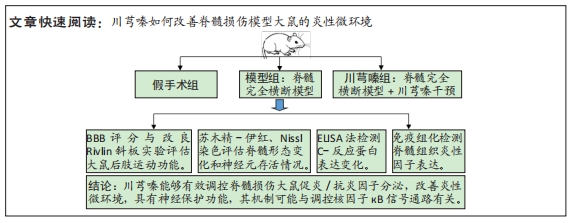
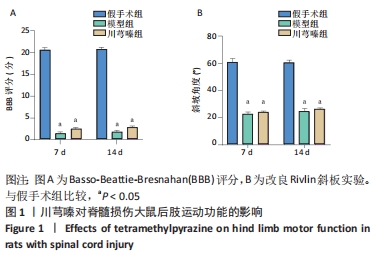
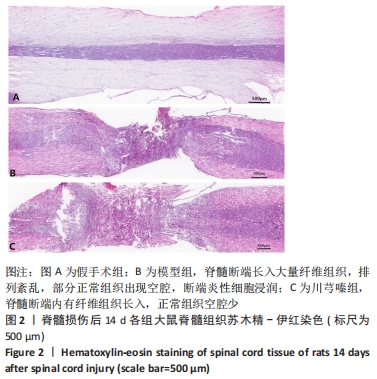
[1] AHUJA CS, NORI S, TETREAULT L, et al. Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury-Repair and Regeneration. Neurosurgery. 2017;80(3S):S9-S22.
[2] KARSY M, HAWRYLUK G. Modern Medical Management of Spinal Cord Injury. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2019;19(9):65.
[3] HAISMA JA, VAN DER WOUDE LH, STAM HJ, et al. Complications following spinal cord injury: occurrence and risk factors in a longitudinal study during and after inpatient rehabilitation. J Rehabil Med. 2007;39(5):393-398.
[4] YUAN X, WU Q, TANG Y, et al. Systemic microcirculation dysfunction after low thoracic spinal cord injury in mice. Life Sci. 2019;221:47-55.
[5] JAIN NB, AYERS GD, PETERSON EN, et al. Traumatic spinal cord injury in the United States, 1993-2012. JAMA. 2015;313(22):2236-2243.
[6] RIVERS CS, FALLAH N, NOONAN VK, et al. Health Conditions: Effect on Function, Health-Related Quality of Life, and Life Satisfaction After Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury. A Prospective Observational Registry Cohort Study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2018;99(3):443-451.
[7] ALIZADEH A, DYCK SM, KARIMI-ABDOLREZAEE S. Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury: An Overview of Pathophysiology, Models and Acute Injury Mechanisms. Front Neurol. 2019;10:282.
[8] FAN B, WEI Z, YAO X, et al. Microenvironment Imbalance of Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Transplant. 2018;27(6):853-866.
[9] BLOOM O, HERMAN PE, SPUNGEN AM. Systemic inflammation in traumatic spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 2020;325:113143.
[10] ORR MB, GENSEL JC. Spinal Cord Injury Scarring and Inflammation: Therapies Targeting Glial and Inflammatory Responses. Neurotherapeutics. 2018;15(3):541-553.
[11] 赵书杰,陈建,凡进,等.创伤性脊髓损伤后脊髓微环境失衡的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2020,30(10):942-947.
[12] DING Y, DU J, CUI F, et al. The protective effect of ligustrazine on rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via activating PI3K/Akt pathway. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2019;38(10):1168-1177.
[13] ZHANG H, DING S, XIA L. Ligustrazine inhibits the proliferation and migration of ovarian cancer cells via regulating miR-211. Biosci Rep. 2021;41(1):BSR20200199.
[14] ZHANG L, LU X, GONG L, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine Protects Blood-Spinal Cord Barrier Integrity by Modulating Microglia Polarization Through Activation of STAT3/SOCS3 and Inhibition of NF-кB Signaling Pathways in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Mice. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2020;10.1007/s10571-020-00878-3.
[15] 蒋昇源,邓博文,徐林,等.川芎嗪修复脊髓损伤的作用及机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(11):1886-1892.
[16] 贺丰,俞兴,穆晓红,等.新型脊髓完全横断缺损模型大鼠的建立[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(5):635-639.
[17] HU J, CAO Y, WU T, et al. Micro-CT as a Tool to Investigate the Efficacy of Tetramethylpyrazine in a Rat Spinal Cord Injury Model. Spine. 2016; 41(16):1272-1278.
[18] BASSO DM, BEATTIE MS, BRESNAHAN JC. A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 1995;12(1):1-21.
[19] RIVLIN AS, TATOR CH. Objective clinical assessment of motor function after experimental spinal cord injury in the rat. J Neurosurg. 1977;47(4):577-581.
[20] SONG HH, SONG TC, YANG T, et al. High mobility group box 1 mediates inflammatory response of astrocytes via cyclooxygenase 2/prostaglandin E2 signaling following spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(9):1848-1855.
[21] LUKACOVA N, KISUCKA A, KISS BIMBOVA K, et al. Glial-Neuronal Interactions in Pathogenesis and Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(24):13577.
[22] SAREMI J, MAHMOODI N, RASOULI M, et al. Advanced approaches to regenerate spinal cord injury: The development of cell and tissue engineering therapy and combinational treatments. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;146:112529.
[23] 柴乐,吕建兰,胡劲涛,等.诱导急性脊髓损伤模型大鼠炎症反应信号通路的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(8):1218-1223.
