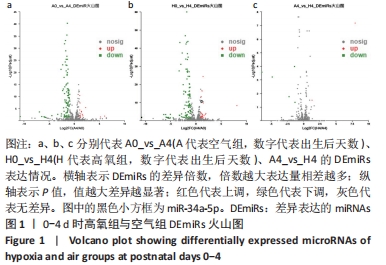
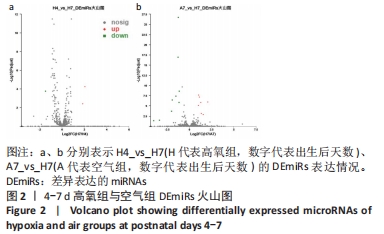
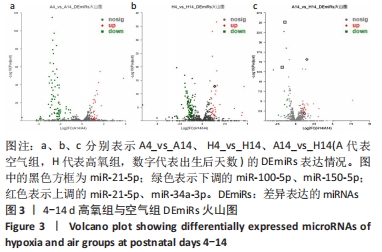
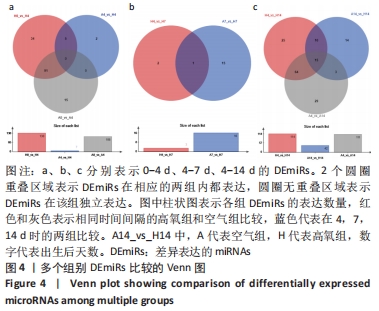
[1] NORTHWAY WH JR, ROSAN RC, PORTER DY. Pulmonary disease following respirator therapy of hyaline-membrane disease. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. N Engl J Med. 1967;276:357-368.
[2] HIGGINS RD, JOBE AH, KOSO-THOMAS M, et al. Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: Executive Summary of a Workshop.J Pediatr. 2018;197:300-308.
[3] BONADIES L, ZARAMELLA P, PORZIONATO A, et al. Present and Future of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. J Clin Med. 2020;9(5):1539.
[4] KALIKKOT THEKKEVEEDU R, GUAMAN MC, SHIVANNA B. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: A review of pathogenesis and pathophysiology. Respir Med. 2017;132: 170-177.
[5] DAY CL, RYAN RM. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: new becomes old again! Pediatr Res. 2017;81:210-213.
[6] IBRAHIM J, BHANDARI V. The definition of bronchopulmonary dysplasia: an evolving dilemma. Pediatr Res. 2018;84:586-588.
[7] JAIN D, FELDMAN A, SANGAM S. Predicting Long-Term Respiratory Outcomes in Premature Infants: Is It Time to Move beyond Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia? Children (Basel). 2020;7(12):283.
[8] JOBE AJ. The new BPD: an arrest of lung development. Pediatr Res. 1999; 46:641-643.
[9] BAUD O, WATTERBERG KL. Prophylactic postnatal corticosteroids: Early hydrocortisone. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019;24:202-206.
[10] HOU Y, LIU M, HUSTED C, et al. Activation of the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway during postnatal lung inflammation preserves alveolarization by suppressing macrophage inflammatory protein-2. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015;309:L593-604.
[11] MOHAMED I, ELREMALY W, ROULEAU T, et al. Oxygen and parenteral nutrition two main oxidants for extremely preterm infants: ‘It all adds up’. J Neonatal Perinatal Med. 2015;8:189-197.
[12] WARNER BB, STUART LA, PAPES RA, et al. Functional and pathological effects of prolonged hyperoxia in neonatal mice. Am J Physiol. 1998;275:L110-117.
[13] ABDEL GHANY EA, ALSHARANY W, ALI AA, et al. Anti-oxidant profiles and markers of oxidative stress in preterm neonates. Paediatr Int Child Health. 2016;36(2):134-140.
[14] TANG J, DIAO P, SHU X, et al. Quercetin and Quercitrin Attenuates the Inflammatory Response and Oxidative Stress in LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Cells: In Vitro Assessment and a Theoretical Model. Biomed Res Int. 2019; 2019:7039802.
[15] ZHANG XF, FODA HD. [Pulmonary apoptosis and necrosis in hyperoxia-induced acute mouse lung injury]. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2004; 27:465-468.
[16] NARASARAJU TA, CHEN H, WENG T, et al. Expression profile of IGF system during lung injury and recovery in rats exposed to hyperoxia: a possible role of IGF-1 in alveolar epithelial cell proliferation and differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 2006;97:984-998.
