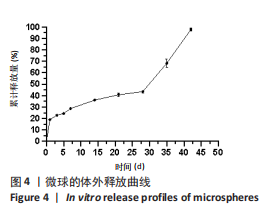
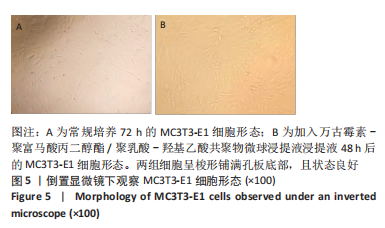
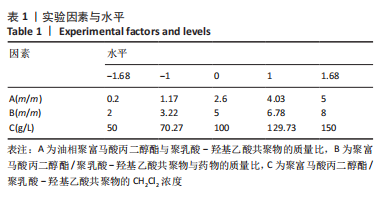
[1] JERZY K, FRANCIS H. Chronic Osteomyelitis - Bacterial Flora, Antibiotic Sensitivity and Treatment Challenges. Open Orthop J. 2018;12(1): 153-163.
[2] HE N, SU S, YE Z, et al. Evidence-based Guideline for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Vancomycin: 2020 Update by the Division of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring, Chinese Pharmacological Society. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71 (Suppl 4):S363-S371.
[3] KREMERS H, NWOJO ME, RANSOM J, et al. Trends in the epidemiology of osteomyelitis: a population-based study, 1969 to 2009. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(10):837-845.
[4] LIU G, CHEN S, FANG J, et al. Vancomycin microspheres reduce postoperative spine infection in an in vivo rabbit model. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016;17(1):61.
[5] BELLOS I, DASKALAKIS G, PERGIALIOTIS V. Relationship of vancomycin trough levels with acute kidney injury risk: an exposure–toxicity meta-analysis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2020;75(10):2725-2734.
[6] TSUTSUURA M, MORIYAMA H, KOJIMA N, et al. The monitoring of vancomycin: a systematic review and meta-analyses of area under the concentration-time curve-guided dosing and trough-guided dosing. BMC Infect Dis. 2021;21(1):153.
[7] LI W, DING Y, RAI R, et al. Preparation and characterization of PHBV microsphere/45S5 bioactive glass composite scaffolds with vancomycin releasing function. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;41:320-328.
[8] VIRINTHORN R, CHANDRASEKARAN M, WANG K, et al. Post-process optimization of 3D printed poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) dental implant scaffold for enhanced structure and mechanical properties: effects of sonication duration and power. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2021;32(8):91.
[9] ARRANZ-ROMERA A,DAVIS BM,BRAVO-OSUNA I, et al. Simultaneous co-delivery of neuroprotective drugs from multi-loaded PLGA microspheres for the treatment of glaucoma. J Control Release. 2019; 297:26-38.
[10] EL-HAMMADI MM, ARIAS JL. Recent Advances in the Surface Functionalization of PLGA-Based Nanomedicines. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022;12(3):354.
[11] ROCHA CV, GONCALVES V, DA SILVA MC, et al. PLGA-Based Composites for Various Biomedical Applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(4):2034.
[12] YUAN S, SHEN Y, LI Z. Injectable Cell- and Growth Factor-Free Poly(4-hydroxybutyrate) (P4HB) Microspheres with Open Porous Structures and Great Efficiency of Promoting Bone Regeneration. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2021;4(5):4432-4440.
[13] SU Y, ZHANG B, SUN R, et al. PLGA-based biodegradable microspheres in drug delivery: recent advances in research and application. Drug Deliv. 2021;28(1):1397-1418.
[14] CAI Z, WAN Y, BECKER ML, et al. Poly(propylene fumarate)-based materials: Synthesis, functionalization, properties, device fabrication and biomedical applications. Biomaterials. 2019;208:45-71.
[15] WANG MO, PIARD CM, MELCHIORRI A, et al. Evaluating changes in structure and cytotoxicity during in vitro degradation of three-dimensional printed scaffolds. Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21(9-10):1642-1653.
[16] LUO Y, DOLDER CK, WALKER JM, et al. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Well-Defined Poly(propylene fumarate) Oligomers and Their Use in 3D Printed Scaffolds. Biomacromolecules. 2016;17(2): 690-700.
[17] ZHOU Z, YAO Q, LI L, et al. Antimicrobial Activity of 3D-Printed Poly(epsilon-Caprolactone) (PCL) Composite Scaffolds Presenting Vancomycin-Loaded Polylactic Acid-Glycolic Acid (PLGA) Microspheres. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:6934-6945.
[18] LU Y, MANTHA SN, CROWDER DC, et al. Microstereolithography and characterization of poly(propylene fumarate)-based drug-loaded microneedle arrays. Biofabrication. 2015;7(4):045001.
[19] AHN CB, KIM Y, PARK SJ, et al. Development of arginine-glycine-aspartate-immobilized 3D printed poly(propylene fumarate) scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2018;29(7-9): 917-931.
