中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (25): 4045-4052.doi: 10.12307/2021.018
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
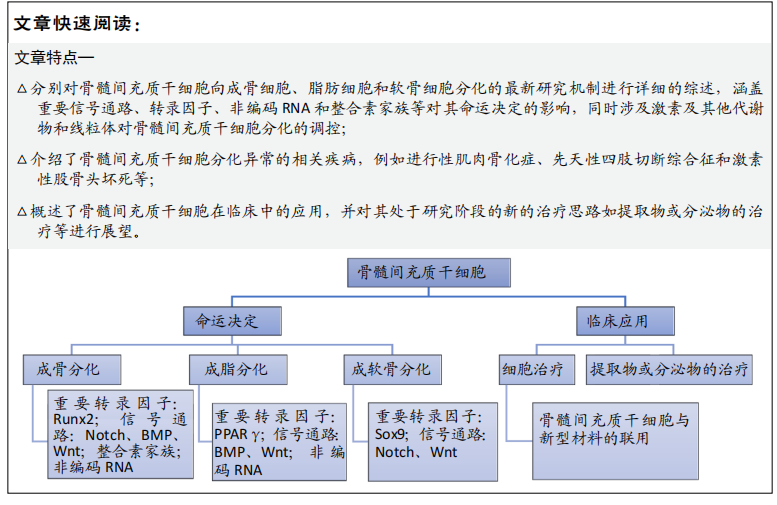
骨骼微环境中谁决定间充质干细胞的分化命运
张纯希,李 想,周钰翔,刘 禛,杨于权,贾 浩
- 上海交通大学医学院基础医学院,上海市肿瘤微环境与炎症重点实验室,上海市 200025
-
收稿日期:2020-05-11修回日期:2020-05-27接受日期:2020-07-06出版日期:2021-09-08发布日期:2021-03-30 -
通讯作者:贾浩,副研究员,硕士生导师,上海交通大学医学院基础医学院,上海市肿瘤微环境与炎症重点实验室,上海市 200025 -
作者简介:张纯希,女,1999年生,上海市人,汉族,上海交通大学医学院本科在读。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金面上项目(31970679),项目负责人:贾浩;上海市青年科技启明星项目(19QA1405000),项目负责人:贾浩;上海高水平地方高校创新团队,项目参与人:贾浩
Fate decision of mesenchymal stem cells in bone microenvironment
Zhang Chunxi, Li Xiang, Zhou Yuxiang, Liu Zhen, Yang Yuquan, Jia Hao
- Shanghai Key Laboratory for Tumor Microenvironment and Inflammation, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China
-
Received:2020-05-11Revised:2020-05-27Accepted:2020-07-06Online:2021-09-08Published:2021-03-30 -
Contact:Jia Hao, Associate researcher, Master’s supervisor, Shanghai Key Laboratory for Tumor Microenvironment and Inflammation, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China -
About author:Zhang Chunxi, Shanghai Key Laboratory for Tumor Microenvironment and Inflammation, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31970679 (to JH); the Shanghai Rising-Star Program, No. 19QA1405000 (to JH); the Shanghai High-Level Local University Innovation Team (to JH)
摘要:
文题释义:
骨骼微环境:指的是骨骼在分子特征或细胞层面的相关骨细胞、基质细胞、微循环、信号转导通路、骨机械负荷、骨pH值环境等多方面、多组分构成的骨细胞或骨骼的生存环境,主要构成有骨髓基质、微血管、成骨细胞、破骨细胞、脂肪细胞、成软骨细胞、造血细胞及相关细胞因子等,是骨吸收、骨重建、造血、免疫的重要场所。骨骼微环境的改变和很多疾病密切相关,如骨质疏松、多发性骨髓瘤、骨髓增生异常综合征等。
间充质干细胞:是来源于发育早期中胚层的一类多能干细胞,主要存在于各种结缔组织以及器官的间质中,以骨髓和脂肪组织中含量最丰富。骨髓间充质干细胞作为成骨细胞、脂肪细胞和软骨细胞的共同祖细胞,在分化平衡方面发挥至关重要的作用,同时外部因子如物化因素、非编码RNA、代谢等共同参与其分化的调控,而其分化失调与多种病理生理过程相关,例如骨质疏松、肥胖和衰老等。
背景:骨髓间充质干细胞是骨髓组织中的一群多能干细胞,是成骨细胞、脂肪细胞和软骨细胞的共同祖细胞,遗传信息和外界刺激共同参与骨髓间充质干细胞分化命运的调控,而其分化失调与多种病理生理过程相关,例如骨质疏松、肥胖和衰老等。中国国家卫生健康委员会2018年调查显示,骨质疏松已经成为中国中老年人群的重要健康问题,50岁以上男性骨质疏松症患病率为6.0%,女性患病率则达到32.1%,65岁以上女性的骨质疏松症患病率更是达到51.6%。
目的:总结骨髓间充质干细胞分化的调控机制,更好地理解骨质疏松等疾病的发生发展,从而为其治疗提供新思路。
方法:检索中国知网全文数据库、PubMed数据库自1997年1月至2020年5月所发表的相关文献,以“BMSCs,cell differentiation,osteoblasts,chondrocytes,adipocytes”为英文检索词,“骨髓间充质干细胞,细胞分化,成骨细胞,软骨细胞,脂肪细胞”为中文检索词。根据纳入与排除标准对所有文章进行初筛后,保留相关性较高的文章进行综述。
结果与结论:BMPs、Wnt和Notch等信号通路,Runx2、C/EBP和PPARγ等转录因子,非编码RNA,激素及线粒体等众多因素共同参与骨髓间充质干细胞分化的调控,任何环节的异常都可能导致病理状态的发生,骨髓间充质干细胞与新型材料的联合应用可能为骨质疏松等疾病提供新的治疗思路。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5207-1618(张纯希)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
张纯希, 李 想, 周钰翔, 刘 禛, 杨于权, 贾 浩. 骨骼微环境中谁决定间充质干细胞的分化命运[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(25): 4045-4052.
