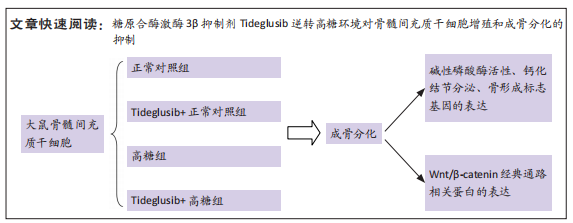
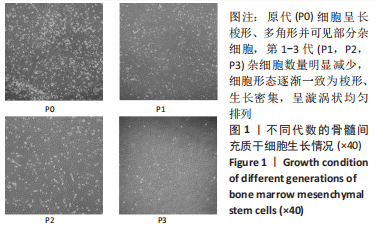
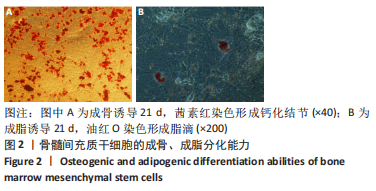
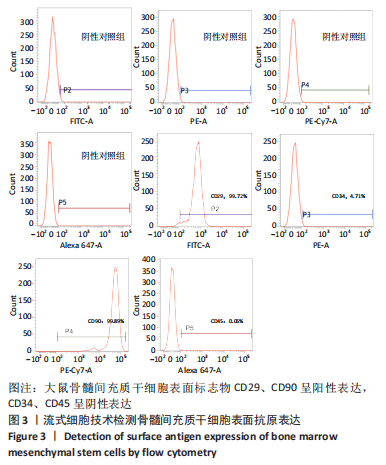
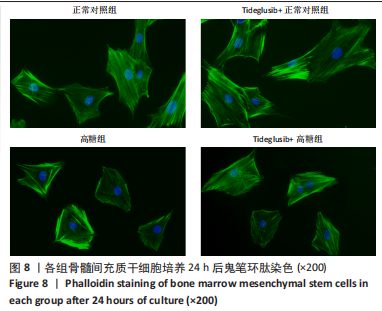
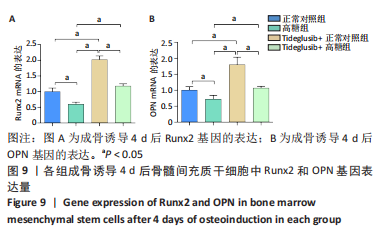
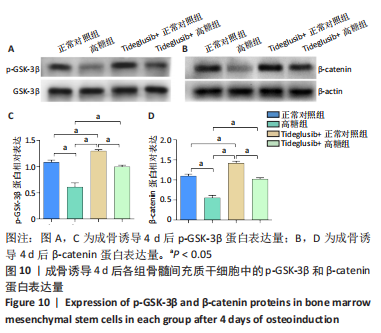
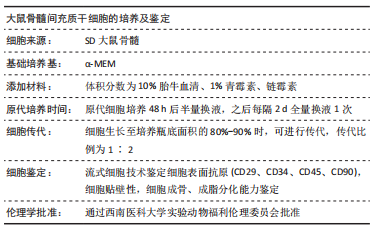
[1] Monje A, Catena A, Borgnakke WS. Association between diabetes mellitus/hyperglycaemia and peri-implant diseases: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Periodontol. 2017;44(6):636-648.
[2] Park SY, Choi KH, Jun JE, et al. Effects of Advanced Glycation End Products on Differentiation and Function of Osteoblasts and Osteoclasts. J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(37):e239.
[3] Kaur J, Khosla S, Farr JN. Effects of diabetes on osteocytes. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2022;29(4):310-317.
[4] Kasperk C, Georgescu C, Nawroth P. Diabetes Mellitus and Bone Metabolism. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2017;125(4):213-217.
[5] Murray CE, Coleman CM. Impact of Diabetes Mellitus on Bone Health. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(19):4873.
[6] 董刚,徐欣,田燕,等.2型糖尿病患者血糖控制水平与种植牙愈合的关系[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2013,39(1):143-147.
[7] Al Zahrani S, Al Mutairi AA. Crestal Bone Loss Around Submerged and Non-Submerged Dental Implants in Individuals with Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 7-Year Prospective Clinical Study. Med Princ Pract. 2019;28(1):75-81.
[8] King S, Klineberg I, Levinger I, et al. The effect of hyperglycaemia on osseointegration: a review of animal models of diabetes mellitus and titanium implant placement. Arch Osteoporos. 2016;11(1):29.
