[1] YÁÑEZ-MÓ M, SILJANDER PR, ANDREU Z, et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:27066.
[2] ZHANG Y, LIU Y, LIU H, et al. Exosomes: biogenesis, biologic function and clinical potential. Cell Biosci. 2019;9:19.
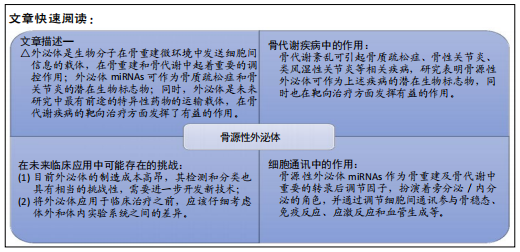
[3] XIE Y, CHEN Y, ZHANG L, et al. The roles of bone-derived exosomes and exosomal microRNAs in regulating bone remodelling. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(5):1033-1041.
[4] VALADI H, EKSTRÖM K, BOSSIOS A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654-659.
[5] JANAS T, JANAS MM, SAPOŃ K, et al. Mechanisms of RNA loading into exosomes. FEBS Lett. 2015;589(13):1391-1398.
[6] HADJIARGYROU M, DELIHAS N. The intertwining of transposable elements and non-coding RNAs. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(7):13307-13328.
[7] GENNARI L, BIANCIARDI S, MERLOTTI D. MicroRNAs in bone diseases. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28(4):1191-1213.
[8] XIAO Z, CAMALIER CE, NAGASHIMA K, et al. Analysis of the extracellular matrix vesicle proteome in mineralizing osteoblasts. J Cell Physiol. 2007;210(2):325-335.
[9] HUYNH N, VONMOSS L, SMITH D, et al. Characterization of Regulatory Extracellular Vesicles from Osteoclasts. J Dent Res. 2016;95(6):673-679.
[10] QIN Y, PENG Y, ZHAO W, et al. Myostatin inhibits osteoblastic differentiation by suppressing osteocyte-derived exosomal microRNA-218: A novel mechanism in muscle-bone communication. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(26):11021-11033.
[11] LI D, LIU J, GUO B, et al. Osteoclast-derived exosomal miR-214-3p inhibits osteoblastic bone formation. Nat Commun. 2016;7:10872.
[12] KOUWAKI T, OKAMOTO M, TSUKAMOTO H, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Deliver Host and Virus RNA and Regulate Innate Immune Response. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(3):666.
[13] BELL E, TAYLOR MA. Functional Roles for Exosomal MicroRNAs in the Tumour Microenvironment. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2016;15:8-13.
[14] ALEXANDER M, HU R, RUNTSCH MC, et al. Exosome-delivered microRNAs modulate the inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7321.
[15] WANG N, CHEN C, YANG D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles, via miR-210, improve infarcted cardiac function by promotion of angiogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017;1863(8):2085-2092.
[16] LUAN X, ZHOU X, TROMBETTA-ESILVA J, et al. MicroRNAs and Periodontal Homeostasis. J Dent Res. 2017;96(5):491-500.
[17] PROFF P, RÖMER P. The molecular mechanism behind bone remodelling: a review. Clin Oral Investig. 2009;13(4):355-362.
[18] MAEDA Y, FARINA NH, MATZELLE MM, et al. Synovium-Derived MicroRNAs Regulate Bone Pathways in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Bone Miner Res. 2017;32(3):461-472.
[19] FASANARO P, GRECO S, LORENZI M, et al. An integrated approach for experimental target identification of hypoxia-induced miR-210. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(50):35134-35143.
[20] SUGATANI T, HRUSKA KA. MicroRNA-223 is a key factor in osteoclast differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 2007;101(4):996-999.
[21] SUN W, ZHAO C, LI Y, et al. Osteoclast-derived microRNA-containing exosomes selectively inhibit osteoblast activity. Cell Discov. 2016;2: 16015.