Zhang Chunxi, Li Xiang, Zhou Yuxiang, Liu Zhen, Yang Yuquan, Jia Hao. Fate decision of mesenchymal stem cells in bone microenvironment[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4045-4052.
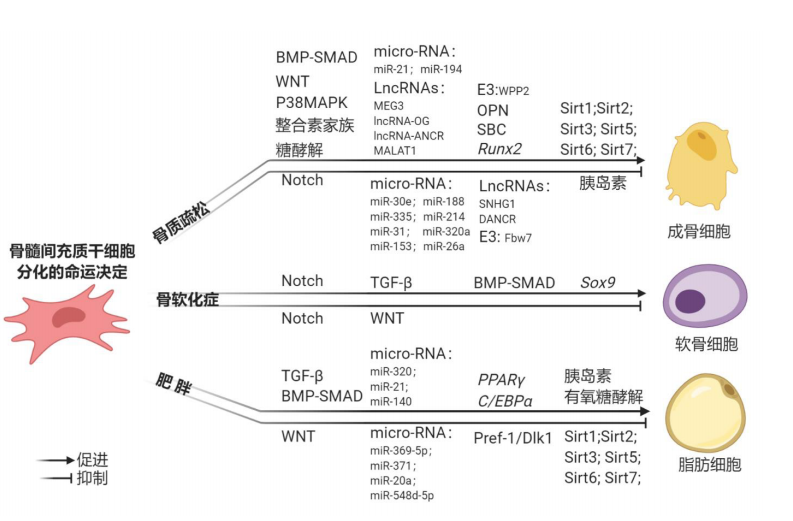
2.1.1 骨形态发生蛋白(bone morphogenetic protein,BMP)信号通路参与骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化 BMPs是转化生长因子β超家族的一员,在骨基质中大量存在[4],通过与Ⅰ型、Ⅱ型BMP受体结合,激活经典的BMPs-SMAD信号通路和非经典的BMPs-MAPK信号通路。重组BMP2和BMP7在颅面畸形、骨折愈合和脊柱融合的临床试验中已被广泛研究[5]。刘小钰等[6]发现补骨脂素能上调 BMP2 基因的表达,提高Smad1、Smad5以及Smad8的磷酸化水平,促进成骨细胞的分化与增殖。BMPⅠ型受体活化素1型受体(Activin A Receptor type 1,ACVR1)突变会导致进行性肌肉骨化症,表现为肌肉等结缔组织进行性骨化[7]。
BMPs-SMAD信号通路受到细胞外蛋白的调控,如
CHORDIN、GREMLIN2,这些蛋白在结构上具有重复的富含半胱氨酸的结构域,通过阻断BMPs和受体的结合抑制
BMPs-SMAD信号通路,可以起到BMP拮抗作用[8]。然而,并非所有具有该结构特点的蛋白质都起到BMP拮抗作用。例如NOGGIN在一些动物模型中通过阻断BMPs和受体结合抑制成骨作用[9],但在人类骨髓间充质干细胞中通过诱导BMP2和骨钙素的生成发挥促进成骨作用[10]。此外,Chordin-Like1
可以通过增强BMP4-SMAD通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨作用[11]。
2.1.2 Wnt信号通路参与骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化 Wnt信号通路已被证实在细胞命运决定、增殖和分化中起重要作用。在经典的Wnt/β-catenin信号通路中,Wnt通过和受体Frizzled以及共受体LRP5/6结合激活胞质内散乱蛋白
(DSH),散乱蛋白的激活抑制由活化蛋白C(APC)、Axin蛋白和糖原合成酶激酶3β (GSK-3β)组成的细胞内复合物来完成。GSK-3β可以磷酸化β-catenin,促进其泛素化降解。Axin/
GSK-3β/APC复合物的抑制使β-catenin在胞质中积聚,进入细胞核内与TCF/LEF结合[5],激活包括Runx2在内的靶基因转录,Runx2基因的启动可以明显促进成骨细胞分化[12]。Wnt6、Wnt10a和Wnt10b均可通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路促进成骨分化[13]。LRP5功能缺失性突变会导致骨质疏松-假性神经性胶质瘤综合征[14],而LRP5功能获得性突变表现为骨量增多[15]。在大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞中靶向敲除β-catenin,大鼠的长骨特别是骨骺区域以及椎间盘均出现严重缺损[16]。Wnt3在人类早期阶段四肢形成过程中有重要作用,Wnt3基因突变会导致一种以四肢完全缺失为特征的罕见病——先天性四肢切断综合征[17]。
在非经典的Wnt信号通路中,Wnt3a信号可以通过LRP5、RAC1激活mTORC2和AKT,促进己糖激酶2(HK2)、磷酸果糖激酶1(PFK1)、果糖-2,6-二磷酸酶3(PFKFB3)等多种糖酵解酶的上调,从而促进有氧糖酵解即Warburg效应,促进成骨分化[18]。Wnt/mTORC1信号通路通过三羧酸循环增加谷氨酰胺的消耗,提供能量的同时,可促进一般性调控阻遏蛋白激酶2(GCN2)介导的综合应激反应(ISR),促进氨基酸供应、tRNA氨基酰化和蛋白质折叠相关基因的表达,进而促进成骨过程中相关蛋白质的合成[19]。
2.1.3 Notch信号通路参与骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化 Notch信号通路在哺乳动物的细胞命运决定中起重要作用,通过相邻细胞的Notch受体(Notch1-4)和Notch配体(Jagged 1,Jagged 2以及Delta-like 1,Delta-like 3,Delta-like 4)相
互作用,Notch蛋白经过3次剪切,Notch胞内段(NICD)释放入胞质,并进入细胞核与转录因子CSL结合,从而激活HES、HEY、HERP等碱性-螺旋-环-螺旋(basic helix-loop-helix,
bHLH)转录抑制因子家族的靶基因,发挥生物学作用[20]。在骨骼内,Notch信号通路可以抑制成骨分化。Notch 2的稳定突变可导致Hajdu-Cheney综合征,以严重的进行性骨质丢失为特征[21]。LEE等[22]发现Notch信号通路通过干扰骨髓间充质干细胞的葡萄糖代谢,抑制其成骨分化,机制如下:Notch信号通路下调果糖-2,6-二磷酸酶3(PFKFB3)、果糖-2,6-二磷酸酶4(PFKFB4)、乳酸脱氢酶 A(LDHA)和线粒体复合体1基因的表达,线粒体的氧化磷酸化减少,活性氧产生减少,AMP依赖的蛋白激酶(AMP-activated protein kinase,AMPK)活性降低,从而葡萄糖的分解代谢进一步降低,抑制骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。
2.1.4 骨髓间充质干细胞促进成骨分化的重要转录因子 转录因子Runx2是成骨细胞分化的重要决定因子,Runx2单倍剂量不足可导致颅骨锁骨发育不全综合征,主要表现为锁骨发育不全和颅缝不闭合[23-24]。Runx2发挥作用与葡萄糖的摄取有重要的关系,葡萄糖是成骨细胞的主要营养物质,主要通过Glut1摄取,在成骨细胞生长发育中有重要的作用[25]。
葡萄糖摄取可以抑制Runx2被蛋白酶体降解,从而引起Runx2积累,促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化;此外,葡萄糖的摄取也可以通过抑制AMPK活性,增强mTORC1活性,增强骨基质的主要成分Ⅰ型胶原的合成。当葡萄糖摄取受到影响后,Runx2不能诱导成骨细胞分化[25]。
骨桥蛋白也可以通过与整合素αvβ1的相互作用调节C/EBPα的表达,抑制骨髓间充质干细胞成脂分化以及促进其成骨分化。实验中通过中和抗体的方法或利用siRNA敲除骨桥蛋白的表达,促进成脂分化和抑制成骨分化[26]。