[9] Neves VC, Babb R, Chandrasekaran D, et al. Promotion of natural tooth repair by small molecule GSK3 antagonists. Sci Rep. 2017;7:39654.
[10] Zaugg LK, Banu A, Walther AR, et al. Translation Approach for Dentine Regeneration Using GSK-3 Antagonists. J Dent Res. 2020;99(5):544-551.
[11] Comeau-Gauthier M, Tarchala M, Luna JLR, et al. Unleashing β-catenin with a new anti-Alzheimer drug for bone tissue regeneration. Injury. 2020;51(11):2449-2459.
[12] Lektemur Alpan A, Çalişir M, Kizildağ A, et al. Effects of a Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 Inhibitor Tideglusib on Bone Regeneration With Calvarial Defects. J Craniofac Surg. 2020;31(5):1477-1482.
[13] Sun Y, Zhu Y, Liu X, et al. Morroniside attenuates high glucose-induced BMSC dysfunction by regulating the Glo1/AGE/RAGE axis. Cell Prolif. 2020; 53(8):e12866.
[14] Li Y, Wang X. Chrysin Attenuates High Glucose-Induced BMSC Dysfunction via the Activation of the PI3K/AKT/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022;16:165-182.
[15] Liu S, Yang X, Zhong X, et al. Involvement of miR-337 in high glucose-suppressed osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via negative regulation of Rap1A. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2021;57(3):350-358.
[16] Li Z, Zhao H, Chu S, et al. miR-124-3p promotes BMSC osteogenesis via suppressing the GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway in diabetic osteoporosis rats. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2020;56(9):723-734.
[17] Zhang B, Liu N, Shi H, et al. High glucose microenvironments inhibit the proliferation and migration of bone mesenchymal stem cells by activating GSK3β. J Bone Miner Metab. 2016;34(2):140-150.
[18] 陈杨. Runx2对高糖环境下干细胞成骨分化作用和机制的初步研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2017.
[19] Fairfield H, Falank C, Harris E, et al. The skeletal cell-derived molecule sclerostin drives bone marrow adipogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2018; 233(2):1156-1167.
[20] Jin P, Zhang X, Wu Y, et al. Streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat-derived bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells have impaired abilities in proliferation, paracrine, antiapoptosis, and myogenic differentiation. Transplant Proc. 2010;42(7):2745-2752.
[21] del Ser T, Steinwachs KC, Gertz HJ, et al. Treatment of Alzheimer’s disease with the GSK-3 inhibitor tideglusib: a pilot study. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013;33(1):205-215.
[22] Atila D, Chen CY, Lin CP, et al. In vitro evaluation of injectable Tideglusib-loaded hyaluronic acid hydrogels incorporated with Rg1-loaded chitosan microspheres for vital pulp regeneration. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;278: 118976.
[23] 孙佳辰,刘馨竹,申传安,等.小分子药物Tideglusib促进大鼠创面愈合的机制研究[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2021,16(3):224-231.
[24] 胡洋,张媛媛,李芳,等.中药有效成分调节细胞骨架功能的研究进展[J].药学研究,2018,37(4):187-193.
[25] Duan P, Bonewald LF. The role of the wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in formation and maintenance of bone and teeth. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016;77(Pt A):23-29.
[26] 姜朝阳,谢兴文,徐世红,等.骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化相关信号通路[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2020,13(5):473-478.
[27] Nusse R, Clevers H. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling, Disease, and Emerging Therapeutic Modalities. Cell. 2017;169(6):985-999.
[28] Maeda K, Kobayashi Y, Koide M, et al. The Regulation of Bone Metabolism and Disorders by Wnt Signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(22):5525.
[29] 史卫东. AGEs、GSK3β、TRPM2对高糖环境下成骨细胞增殖影响的机制研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2019.
[30] Cheng J, Xu HY, Liu MM, et al. Catalpol Promotes the Proliferation and Differentiation of Osteoblasts Induced by High Glucose by Inhibiting KDM7A. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020;13:705-712.
[31] Chen Y, Chen L, Huang R, et al. Investigation for GSK3β expression in diabetic osteoporosis and negative osteogenic effects of GSK3β on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under a high glucose microenvironment. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;534:727-733.
[32] Antika LD, Lee EJ, Kim YH, et al. Dietary phlorizin enhances osteoblastogenic bone formation through enhancing β-catenin activity via GSK-3β inhibition in a model of senile osteoporosis. J Nutr Biochem. 2017;49:42-52.
|