-coronary artery bypass graft inflammation in coronary arteries. Mol Biol Rep. 2022;49(4):3123-3134.
[32] STORNIOLO CE, PEQUERA M, VILARIÑO A, et al. Specialized pro-resolvin mediators induce cell growth and improve wound repair in intestinal epithelial caco-2 cell cultures. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2022;187:102520.
[33] GRAZDA R, SEYFRIED AN, MADDIPATTI KR, et al. Impaired inflammation resolution in murine bone marrow failure is rescued by resolvin E1 treatment. Biorxiv. 2023. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.15.528688.
[34] LIU X, WANG C, PANG L, et al. Combination of resolvin E1 and lipoxin A4 promotes the resolution of pulpitis by inhibiting NF-ΚB activation through upregulating sirtuin 7 in dental pulp fibroblasts. Cell Prolif. 2022;55(5):e13227.
[35] 潘亮亮,张旗.消退素 E1 对牙髓炎中性粒细胞凋亡的影响[J].口腔医学研究, 2022,38(8):742-746.
[36] CHEN J, XU H, XIA K, et al. Resolvin E1 accelerates pulp repair by regulating inflammation and stimulating dentin regeneration in dental pulp stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):75.
[37] KANG W, WANG Y, LI J, et al. TAS2R supports odontoblastic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells in the inflammatory microenvironment. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):374.
[38] ORTI V, COLLART-DUTILLEUL PY, PIGLIONICO S, et al. Pulp regeneration concepts for nonvital teeth: from tissue engineering to cinical approaches. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2018;24(6):419-442.
[39] YANG J, YUAN G, CHEN Z. Pulp regeneration: current approaches and future challenges. Front Physiol. 2016;7:58.
[40] XIAO M, YAO B, BAI Y, et al. Stromal-derived factor-1α signaling is involved in bone morphogenetic protein-2-induced odontogenic differentiation of stem cells from apical papilla via the smad and Erk signaling pathways. Exp Cell Res. 2019;381(1):39-49.
[41] YANG J, ZHANG Y, WAN C, et al. Autophagy in SDF-1α-mediated DPSC migration and pulp regeneration. Biomaterials. 2015;44:11-23.
[42] HE B, ZHANG M, YIN L, et al. BFGF-incorporated composite biomaterial for bone regeneration. Mater Des. 2022;215:110469.
[43] BIAN D, WU Y, SONG G. Basic fibroblast growth factor combined with extracellular matrix-inspired mimetic systems for effective skin regeneration and wound healing. Mater Today Commun. 2023;35:105876.
[44] LIU L, SHU S, CHEUNG GS, et al. Effect of MiR-146a/BFGF/PEG-PEI nanoparticles on inflammation response and tissue regeneration of human dental pulp cells. BioMed Res Int. 2016;2016:3892685.
[45] LIU K, YU S, YE L, et al. The regenerative potential of BFGF in dental pulp repair and regeneration. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:680209.
[46] VERMA R, NEGI G, KANDWAL A, et al. Effect of autologous PRP on wound healing in dental regenerative surgeries and its correlation with PDGF levels. Asian J Transfus Sci. 2019;13(1):47-53.
[47] ZHANG M, JIANG F, ZHANG X, et al. The effects of platelet-derived growth factor-BB on human dental pulp stem cells mediated dentin-pulp complex regeneration. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(12):2126-2134.
[48] LI L, WANG Z. PDGF-BB, NGF and BDNF enhance pulp-like tissue regeneration via cell Homing. RSC Adv. 2016;6(111):109519-109527.
[49] CAI Y, WANG Z, LIAO B, et al. Anti-inflammatory and chondroprotective effects of platelet-derived growth factor-BB on osteoarthritis rat models. J Gerontol Ser A. 2023; 78(1):51-59.
[50] NIWA T, YAMAKOSHI Y, YAMAZAKI H, et al. The dynamics of TGF-β in dental pulp, odontoblasts and dentin. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):4450.
[51] DIANA R, ARDHANI R, KRISTANTI Y, et al. Dental pulp stem cells response on the nanotopography of scaffold to regenerate dentin-pulp complex tissue. Regen Ther. 2020;15:243-250.
[52] CHANG MC, CHANG HH, LIN PS, et al. Effects of TGF-Β1 on plasminogen activation in human dental pulp cells: role of ALK5/Smad2, TAK1 and MEK/ERK signalling. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(4):854-863.
[53] LIN PS, CHENG RH, CHANG MC, et al. TGF-Β1 stimulates cyclooxygenase-2 expression and PGE2 production of human dental pulp cells: role of ALK5/Smad2 and MEK/ERK signal transduction pathways. J Formos Med Assoc. 2017;116(10):748-754.
[54] MOUSSA DG, APARICIO C. Present and future of tissue engineering scaffolds for dentin-pulp complex regeneration. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(1):58-75.
[55] COLOMBO JS, MOORE AN, HARTGERINK JD, et al. Scaffolds to control inflammation and facilitate dental pulp regeneration. J Endod. 2014;40(4):S6-S12.
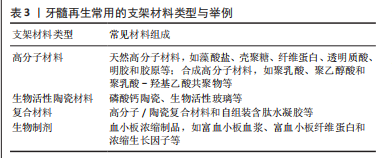
[56] 周易,赵玉鸣.牙髓再生支架材料的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2022,49(1): 19-26.
[57] ZHANG S, THIEBES A L, KREIMENDAHL F, et al. Extracellular vesicles-loaded fibrin gel supports rapid neovascularization for dental pulp regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(12):4226.
[58] FIROUZI N, YAVARI HR, RAHIMI S, et al. Concentrated growth factors combined with lipopolysaccharide stimulate the in vitro regenerative and osteogenic activities of human dental pulp stem cells by balancing inflammation. Int J Dent. 2022;2022:2316666.
[59] DA ROSA WLO, PIVA E, DA SILVA AF. Disclosing the physiology of pulp tissue for vital pulp therapy. Int Endod J. 2018;51(8):829-846.
[60] LUO H, LIU W, ZHOU Y, et al. Concentrated growth factor regulates the macrophage-mediated immune response. Regen Biomater. 2021;8(6):rbab049.
[61] TABATABAEI F, AGHAMOHAMMADI Z, TAYEBI L. In vitro and in vivo effects of concentrated growth factor on cells and tissues. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2020;108(6):1338-1350. |