泛素连接酶WWP2和Fbw7在骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化中起重要作用[27-28]。作为泛素连接酶,WWP2可以通过单泛素化Runx2增强其转录活性,促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化,而Fbw7通过泛素化降解Runx2,抑制骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。
2.1.5 整合素家族参与骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化 整合素家族在体内参与了骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化调控的过
程[26]。整合素使局灶性黏附激酶(FAK)磷酸化[29],FAK进一步介导ERK1/2和p38的活化,而p38的活化可以激活Runx2,从而促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨分化。
整合素还可以将机械信号转导到肌动蛋白细胞骨架,这一作用同样可以促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化并抑制成脂分化,主要是SRC家族激酶Fyn可以介导mTORC2的机械活化和FAK的磷酸化[30];同时FAK也是mTORC2活化的增强剂,可以进一步活化 mTORC2。Fyn/Fak/mTORC2信号通路通过进一步激活β-catenin信号转导从而抑制骨髓间充质干细胞向脂肪分化[31]。
外界微环境产生的空间边界条件可以施加特定的几何和空间约束,影响器官的生长和组织结构的稳态[32]。研究表明骨髓间充质干细胞对空间边界条件产生的机械信号十分敏感。通过单分散孔三维支架及均匀球形几何结构对成骨细胞分化的研究发现,在直径为100 μm和150 μm空间边界条件下培养的骨髓间充质干细胞具有最强的成骨分化能力。这种现象与骨髓间充质干细胞形态、肌动蛋白细胞骨架组织、α2和α5整合素的局部黏附分布密切相关,沉默整合素α2或α5后,可以显著降低上述机械敏感性,因此可以说明整合素α2和α5作为机械敏感性分子,可以介导骨髓间充质干细胞在球形微环境下增强成骨分化能力。
2.1.6 非编码RNA参与骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化 常见的非编码RNA包括长链非编码RNA(long non-coding RNA,lncRNA)、微小RNA(micro-RNA)和环状RNA(circ-RNA)等。研究发现这些非编码RNA在骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化中发挥着不同的作用。JIANG等[33]发现lncRNA SNHG1可以抑制骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。在骨质疏松小鼠模型中,研究发现lncRNA SNHG1表达明显上调,lncRNA SNHG1通过促进泛素连接酶Nedd4和p-p38的相互作用,加速了p-p38的泛素化降解,通过抑制p38-MAPKs信号通路阻碍了骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。ZHANG等[34]研究发现lncRNA DANCR通过抑制p38-MAPKs信号通路进而抑制骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。ZHUANG等[35]研究发现MEG3主要通过激活BMP4的转录活性,促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。TANG等[36]运用基因微阵列的方法,发现了lncRNA-OG可以通过与异质性胞核核糖核蛋白K(hnRNPK)相互作用,激活BMP信号通路,促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化。研究还发现了lncRNA-ANCR和MALAT1均可以促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[37-38]。
微小RNA在骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的命运决定中也发挥了重要的作用。研究发现MiR-30e通过降解LRP6和IGF2抑制骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[39]。MiR-188通过靶向HDAC9抑制骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[40]。MiR-335通过降解Runx2抑制骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[26]。MiR-214通过降解 FGFR1抑制骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[41]。MiR-31
也是负调控骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的微小RNA [42]。
MiR-320a过表达可以抑制BMP的同源序列HOXA10,从而抑制骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[43]。MiR-153可以直接靶向降解BMPR2,抑制骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[26]。但是也有微小RNA可以促进成骨分化,如miR-26a通过抑制Tob1或者GSK3β蛋白的表达水平[26],激活BMP-Smad信号通路。MiR-21通过上调Runx2的表达,促进了骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的能力[44]。MiR-194通过激活COUP-TFII,促进了骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的能力[26]。综上所述,非编码RNA在骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化过程中起着非常关键的作用。
2.2 骨髓间充质干细胞向脂肪细胞分化的机制研究