[20] OLTHOF MGL, KEMPEN DHR, HERRICK JL, et al. Effect of different sustained bone morphogenetic protein-2 release kinetics on bone formation in poly(propylene fumarate) scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2018;106(2):477-487.
[21] LIU X, GEORGE MN, PARK S, et al. 3D-printed scaffolds with carbon nanotubes for bone tissue engineering: Fast and homogeneous one-step functionalization. Acta Biomater. 2020;111:129-140.
[22] KEMPEN DH, LU L, ZHU X, et al. Development of biodegradable poly(propylene fumarate)/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) blend microspheres. I. Preparation and characterization. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2004;70(2):283-292.
[23] 于海峰,王洪光,徐元广,等.星点设计-效应面优化乳化交联法制备恩诺沙星壳聚糖微球[J].应用化工,2014,43(4):688-695.
[24] 林卫瑞,王洪光,杜昌余.星点设计-效应面法优化氟苯尼考缓释微球制备工艺[J].中国抗生素杂志,2013,38(8):609-613.
[25] 史琼,游国业.星点设计效应面法优化阿霉素胶束的处方工艺[J].辽宁化工,2021,50(3):323-325.
[26] 杨蕾,彭博,王明新,等.阿立哌唑缓释微球的工艺优化及体内药动学研究[J].中国新药杂志,2012,21(2):189-201.
[27] 王梦范,张丹丹.星点设计效应面法优化姜黄素微球的制备工艺[J].生物加工过程,2020,18(5):627-630.
[28] ZHU S. Optimization of Extraction of Polyphenol from Panax Quinquefolius L. Using Central Composite Design/Response Surface Methodology. Starch - Stärke. 2021;73(7-8).https://doi.org/10.1002/star.202100020
[29] WANG D, XIAO D, LU M, et al. Immobilization of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres on bone implant materials for antibiotic release and the binding mechanisms. RSC Adv. 2020;10(12):7251-7258.
[30] 邱晓明.β-磷酸三钙支架负载万古霉素/PLGA微球治疗感染性骨缺损的实验研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2018.
[31] SI W, YANG Q, ZONG Y, et al. Toward Understanding the Effect of Solvent Evaporation on the Morphology of PLGA Microspheres by Double Emulsion Method. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2021;60(25):9196-9205.
[32] BEIG A, FENG L, WALKER J, et al. Development and characterization of composition-equivalent formulations to the Sandostatin LAR(R) by the solvent evaporation method. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022;12(3): 695-707.
[33] 王飞.万古霉素PLGA缓释微球局部注射治疗椎间盘炎的实验研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2010.
[34] 刘亚珍,邱晓明,李松凯.正交设计优化万古霉素/聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物微球的制备及体外药物释放[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(2):211-217.
[35] HAO L, JIANG Y, ZHANG R, et al. Preparation and in vivo/in vitro characterization of Ticagrelor PLGA sustained-release microspheres for injection. Des Monomers Polym. 2021;24(1):305-319.
[36] 方玲,吴依繁,程光敏,等.血浆和腹膜透析液中万古霉素浓度的测定及在腹膜透析相关性腹膜炎患者中的应用[J].药学服务与研究,2021,21(2):128-132,145.
[37] 黄晓会,林志燕,沈艳琳,等.高效液相色谱法测定人脑脊液中万古霉素浓度及临床应用[J].药学与临床研究,2021,29(1):12-14.
[38] International standard ISO-10993-12. 2012.
[39] USP 42-NF37 biological reactivity tests, in vivo. 2019.
[40] 高欢,尹东锋.基于普朗尼克双配体修饰的载药纳米靶向聚合物胶束制备工艺的筛选及靶向性评价[J].军事医学,2021,45(8):614-631.
[41] WEI P, JING W, YUAN Z, et al. Vancomycin- and Strontium-Loaded Microspheres with Multifunctional Activities against Bacteria, in Angiogenesis, and in Osteogenesis for Enhancing Infected Bone Regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(34):30596-30609.
[42] DU L, YANG S, LI W, et al. Scaffold composed of porous vancomycin-loaded poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres: A controlled-release drug delivery system with shape-memory effect. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;78:1172-1178.
[43] MAO Y, ZHAO M, GE Y, et al. Novel Alginate-Chitosan Composite Microspheres for Implant Delivery of Vancomycin and In Vivo Evaluation. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2016;88(3):434-440.
[44] 王峰,涂家生,张钧寿,等.PLGA微球控释系统的突释及其控制[J].药学进展,2003,27(3):142-146.
[45] 孙美丽,班俊峰,黄思玉,等.PLGA微球载药量和包封率的影响因素及控制[J].广东药学院学报,2011,27(6):643-647.
[46] 邵陇龙.3D打印β-TCP负载INH/RFPPLGA缓释微球的构建及其抗感染成骨作用研究[D].兰州:甘肃中医药大学,2018.
|