[22] CHEN X, WANG Z, DUAN N, et al. Osteoblast-osteoclast interactions. Connect Tissue Res. 2018;59(2):99-107.
[23] HADJIARGYROU M, KOMATSU DE. The Therapeutic Potential of MicroRNAs as Orthobiologics for Skeletal Fractures. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34(5):797-809.
[24] DENG L, WANG Y, PENG Y, et al. Osteoblast-derived microvesicles: A novel mechanism for communication between osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Bone. 2015;79:37-42.
[25] BAGLIO SR, PEGTEL DM, BALDINI N. Mesenchymal stem cell secreted vesicles provide novel opportunities in (stem) cell-free therapy. Front Physiol. 2012;3:359.
[26] PLOTKIN LI, BELLIDO T. Osteocytic signalling pathways as therapeutic targets for bone fragility. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016;12(10):593-605.
[27] SATO M, SUZUKI T, KAWANO M, et al. Circulating osteocyte-derived exosomes contain miRNAs which are enriched in exosomes from MLO-Y4 cells. Biomed Rep. 2017;6(2):223-231.
[28] EKSTRÖM K, OMAR O, GRANÉLI C, et al. Monocyte exosomes stimulate the osteogenic gene expression of mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e75227.
[29] XU JF, YANG GH, PAN XH, et al. Altered microRNA expression profile in exosomes during osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(12):e114627.
[30] ZHAO L, JIANG S, HANTASH BM. Transforming growth factor beta1 induces osteogenic differentiation of murine bone marrow stromal cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(2):725-733.
[31] NARAYANAN R, HUANG CC, RAVINDRAN S. Hijacking the Cellular Mail: Exosome Mediated Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:3808674.
[32] LIU S, LIU D, CHEN C, et al. MSC Transplantation Improves Osteopenia via Epigenetic Regulation of Notch Signaling in Lupus. Cell Metab. 2015;22(4):606-618.
[33] QIN Y, WANG L, GAO Z, et al. Bone marrow stromal/stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles regulate osteoblast activity and differentiation in vitro and promote bone regeneration in vivo. Sci Rep. 2016;6:21961.
[34] SANTOS TS, ABUNA RP, CASTRO RAUCCI LM, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Repress Osteoblast Differentiation Under Osteogenic-Inducing Conditions. J Cell Biochem. 2015;116(12):2896-2902.
[35] DAVIS C, DUKES A, DREWRY M, et al. MicroRNA-183-5p Increases with Age in Bone-Derived Extracellular Vesicles, Suppresses Bone Marrow Stromal (Stem) Cell Proliferation, and Induces Stem Cell Senescence. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017;23(21-22):1231-1240.
[36] CHEN W, HUANG Y, HAN J, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of mesenchymal stromal cells-derived exosome. Immunol Res. 2016;64(4): 831-840.
[37] DEL FATTORE A, LUCIANO R, PASCUCCI L, et al. Immunoregulatory Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles on T Lymphocytes. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(12):2615-2627.
[38] PACHLER K, KETTERL N, DESGEORGES A, et al. An In Vitro Potency Assay for Monitoring the Immunomodulatory Potential of Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(7):1413.
[39] SILVA AM, ALMEIDA MI, TEIXEIRA JH, et al. Dendritic Cell-derived Extracellular Vesicles mediate Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell recruitment. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):1667.
[40] YAVROPOULOU MP, ANASTASILAKIS AD, MAKRAS P, et al. Expression of microRNAs that regulate bone turnover in the serum of postmenopausal women with low bone mass and vertebral fractures. Eur J Endocrinol. 2017;176(2):169-176.
[41] MARTIN PJ, HAREN N, GHALI O, et al. Adipogenic RNAs are transferred in osteoblasts via bone marrow adipocytes-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs). BMC Cell Biol. 2015;16:10.
[42] WEILNER S, SCHRAML E, WIESER M, et al. Secreted microvesicular miR-31 inhibits osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Aging Cell. 2016;15(4):744-754.