2.2.1 BMP 信号通路参与骨髓间充质干细胞的成脂分化 BMP信号通路可以通过促进成脂分化的关键转录因子过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ(Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ,PPARγ) 和C/EBPα的表达,增加脂肪生成。参与间充质干细胞向脂肪细胞分化的主要有BMP2和BMP4,它们作为配体与细胞表面的BMPR1A受体结合使Smad1磷酸化,Smad1与Smad4形成复合物并进入核内[45]。Smad1/4信号的激活也可以促进Shn2进入细胞核并与PPARγ启动子结合,在C/EBPα的协同作用下促进PPARγ的转录生成,从而促进脂肪生成。在BMP信号通路中,BMP2既能促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成脂分化也能促进其成骨分化,ZUR NIEDEN等[46]研究表明低剂量的BMP2可以促进C3H10T1/2成脂分化,而高剂量的BMP 2可以促进C3H10T1/2成骨和成软骨分化,因此,BMP2对于骨髓间充质干细胞的分化是具有剂量依赖性的。此外,XU等[47]发现BMP途径下游的p38 MAPK信号级联对脂肪细胞的生成也有重要作用,在相同的细胞模型中,p38基因的敲除会导致骨髓间充质干细胞成脂肪分化异常。
2.2.2 Wnt信号通路参与骨髓间充质干细胞的成脂分化 Wnt信号通路的经典途径和非经典途径均可以通过抑制成脂分化的关键转录因子PPARγ和C/EBPα的表达,从而抑制脂肪生成。在经典途径中,PPARγ的抑制作用主要是通过β-catenin完成的,配体的结合通过抑制磷酸化稳定β-catenin,未磷酸化的β-catenin进入细胞核不仅能阻断PPARγ的合成,还可以干扰其转录活性[48-49]。在非经典途径中,Wnt的结合刺激细胞内Ca2+释放,使钙离子依赖性蛋白(CaMKⅡ蛋白激酶C和钙调神经磷酸酶)被激活,进而调节下游靶点TAK1、TAB2,最终抑制PPARγ,抑制脂肪分化。因此,Wnt信号通路的负调控蛋白,例如硬化蛋白(SOST)和Dickkopf-1(DKK1)
等[6],可以促进脂肪细胞的生成,而Sirtuin 1(SIRT1)等可以通过激活Wnt信号通路以及抑制Wnt信号通路的负调控因子抑制脂肪的生成[50]。在该信号通路中,Wnt10b被认为是Wnt信号中最重要的内源性调控因子,过表达Wnt10b的小鼠可以抵抗由饮食引起的肥胖以及相关的葡萄糖耐受不
良[51]。此外,衰老相关的脂肪细胞增加也被认为与Wnt10b的减少有关。
2.2.3 骨髓间充质干细胞促进成脂分化的重要转录因子 PPARγ是类固醇/甲状腺激素受体基因超家族成员,存在于哺乳动物中,由多不饱和脂肪酸及其代谢产物激活[52],通过与视黄质X受体形成异二聚体,与靶基因位点相互作用,招募共激活蛋白促进成脂分化相关基因如aP2,CD36,LPL,PEPCK等的转录[53]。PPARγ是几乎所有脂肪生成信号通路的汇集点,它在骨髓间充质干细胞成脂肪分化的2个阶段中表达均增强:在脂肪生成阶段,锌指蛋白Zfp423在早期通过一系列非Smad依赖的过程促进PPARγ表达;在脂肪生成的终端分化阶段,PPARγ在C/EBPα的正反馈作用下表达量逐渐增加,从而促进脂肪细胞生成,PPARγ蛋白的缺失会导致几乎所有的脂肪生成途径都不能顺利进行[54]。在前脂肪细胞中,PPARγ发挥作用不需要外源性配体的激活,但非成脂的成纤维细胞向脂肪细胞分化需要TZD(噻唑烷二酮类)的激活。此外,WALKEY等[55]发现异位表达一种没有功能配体结合域的PPARγ也能够支持脂肪细胞分化,这在一定程度上质疑了PPARγ促进脂肪生成的条件。在激素诱导的激素性股骨头坏死小鼠模型中,miR-27a的显著下调可以导致PPARγ的上调,引起骨髓间充质干细胞成脂肪分化增高从而导致骨髓内脂肪组织增生,最终引起骨内压增高,局部骨组织缺血变性坏死,因此PPARγ的异常是激素性股骨头坏死的病因之
一[56]。Pref-1/Dlk1是一种已知的脂肪细胞分化的负向调节因子,在发育过程中与骨骼畸形、生长迟缓和肥胖有关[57]。Pref-1可以通过与纤维连接蛋白相互作用抑制脂肪生成。纤维连接蛋白是细胞外基质中的重要组成部分,可与各种整合素受体相互作用并抑制PPARγ的转录活性,抑制骨髓间充质干细胞成脂分化。相对于骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,成脂分化是一个更加复杂的过程,这个过程不仅存在一个复杂转录因子网络的激活,还存在许多转录因子的抑制,多种调控方式构成复杂的调控网络,从而可以精确地调控骨髓间充质干细胞的成脂分化[58]。
2.2.4 非编码RNA参与骨髓间充质干细胞的成脂分化 在骨髓间充质干细胞成脂分化过程中,miR-369-5p和miR-371
可以抑制骨髓间充质干细胞的成脂作用[59]。miR-20a和
miR-548d-5p通过抑制 PPARγ信号通路,从而抑制骨髓间充质干细胞成脂分化[60]。另外,miR-320家族包括miR-320a,miR-320b,miR-320c,miR-320d 和 miR-320e,在骨髓间充质干细胞成脂分化的过程中表达上调[61]。miR-21通过阻断TGF-β信号通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成脂作用[62]。另外,miR-140 可以通过下调骨硬骨症相关跨膜蛋白Ostm1进而影响Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成脂分化[63]。
2.3 骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨细胞分化的机制研究
2.3.1 Wnt 信号通路参与骨髓间充质干细胞的成软骨分化 经典的Wnt信号通路参与骨髓间充质干细胞成软骨分化、间充质的凝集及成熟肥大的所有阶段。Wnt1类蛋白的表达激活直接调控骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨分化,一般是抑制骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨分化的作用[64]。β-catenin 通过与Sox9、Cyclin D1、TCF/LEF等相互作用调控骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨分化,如Sox9可与β-catenin竞争结合TCF/LEF,从而抑制β-catenin-TCF/LEF复合体的形成,促进Sox9-β-catenin形成并降解β-catenin,降解产物与形成的复合物通过作用于Cyclin D1促进骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨的分化和成熟。此外Sox9-β-catenin还起反馈抑制作用,促进Sox9的降解,抑制骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨分化[65]。β-catenin还会与钙黏着蛋白相互作用形成复合物,发挥抑制软骨形成的作用。该通路除了可以直接调控软骨细胞分化与成熟之外,还可与TGF-β/Smad、MAPK/P38[66]、FGF等信号通路相互作用,共同调控骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨细胞分化。研究发现非经典的Wnt途径也参与调控了骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨分化,目前已证实Wnt5a[67]、Wnt3a与软骨分化相关,其中Wnt5a的表达可以促进早期成软骨化而Wnt3a的持续过表达会促进经典Wnt途径中骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖[68],并引起非经典途径中Ca2+与钙依赖性蛋白激酶的浓度增加,抑制骨髓间充质干细胞的成软骨分化。