[17] DU T, ZAMORE PD. microPrimer: the biogenesis and function of microRNA. Development. 2005;132:4645-4652.
[18] SAHNI M, BHANDARI V. Recent advances in understanding and management of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. F1000Res. 2020;9:F1000 Faculty Rev-703. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.25338.1. eCollection 2020.
[19] AMEIS D, KHOSHGOO N, IWASIOW BM, et al. MicroRNAs in Lung Development and Disease. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2017;22:38-43.
[20] LAL CV, OLAVE N, TRAVERS C, et al. Exosomal microRNA predicts and protects against severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia in extremely premature infants. JCI Insight. 2018;3(5):e93994.
[21] SCHITTNY JC. Development of the lung. Cell Tissue Res. 2017;367:427-444.
[22] DONG J, JIANG G, ASMANN YW, et al. MicroRNA networks in mouse lung organogenesis. PLoS One. 2010;5:e10854.
[23] LIGNELLI E, PALUMBO F, MYTI D, et al. Recent advances in our understanding of the mechanisms of lung alveolarization and bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2019;317:L832-l887.
[24] AMBALAVANAN N, COTTEN CM, PAGE GP, et al. Integrated genomic analyses in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Pediatr. 2015;166:531-537 e513.
[25] ZHU X, LEI X, WANG J, et al. Protective effects of resveratrol on hyperoxia-induced lung injury in neonatal rats by alleviating apoptosis and ROS production. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020;33:4150-4158.
[26] SURATE SOLALIGUE DE, RODRÍGUEZ-CASTILLO JA, AHLBRECHT K, et al. Recent advances in our understanding of the mechanisms of late lung development and bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017;313(6):L1101-L1153.
[27] BURRI PH. Structural aspects of postnatal lung development - alveolar formation and growth. Biol Neonate. 2006;89:313-322.
[28] POPOVA AP, BENTLEY JK, CUI TX, et al. Reduced platelet-derived growth factor receptor expression is a primary feature of human bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014;307:L231-239.
[29] COHEN ED, IHIDA-STANSBURY K, LU MM, et al. Wnt signaling regulates smooth muscle precursor development in the mouse lung via a tenascin C/PDGFR pathway. J Clin Invest. 2009;119:2538-2549.
[30] RHEE CK, LEE SH, YOON H, et al. Effect of nilotinib on bleomycin-induced acute lung injury and pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Respiration. 2011;82:273-287.
[31] GORTNER L, SHEN J, TUTDIBI E. Sexual dimorphism of neonatal lung development. Klin Padiatr. 2013;225 64-69.
[32] RUIZ-CAMP J, QUANTIUS J, LIGNELLI E, et al. Targeting miR-34a/Pdgfra interactions partially corrects alveologenesis in experimental bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Embo Mol Med. 2019;11:17.
[33] SYED M, DAS P, PAWAR A, et al. Hyperoxia causes miR-34a-mediated injury via angiopoietin-1 in neonatal lungs. Nat Commun. 2017;8:1173.
[34] SULTAN M, ALGHETAA H, MOHAMMED A, et al. The Endocannabinoid Anandamide Attenuates Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome by Downregulating miRNA that Target Inflammatory Pathways. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:644281.
[35] ALHARRIS E, ALGHETAA H, SETH R, et al. Resveratrol Attenuates Allergic Asthma and Associated Inflammation in the Lungs Through Regulation of miRNA-34a That Targets FoxP3 in Mice. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2992.
[36] SACHINIDIS A, LOCHER R, VETTER W, et al. Different effects of platelet-derived growth factor isoforms on rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:10238-10243.
[37] ANDRAE J, GALLINI R, BETSHOLTZ C. Role of platelet-derived growth factors in physiology and medicine. Genes Dev. 2008;22:1276-1312.
[38] HE C, MEDLEY SC, KIM J, et al. STAT1 modulates tissue wasting or overgrowth downstream from PDGFRbeta. Genes Dev. 2017;31:1666-1678.
[39] LI J, MA J, LI M, et al. GYY4137 alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting the PDGFRβ/Akt/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway. Life Sci. 2021; 271:119192.
[40] PARSI S, SOLTANI BM, HOSSEINI E, et al. Experimental verification of a predicted intronic microRNA in human NGFR gene with a potential pro-apoptotic function. PLoS One. 2012;7:e35561.