[43] QIU M, ZHAI S, FU Q, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal microRNA-150-3p promotes osteoblast proliferation and differentiation in osteoporosis. Hum Gene Ther. 2020 Oct 27. doi: 10.1089/hum.2020.005. Online ahead of print.
[44] ANDERSON HC, MULHALL D, GARIMELLA R. Role of extracellular membrane vesicles in the pathogenesis of various diseases, including cancer, renal diseases, atherosclerosis, and arthritis. Lab Invest. 2010; 90(11):1549-1557.
[45] XIE Q, WEI M, KANG X, et al. Reciprocal inhibition between miR-26a and NF-κB regulates obesity-related chronic inflammation in chondrocytes. Biosci Rep. 2015;35(3):e00204.
[46] KATO T, MIYAKI S, ISHITOBI H, et al. Exosomes from IL-1β stimulated synovial fibroblasts induce osteoarthritic changes in articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(4):R163.
[47] KOLHE R, HUNTER M, LIU S, et al. Gender-specific differential expression of exosomal miRNA in synovial fluid of patients with osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):2029.
[48] YIN X, WANG JQ, YAN SY. Reduced miR‑26a and miR‑26b expression contributes to the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis via the promotion of p65 translocation. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15(2):551-558.
[49] TAO SC, YUAN T, ZHANG YL, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-140-5p-overexpressing human synovial mesenchymal stem cells enhance cartilage tissue regeneration and prevent osteoarthritis of the knee in a rat model. Theranostics. 2017;7(1):180-195.
[50] CHEN X, SHI Y, XUE P, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-136-5p inhibits chondrocyte degeneration in traumatic osteoarthritis by targeting ELF3. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020;22(1):256.
[51] WANG Z, YAN K, GE G, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-155-5p-overexpressing synovial mesenchymal stem cells prevent osteoarthritis via enhancing proliferation and migration, attenuating apoptosis, and modulating extracellular matrix secretion in chondrocytes. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2020 Oct 25. doi: 10.1007/s10565-020-09559-9. Online ahead of print.
[52] ZAFARI P, ZARIFIAN A, ALIZADEH-NAVAEi R, et al. Asymmetric and symmetric dimethylarginine concentration as an indicator of cardiovascular diseases in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of case-control studies. Clin Rheumatol. 2020;39(1):127-134.
[53] WITHROW J, MURPHY C, LIU Y, et al. Extracellular vesicles in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18(1):286.
[54] STANCZYK J, PEDRIOLI DM, BRENTANO F, et al. Altered expression of MicroRNA in synovial fibroblasts and synovial tissue in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(4):1001-1009.
[55] NAKASA T, MIYAKI S, OKUBO A, et al. Expression of microRNA-146 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(5): 1284-1292.
[56] BHAUMIK D, SCOTT GK, SCHOKRPUR S, et al. MicroRNAs miR-146a/b negatively modulate the senescence-associated inflammatory mediators IL-6 and IL-8. Aging (Albany NY). 2009;1(4):402-411.
[57] MENG Q, QIU B. Exosomal MicroRNA-320a Derived From Mesenchymal Stem Cells Regulates Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-Like Synoviocyte Activation by Suppressing CXCL9 Expression. Front Physiol. 2020;11: 441.
[58] VAN DER POL E, BÖING AN, HARRISON P, et al. Classification, functions, and clinical relevance of extracellular vesicles. Pharmacol Rev. 2012; 64(3):676-705.
[59] MAUSE SF, WEBER C. Microparticles: protagonists of a novel communication network for intercellular information exchange. Circ Res. 2010;107(9):1047-1057.
[60] VAN DER POL E, HOEKSTRA AG, STURK A, et al. Optical and non-optical methods for detection and characterization of microparticles and exosomes. J Thromb Haemost. 2010;8(12):2596-2607.
(责任编辑:MZH,ZN,SX)
|