2.3.2 Notch信号通路参与骨髓间充质干细胞的成软骨分化 Notch信号通路在骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨分化的3个阶段中发挥着不同的调节作用[69]。TIAN等[70]发现Notch信号通路在诱导分化期主要起抑制作用,Notch 抑制软骨细胞的分化主要是通过Twist1实现的。Twist1使NICD1过表达,从而抑制成软骨的诱导分化。在分化期,Notch主要起促进或抑制作用,如阻断Notch信号通路会抑制下颌髁突软骨中的软骨细胞增殖,但会促进软骨细胞的分化。ZANOTTI等[71]发现Notch通路的Hes1和Hey1可结合Sox9,从而抑制软骨特异性胶原蛋白Ⅱ的合成,从而抑制骨髓间充质干细胞成软骨分化。在终末分化阶段,Notch信号主要起抑制作用,如骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨分化的后期,持续激活过表达Notch配体Jagged1会抑制成软骨化[72];此外,DONG等[73]研究也认为抑制软骨细胞中Notch通路的相关信号,则会促进成软骨分化,从而抑制骨的形成。
2.3.3 重要转录因子参与骨髓间充质干细胞的成软骨分化 调节软骨生成的相关转录因子众多,有文献提及的包括Sox家族的Sox9、T-box转录因子家族的Brachyury、C-myc、ERG和Runx2等。Sox9是骨髓间充质干细胞软骨分化中较为重要的一类转录因子。Sox基因属于编码转录因子的高迁移组盒子超家族,编码的蛋白可发挥转录调控作用[74]。在Wnt通路经典途径中,Sox9可结合β-catenin形成复合物,从而调节成软骨分化。Sox9也可抑制BMP-2诱导的Smad7及相关因子的表达,从而增强成软骨分化,阻碍软骨内成骨,即软骨终末未分化期[75]。
相关信号通路出现异常后,往往会影响骨髓间充质干细胞正常的成软骨分化。骨髓间充质干细胞成软骨分化异常会导致关节软骨受损或变异增多(骨软骨症、软骨软化症以及局部骨的病变如髌骨软骨病),进而导致关节炎(如髌骨关节炎软骨病)等渐进性疾病。成熟的透明软骨由于缺乏神经支配和血管供应,且软骨细胞增殖能力差,所以很难自我修复。软骨分化受到影响后,软骨损伤可进行纤维性修复,修复的纤维软骨与正常透明软骨不同,为不可逆退变。
2.4 骨髓间充质干细胞参与调控间充质干细胞命运的其他因素
2.4.1 激素及其他代谢物参与调控骨髓间充质干细胞分化的命运 胰岛素信号通路和有氧糖酵解、氧化磷酸化都参与了骨髓间充质干细胞分化的命运。用胰岛素信号抑制剂S961处理骨髓间充质干细胞之后,研究发现骨髓间充质干细胞成脂分化减少,反之在高脂饮食喂养小鼠后,可以看到胰岛素信号通路激活,骨髓间充质干细胞成脂分化增加。同样利用氧化磷酸化抑制剂寡霉素处理骨髓间充质干细胞,也证实骨髓间充质干细胞成脂分化能力减弱。通过比对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨祖细胞和成脂祖细胞的代谢组学发现,骨髓间充质干细胞成骨祖细胞偏向于利用糖酵解获取能量,并且胰岛素信号通路的激活被抑制。骨髓间充质干细胞成骨祖细胞定位于骨表面,处于低氧环境,更有利于糖酵解,能够快速产生能量,用于骨的重塑[76]。
2.4.2 线粒体参与调控骨髓间充质干细胞分化的命运 研究发现线粒体活性氧的活性参与调控骨髓间充质干细胞分化的命运。骨髓间充质干细胞的线粒体活性氧在分化前呈现出较低的活性水平,向成骨分化时,参与线粒体生物发生的一系列蛋白质的表达水平均增加,包括PGC-1α、mttfa、DNA聚合酶γ、三羧酸循环的酶和呼吸酶的蛋白质亚单位。PGC-1α对于间充质干细胞的维持和分化至关重要。线粒体内的去乙酰化酶Sirtuins能够让多种底物去乙酰化,Sirt1的激活会抑制骨髓间充质干细胞成脂分化并促进成骨分化,而Sirt2的激活通过调控PPARγ的活性抑制骨髓间充质干细胞向脂肪细胞分化。此外,Sirt3、Sirt5和Sirt7也参与了线粒体的生物发生和脂肪分化过程中线粒体的激活,例如Sirt6的缺失促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨和软骨分化[77]。
| [1] ZUK PA, ZHU M, MIZUNO H, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2):211-228. [2] ERICES A, CONGET P, MINGUELL JJ. Mesenchymal progenitor cells in human umbilical cord blood. Br J Haematol. 2000;109(1):235-242. [3] FRIEDENSTEIN AJ, PETRAKOVA KV, KUROLESOVA AI, et al. Heterotopic of bone marrow. Analysis of precursor cells for osteogenic and hematopoietic tissues. Transplantation. 1968;6(2):230-247. [4] 施彦龙,李应福,谢兴文,等.BMP/Smads、OPG/RANK/RANKL信号通路与骨质疏松关系的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2020, 26(4):600-604. [5] JAMES AW. Review of Signaling Pathways Governing MSC Osteogenic and Adipogenic Differentiation. Scientifica (Cairo). 2013;2013:684736. [6] 刘小钰,宋敏,蒋林博,等.补骨脂活性成分对骨质疏松相关信号通路影响的研究概况[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2017,23(6):831-836. [7] WU M, CHEN G, LI YP. TGF-β and BMP signaling in osteoblast, skeletal development, and bone formation, homeostasis and disease. Bone Res. 2016;4:16009. [8] CHANG C. Agonists and Antagonists of TGF-β Family Ligands. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016;8(8):a021923. [9] CUI ZK, SUN JA, BALJON JJ, et al. Simultaneous delivery of hydrophobic small molecules and siRNA using Sterosomes to direct mesenchymal stem cell differentiation for bone repair. Acta Biomater. 2017;58: 214-224. [10] CHEN C, ULUDAĞ H, WANG Z, et al. Noggin suppression decreases BMP-2-induced osteogenesis of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. J Cell Biochem. 2012;113(12): 3672-3680. [11] LIU T, LI B, ZHENG XF, et al. Chordin-Like 1 Improves Osteogenesis of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Through Enhancing BMP4-SMAD Pathway. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019;10:360. [12] GAUR T, LENGNER CJ, HOVHANNISYAN H, et al. Canonical WNT signaling promotes osteogenesis by directly stimulating Runx2 gene expression. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(39):33132-33140. [13] CAWTHORN WP, BREE AJ, YAO Y, et al. Wnt6, Wnt10a and Wnt10b inhibit adipogenesis and stimulate osteoblastogenesis through a β-catenin-dependent mechanism. Bone. 2012;50(2):477-489. [14] GONG Y, SLEE RB, FUKAI N, et al. LDL receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) affects bone accrual and eye development. Cell. 2001;107(4):513-523. [15] BOYDEN LM, MAO J, BELSKY J, et al. High bone density due to a mutation in LDL-receptor-related protein 5. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346(20):1513-1521. [16] WANG T, LI J, ZHOU GQ, et al. Specific Deletion of β-Catenin in Col2-Expressing Cells Leads to Defects in Epiphyseal Bone. Int J Biol Sci. 2017;13(12):1540-1546. [17] WANG Y, LI YP, PAULSON C, et al. Wnt and the Wnt signaling pathway in bone development and disease. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2014; 19:379-407. [18] ESEN E, CHEN J, KARNER CM, et al. WNT-LRP5 signaling induces Warburg effect through mTORC2 activation during osteoblast differentiation. Cell Metab. 2013;17(5):745-755. [19] KARNER CM, ESEN E, OKUNADE AL, et al. Increased glutamine catabolism mediates bone anabolism in response to WNT signaling. J Clin Invest. 2015;125(2):551-562. [20] KOPAN R, ILAGAN MX. The canonical Notch signaling pathway: unfolding the activation mechanism. Cell. 2009;137(2):216-233. [21] SIMPSON MA, IRVING MD, ASILMAZ E, et al. Mutations in NOTCH2 cause Hajdu-Cheney syndrome, a disorder of severe and progressive bone loss. Nat Genet. 2011;43(4):303-305. [22] LEE SY, LONG F. Notch signaling suppresses glucose metabolism in mesenchymal progenitors to restrict osteoblast differentiation. J Clin Invest. 2018;128(12):5573-5586. [23] LONG F. Building strong bones: molecular regulation of the osteoblast lineage. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011;13(1):27-38. [24] KARSENTY G, KRONENBERG HM, SETTEMBRE C. Genetic control of bone formation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2009;25:629-648. [25] WEI J, SHIMAZU J, MAKINISTOGLU MP, et al. Glucose Uptake and Runx2 Synergize to Orchestrate Osteoblast Differentiation and Bone Formation. Cell. 2015;161(7):1576-1591. [26] CHEN Q, SHOU P, ZHENG C, et al. Fate decision of mesenchymal stem cells: adipocytes or osteoblasts? Cell Death Differ. 