[1] VALM AM. The structure of dental plaque microbial communities in the transition from health to dental caries and periodontal disease. J Mol Biol. 2019;431(16):2957-2969.
[2] BIHAREE A, SHARMA A, KUMAR A, et al. Antimicrobial flavonoids as a potential substitute for overcoming antimicrobial resistance. Fitoterapia. 2020;146:104720.
[3] KULKARNI N, SHINDE SD, JADHAV GS, et al. Peptide-chitosan engineered scaffolds for biomedical applications. Bioconjug Chem. 2021;32(3):448-465.
[4] YU D, FENG J, YOU H, et al. The microstructure, antibacterial and antitumor activities of chitosan oligosaccharides and derivatives. Mar Drugs. 2022;20(1):69.
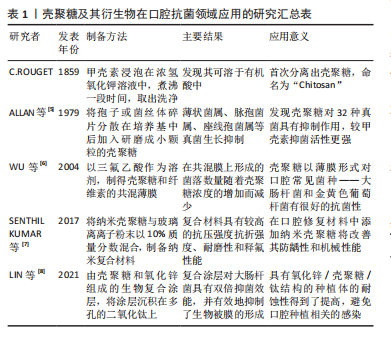
[5] ALLAN C, ADNIGER LA. The fungicidal effect of chitosan on fungi of varying cell wall composition. Exp Mycol. 1979;3:285-287.
[6] WU YB, YU SH, MI FL, et al. Preparation and characterization on mechanical and antibacterial properties of chitsoan/cellulose blends. Carbohydrate Polymers. 2004;57(4):435-440.
[7] SENTHIL KUMAR R, RAVIKUMAR N, KAVITHA S, et al. Nanochitosan modified glass ionomer cement with enhanced mechanical properties and fluoride release. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;104(Pt B):1860-1865.
[8] LIN MH, WANG YH, KUO CH, et al. Hybrid ZnO/chitosan antimicrobial coatings with enhanced mechanical and bioactive properties for titanium implants. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;257:117639.
[9] 崔升,袁美玉,付俊杰,等.抗菌用壳聚糖及其金属粒子复合材料研究进展[J].精细化工,2021,38(9):1757-1764, 1778.
[10] LI J, TIAN X, HUA T, et al. Chitosan natural polymer material for improving antibacterial properties of textiles. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2021;4(5):4014-4038.
[11] BABU A, RAMESH R. Multifaceted applications of chitosan in cancer drug delivery and therapy. Mar Drugs. 2017;15(4):96.
[12] RIAZ RAJOKA MS, MEHWISH HM, WU Y, et al. Chitin/chitosan derivatives and their interactions with microorganisms: a comprehensive review and future perspectives. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2020;40(3):365-379.
[13] PAVINATTO A, SOUZA A L, DELEZUK JA, et al. Interaction of O-acylated chitosans with biomembrane models: probing the effects from hydrophobic interactions and hydrogen bonding. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014;114:53-59.
[14] ABRICA-GONZÁLEZ P, ZAMORA-JUSTO JA, SOTELO-LÓPEZ A, et al. Gold nanoparticles with chitosan, N-acylated chitosan, and chitosan oligosaccharide as DNA carriers. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2019;14(1):258.
[15] DU X, WU L, YAN H, et al. Microchannelled alkylated chitosan sponge to treat noncompressible hemorrhages and facilitate wound healing. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):4733.
[16] SHEN J, JIN B, QI YC, et al. Carboxylated chitosan/silver-hydroxyapatite hybrid microspheres with improved antibacterial activity and cytocompatibility. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;78:589-597.
[17] YI Y, FEI J, XU Y X, et al. Preparation and characterization of a Schiff-based chitosan-fructose quaternary ammonium salt for medical applications. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2020;31(6):804-815.
[18] ISLAM S, ARNOLD L, PADHYE R. Comparison and characterisation of regenerated chitosan from 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride and chitosan from crab shells. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:874316.
[19] KHATTAK S, WAHID F, LIU LP, et al. Applications of cellulose and chitin/chitosan derivatives and composites as antibacterial materials:current state and perspectives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019;103(5): 1989-2006.
[20] SAITO H, SAKAKIBARA Y, SAKATA A, et al. Antibacterial activity of lysozyme-chitosan oligosaccharide conjugates (LYZOX) against pseudomonas aeruginosa, acinetobacter baumannii and methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus. PLoS One. 2019;14(5):e0217504.