[24] HELLENBRAND DJ, QUINN CM, PIPER ZJ, et al. Inflammation after spinal cord injury: a review of the critical timeline of signaling cues and cellular infiltration. J Neuroinflammation. 2021;18(1):284.
[25] BECK KD, NGUYEN HX, GALVAN MD, et al. Quantitative analysis of cellular inflammation after traumatic spinal cord injury: evidence for a multiphasic inflammatory response in the acute to chronic environment. Brain. 2010;133(Pt 2):433-447.
[26] ANDERSON KM, WELSH CJ, YOUNG C, et al. Acute Phase Proteins in Cerebrospinal Fluid from Dogs with Naturally-Occurring Spinal Cord Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2015;32(21):1658-1665.
[27] 宋洁菲,周雨昕,张宇,等.炎症因子及其相关信号通路在脊髓损伤调控机制中的研究进展[J].中国医药导报,2021,18(32):38-41.
[28] LIN S, XU C, LIN J, et al. Regulation of inflammatory cytokines for spinal cord injury recovery. Histol Histopathol. 2021;36(2):137-142.
[29] CHEN J, CHEN YQ, SHI YJ, et al. VX-765 reduces neuroinflammation after spinal cord injury in mice. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(9):1836-1847.
[30] 邓贵营,曾高峰,岑忠喜,等.miRNA-136-5p对急性脊髓损伤模型大鼠炎症因子的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(15):2397-2402.
[31] 周小珏,赵小华,张安仁.脊髓损伤炎症中的NF-кB信号通路[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2020,36(10):1159-1164.
[32] ZHAO H, MEI X, YANG D, et al. Resveratrol inhibits inflammation after spinal cord injury via SIRT-1/NF-κB signaling pathway. Neurosci Lett. 2021;762:136151.
[33] XU L, BOTCHWAY BOA, ZHANG S, et al. Inhibition of NF-κB Signaling Pathway by Resveratrol Improves Spinal Cord Injury. Front Neurosci. 2018;12:690.
[34] 李敏,杨孝,孙年怡,等.脊髓损伤中TNF-α诱导细胞凋亡和坏死性凋亡的研究进展[J].广东医学,2018,39(18):2841-2844.
[35] HELLENBRAND DJ, REICHL KA, TRAVIS BJ, et al. Sustained interleukin-10 delivery reduces inflammation and improves motor function after spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;16(1):93.
[36] LI J, WEI J, WAN Y, et al. TAT-modified tetramethylpyrazine-loaded nanoparticles for targeted treatment of spinal cord injury. J Control Release. 2021;335:103-116.
[37] JIANG G, XIN R, YUAN W, et al. Ligustrazine ameliorates acute kidney injury through downregulation of NOD2mediated inflammation. Int J Mol Med. 2020;45(3):731-742.
[38] YU T, QU J, WANG Y, et al. Ligustrazine protects chondrocyte against IL-1β induced injury by regulation of SOX9/NF-κB signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(9):7419-7430.
[39] JI L, LI W, QIAN W, et al. The Role of Nanoparticles-Mediated Ligustrazine in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis and Its Effect on Matrix Metalloproteinases and Upstream NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Knee Osteoarthritis. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2021;21(2):1372-1377.
[40] ZHAO T, FU Y, SUN H, et al. Ligustrazine suppresses neuron apoptosis via the Bax/Bcl-2 and caspase-3 pathway in PC12 cells and in rats with vascular dementia. IUBMB Life. 2018;70(1):60-70.
[41] ZHANG Q, WANG J, ZHU L, et al. Ligustrazine Attenuates Hyperhomocysteinemia-induced Alzheimer-like Pathologies in Rats. Curr Med Sci. 2021;41(3):548-554.
[42] DU HY, WANG R, LI JL, et al. Ligustrazine protects against chronic hypertensive glaucoma in rats by inhibiting autophagy via the PI3K-Akt/mTOR pathway. Mol Vis. 2021;27:725-733.
[43] REN S, JIAO L, YANG S, et al. A Novel Co-Crystal of Bexarotene and Ligustrazine Improves Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Bexarotene in SD Rats. Pharmaceutics. 2020;12(10):906.
[44] TANG X, WANG H, CHEN H, et al. Protective Effects of Astragalus Membranaceus and Ligustrazine on Rat Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cell Injury after Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/ Reoxygenation by Suppressing the PKCδ/MARCKS Pathway. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2021;24(7):947-956.
[45] ZENG M, PAN L, QI S, et al. Systematic review of recent advances in pharmacokinetics of four classical Chinese medicines used for the treatment of cerebrovascular disease. Fitoterapia. 2013;88:50-75.
[46] 李洁,赵坤,马贤德.川芎嗪对脑缺血再灌注大鼠神经元抗凋亡作用及机制的实验研究[J].中华中医药学刊:1-14[2022-04-24].
[47] JIN Z, LIANG J, KOLATTUKUDY PE. Tetramethylpyrazine Preserves the Integrity of Blood-Brain Barrier Associated With Upregulation of MCPIP1 in a Murine Model of Focal Ischemic Stroke. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:710358.
[48] 张毅,祁文,吴迪,等.基于转录组测序技术研究川芎嗪对急性脊髓损伤模型大鼠基因表达的影响[J].中国药房,2020,31(11):1327-1335.
|