2016;23(7): 1128-1139. [27] ZHU W, HE X, HUA Y, et al. The E3 ubiquitin ligase WWP2 facilitates RUNX2 protein transactivation in a mono-ubiquitination manner during osteogenic differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(27):11178-11188. [28] KUMAR Y, KAPOOR I, KHAN K, et al. Withdrawal: E3 ubiquitin ligase Fbw7 negatively regulates osteoblast differentiation by targeting Runx2 for degradation. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(1):68. [29] VISAVADIYA NP, KEASEY MP, RAZSKAZOVSKIY V, et al. Erratum to: Integrin-FAK signaling rapidly and potently promotes mitochondrial function through STAT3. Cell Commun Signal. 2017;15(1):11. [30] GURI Y, COLOMBI M, DAZERT E, et al. mTORC2 Promotes Tumorigenesis via Lipid Synthesis. Cancer Cell. 2017;32(6):807-823. [31] ZHENG W, GU X, SUN X, et al. FAK mediates BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation via Wnt and MAPK signaling pathway in synovial mesenchymal stem cells. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47(1):2641-2649. [32] HUANG G, LI F, ZHAO X, et al. Functional and Biomimetic Materials for Engineering of the Three-Dimensional Cell Microenvironment. Chem Rev. 2017;117(20):12764-12850. [33] JIANG Y, WU W, JIAO G, et al. LncRNA SNHG1 modulates p38 MAPK pathway through Nedd4 and thus inhibits osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Life Sci. 2019;228:208-214. [34] ZHANG J, TAO Z, WANG Y. Long non‑coding RNA DANCR regulates the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human bone-derived marrow mesenchymal stem cells via the p38 MAPK pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(1):213-219. [35] ZHUANG W, GE X, YANG S, et al. Upregulation of lncRNA MEG3 Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells From Multiple Myeloma Patients By Targeting BMP4 Transcription. Stem Cells. 2015;33(6):1985-1997. [36] TANG S, XIE Z, WANG P, et al. LncRNA-OG Promotes the Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Under the Regulation of hnRNPK. Stem Cells. 2019;37(2):270-283. [37] JIA Q, JIANG W, NI L. Down-regulated non-coding RNA (lncRNA-ANCR) promotes osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells. Arch Oral Biol. 2015;60(2):234-241. [38] GAO Y, XIAO F, WANG C, et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 promotes osterix expression to regulate osteogenic differentiation by targeting miRNA-143 in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(8):6986-6996. [39] DING W, LI J, SINGH J, et al. miR-30e targets IGF2-regulated osteogenesis in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells, aortic smooth muscle cells, and ApoE-/- mice. Cardiovasc Res. 2015;106(1): 131-142. [40] LI CJ, CHENG P, LIANG MK, et al. MicroRNA-188 regulates age-related switch between osteoblast and adipocyte differentiation. J Clin Invest. 