[21] JAMSHIDI D, SAZEGAR MR. Antibacterial activity of a novel biocomposite chitosan/graphite based on zinc-grafted mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:871-883.
[22] AMIDI M, MASTROBATTISTA E, JISKOOT W, et al. Chitosan-based delivery systems for protein therapeutics and antigens. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010;62(1):59-82.
[23] SHIH PY, LIAO YT, TSENG YK, et al. A potential antifungal effect of chitosan against candida albicans is mediated via the inhibition of SAGA complex component expression and the subsequent alteration of cell surface integrity. Front Microbiol. 2019;10:602.
[24] XIAO X, YU Y, SUN Y, et al. Heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions by chitosan-based magnetic composite flocculants. J Environ Sci (China). 2021;108:22-32.
[25] GRANDE-TOVAR CD, CHAVES-LOPEZ C, SERIO A, et al. Chitosan coatings enriched with essential oils: effects on fungi involved in fruit decay and mechanisms of action. Trends Food Sci Tech. 2018;78:61-71.
[26] WEIßPFLOG J, GÜNDEL A, VEHLOW D, et al. Solubility and selectivity effects of the anion on the adsorption of different heavy metal ions onto chitosan. Molecules. 2020;25(11):2482.
[27] CHUNG YC, YEH JY, TSAI CF. Antibacterial characteristics and activity of water-soluble chitosan derivatives prepared by the Maillard reaction. Molecules. 2011;16(10):8504-8514.
[28] ARDEAN C, DAVIDESCU CM, NEMEŞ NS, et al. Factors influencing the antibacterial activity of chitosan and chitosan modified by functionalization. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(14):7449.
[29] BYUN SM, NO HK, HONG JH, et al. Comparison of physicochemical, binding, antioxidant and antibacterial properties of chitosans prepared from ground and entire crab leg shells. Int J Food Sci Tech. 2013;48(1):136-142.
[30] MA J, FAQIR Y, TAN C, et al. Terrestrial insects as a promising source of chitosan and recent developments in its application for various industries. Food Chem. 2022;373(Pt A):131407.
[31] SRIMANEEPONG V, THANAMEE T, WATTANASIRMKIT K, et al. Efficacy of low-molecular weight chitosan against Candida albicans biofilm on polymethyl methacrylate resin. Aust Dent J. 2021;66(3):262-269.
[32] KAŠPAROVÁ P, ZMUDA M, VAŇKOVÁ E, et al. Low-molecular weight chitosan enhances antibacterial effect of antibiotics and permeabilizes cytoplasmic membrane of Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm cells. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2021;66(6):983-996.
[33] LI J, FU J, TIAN X, et al. Characteristics of chitosan fiber and their effects towards improvement of antibacterial activity. Carbohydr Polym. 2022; 280:119031.
[34] VISHU KUMAR AB, VARADARAJ MC, GOWDA LR, et al. Characterization of chito-oligosaccharides prepared by chitosanolysis with the aid of papain and Pronase, and their bactericidal action against Bacillus cereus and Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 2005;391(Pt 2):167-175.
[35] HOSSEINNEJAD M, JAFARI SM. Evaluation of different factors affecting antimicrobial properties of chitosan. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;85:467-475.
[36] HASSAN MI, MOHAMED AF, TAHER FA, et al. Antimicrobial activities of chitosan nanoparticles prepared-from lucila cuprina maggots (diptera: calliphoridae). J Egypt Soc Parasitol. 2016;46(3):563-570.
[37] RISTIC T, HRIBERNIK S, FRAS-ZEMLJIC L. Electrokinetic properties of fibres functionalised by chitosan and chitosan nanoparticles. Cellulose. 2015;22(6):3811-3823.
[38] MENG X, XING R, LIU S, et al. Molecular weight and pH effects of aminoethyl modified chitosan on antibacterial activity in vitro. Int J Biol Macromol. 2012;50(4):918-924.
[39] NO HK, PARK NY, LEE SH, et al. Antibacterial activity of chitosans and chitosan oligomers with different molecular weights. Int J Food Microbiol. 2002;74(1-2):65-72.
[40] ARDILA N, DAIGLE F, HEUZEY MC, et al. Effect of chitosan physical form on its antibacterial activity against pathogenic bacteria. J Food Sci. 2017;82(3):679-686.