[41] CHANG L, KARIN M. Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature. 2001;410:37-40.
[42] CARGNELLO M, ROUX PP. Activation and Function of the MAPKs and Their Substrates, the MAPK-Activated Protein Kinases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2011;75(1):50-83.
[43] HAMVAS A, FENG R, BI Y, et al. Exome sequencing identifies gene variants and networks associated with extreme respiratory outcomes following preterm birth. BMC Genet. 2018;19:94.
[44] LI J, LI Y, HE H, et al. Csk/Src/EGFR signaling regulates migration of myofibroblasts and alveolarization. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016; 310:L562-571.
[45] DAMMANN CE, NIELSEN HC, CARRAWAY KL, 3RD. Role of neuregulin-1 beta in the developing lung. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;167:1711-1716.
[46] PUREVDORJ E, ZSCHEPPANG K, HOYMANN HG, et al. ErbB4 deletion leads to changes in lung function and structure similar to bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008;294:L516-522.
[47] LIN CK, LIN YH, HUANG TC, et al. VEGF mediates fat embolism-induced acute lung injury via VEGF receptor 2 and the MAPK cascade. Sci Rep. 2019; 9:11713.
[48] REINHARDT J, LANDSBERG J, SCHMID-BURGK JL, et al. MAPK Signaling and Inflammation Link Melanoma Phenotype Switching to Induction of CD73 during Immunotherapy. Cancer Res. 2017;77:4697-4709.
[49] MO W, LI Y, CHANG W, et al. The Role of LncRNA H19 in MAPK Signaling Pathway Implicated in the Progression of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Cell Transplant. 2020;29:963689720918294.
[50] ZHAO W, MA L, CAI C, et al. Caffeine Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation by Suppressing MAPK/NF-κB and A2aR Signaling in LPS-Induced THP-1 Macrophages. Int J Biol Sci. 2019;15:1571-1581.
[51] KANODIA J, CHAI D, VOLLMER J, et al. Deciphering the mechanism behind Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) induced biphasic signal-response profiles. Cell Commun Signal. 2014;12:34.
[52] SHRESTHA AK, MENON RT, YALLAMPALLI C, et al. Adrenomedullin Deficiency Potentiates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Experimental Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Neonatal Mice. Am J Pathol. 2021;191(12):2080-2090.
[53] ZHANG ZQ, HONG H, LI J, et al. MicroRNA-214 promotes alveolarization in neonatal rat models of bronchopulmonary dysplasia via the PlGF-dependent STAT3 pathway. Mol Med. 2021;27:109.
[54] ZHAO YR, WANG D, LIU Y, et al. The PI3K/Akt, p38MAPK, and JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathways mediate the protection of SO2 against acute lung injury induced by limb ischemia/reperfusion in rats. J Physiol Sci. 2016;66:229-239.
[55] FRUMAN DA, CHIU H, HOPKINS BD, et al. The PI3K Pathway in Human Disease. Cell. 2017;170:605-635.
[56] ZHANG L, WANG P, SHEN Y, et al. Mechanism of lncRNA H19 in Regulating Pulmonary Injury in Hyperoxia-Induced Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia Newborn Mice. Am J Perinatol. 2020. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1721498.
[57] MENG A, ZHANG X, SHI Y. Role of p38 MAPK and STAT3 in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated mouse alveolar macrophages. Exp Ther Med. 2014;8:1772-1776.
[58] NI Y, WU S, WANG X, et al. Cucurbitacin I induces pro-death autophagy in A549 cells via the ERK-mTOR-STAT3 signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2018; 119:6104-6112.
[59] LIU X, CHEN M, CHEN B, et al. Advance in research of microRNA-21-5p regulate autophagy by targeting gene. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020;32:112-117.
[60] QIN S, CHEN M, JI H, et al. miR-21-5p regulates type II alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis in hyperoxic acute lung injury. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17:5796-5804.
[61] ZHANG W, XU L, CHEN M, et al. Effect of overexpression of microRNA-21-5p on early apoptosis of type II alveolar epithelial cells in rats with hyperoxic acute lung injury. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019;31:978-982.
[62] QI A, WANG T, LI W, et al. The effect of miR-21-5p on the MAP2K3 expressions and cellular apoptosis in the lung tissues of neonatal rats with hyperoxia-induced lung injuries. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13:2784-2793.
|