[41] CHUNG YC, SU YP, CHEN CC, et al. Relationship between antibacterial activity of chitosan and surface characteristics of cell wall. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2004;25(7):932-936.
[42] CHUNG YC, WANG HL, CHEN YM, et al. Effect of abiotic factors on the antibacterial activity of chitosan against waterborne pathogens. Bioresour Technol. 2003;88(3):179-184.
[43] CARACCIOLO G, VALI H, MOORE A, et al. Challenges in molecular diagnostic research in cancer nanotechnology. Nano Today. 2019;27: 6-10.
[44] RYU JH, CHOI JS, PARK E, et al. Chitosan oral patches inspired by mussel adhesion. J Control Release. 2020;317:57-66.
[45] DUBASHYNSKAYA NV, RAIK SV, DUBROVSKII YA, et al. Hyaluronan/diethylaminoethyl chitosan polyelectrolyte complexes as carriers for improved colistin delivery. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(16):8381.
[46] 杨梦璐.壳聚糖基防龋基因疫苗载体的制备及性能研究[D].遵义:遵义医科大学,2021.
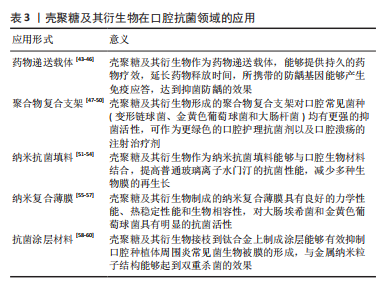
[47] PHUANGKAEW T, BOORANABUNYAT N, KIATKAMJORNWONG S, et al. Amphiphilic quaternized chitosan: synthesis, characterization, and anti-cariogenic biofilm property. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;277:118882.
[48] PIEGAT A, ŻYWICKA A, NIEMCZYK A, et al. Antibacterial activity of N,O-Acylated chitosan derivative. Polymers (Basel). 2020;13(1):107.
[49] LUO Z, XUE K, ZHANG X, et al. Thermogelling chitosan-based polymers for the treatment of oral mucosa ulcers. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(5): 1364-1379.
[50] WANG N, JI Y, ZHU Y, et al. Antibacterial effect of chitosan and its derivative on enterococcus faecalis associated with endodontic infection. Exp Ther Med. 2020;19(6):3805-3813.
[51] ABUSREWIL S, BROWN JL, DELANEY C, et al. Chitosan enhances the anti-biofilm activity of biodentine against an interkingdom biofilm model. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021;10(11):1317.
[52] WALCZAK K, SCHIERZ G, BASCHE S, et al. Antifungal and surface properties of chitosan-salts modified PMMA denture base material. Molecules. 2020;25(24):5899.
[53] DE MORI A, DI GREGORIO E, KAO AP, et al. Antibacterial PMMA composite cements with tunable thermal and mechanical properties. ACS Omega. 2019;4(22):19664-19675.
[54] IBRAHIM MA, NEO J, ESGUERRA RJ, et al. Characterization of antibacterial and adhesion properties of chitosan-modified glass ionomer cement. J Biomater Appl. 2015;30(4):409-419.
[55] ZHANG X, ZHANG Z, WU W, et al. Preparation and characterization of chitosan/Nano-ZnO composite film with antimicrobial activity. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2021;44(6):1193-1199.
[56] YIN M, LIN X, REN T, et al. Cytocompatible quaternized carboxymethyl chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol) blend film loaded copper for antibacterial application. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;120(Pt A):992-998.
[57] ZHANG M, YANG M, WOO MW, et al. High-mechanical strength carboxymethyl chitosan-based hydrogel film for antibacterial wound dressing. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;256:117590.
[58] CAMACHO-ALONSO F, SALINAS J, SÁNCHEZ-SILES M, et al. Synergistic antimicrobial effect of photodynamic therapy and chitosan on the titanium-adherent biofilms of staphylococcus aureus, escherichia coli, and pseudomonas aeruginosa: an in vitro study. J Periodontol. 2021. doi: 10.1002/JPER.21-0306.
[59] LIU G, LI K, LUO Q, et al. PEGylated chitosan protected silver nanoparticles as water-borne coating for leather with antibacterial property. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2017;490:642-651.
[60] D’ALMEIDA M, ATTIK N, AMALRIC J, et al. Chitosan coating as an antibacterial surface for biomedical applications. PLoS One. 2017; 12(12):e0189537. |