2015;125(4):1509-1522. [41] WANG CG, LIAO Z, XIAO H, et al. LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 promoted BMP2 expression to regulate osteogenic differentiation by sponging miRNA-214. Exp Mol Pathol. 2019;107:77-84. [42] DENG Y, WU S, ZHOU H, et al. Effects of a miR-31, Runx2, and Satb2 regulatory loop on the osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(16):2278-2286. [43] WANG JL, WEI X, WANG AG, et al. KCNQ1OT1 regulates osteogenic differentiation of hBMSC by miR-320a/Smad5 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(6):2843-2854. [44] YANG C, LIU X, ZHAO K, et al. miRNA-21 promotes osteogenesis via the PTEN/PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α pathway and enhances bone regeneration in critical size defects. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):65. [45] TANG QQ, LANE MD. Adipogenesis: from stem cell to adipocyte. Annu Rev Biochem. 2012;81:715-736. [46] ZUR NIEDEN NI, KEMPKA G, RANCOURT DE, et al. Induction of chondro-, osteo- and adipogenesis in embryonic stem cells by bone morphogenetic protein-2: effect of cofactors on differentiating lineages. BMC Dev Biol. 2005;5:1. [47] XU B, JU Y, SONG G. Role of p38, ERK1/2, focal adhesion kinase, RhoA/ROCK and cytoskeleton in the adipogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Biosci Bioeng. 2014;117(5):624-631. [48] KAWAI M, MUSHIAKE S, BESSHO K, et al. Wnt/Lrp/beta-catenin signaling suppresses adipogenesis by inhibiting mutual activation of PPARgamma and C/EBPalpha. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007; 363(2):276-282. [49] MURUGANANDAN S, ROMAN AA, SINAL CJ. Adipocyte differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: cross talk with the osteoblastogenic program. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009;66(2):236-253. [50] ZHOU Y, SONG T, PENG J, et al. SIRT1 suppresses adipogenesis by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling in vivo and in vitro. Oncotarget. 2016;7(47):77707-77720. [51] BENNETT CN, LONGO KA, WRIGHT WS, et al. Regulation of osteoblastogenesis and bone mass by Wnt10b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(9):3324-3329. [52] NEELS JG, GRIMALDI PA. Physiological functions of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor β. Physiol Rev. 2014;94(3):795-858. [53] TONTONOZ P, SPIEGELMAN BM. Fat and beyond: the diverse biology of PPARgamma. Annu Rev Biochem. 2008;77:289-312. [54] SCHUPP M, LAZAR MA. Fingered for a fat fate. Cell Metab. 2010;11(4): 244-245. [55] WALKEY CJ, SPIEGELMAN BM. A functional peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma ligand-binding domain is not required for adipogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(36):24290-24294. [56] GU C, XU Y, ZHANG S, et al. miR-27a attenuates adipogenesis and promotes osteogenesis in steroid-induced rat BMSCs by targeting PPARγ and GREM1. Sci Rep. 2016;6:38491. [57] WANG Y, ZHAO L, SMAS C, et al. Pref-1 interacts with fibronectin to inhibit adipocyte differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 2010;30(14):3480-3492. [58] RAUCH A, HAAKONSSON AK, MADSEN JGS, et al. Osteogenesis depends on commissioning of a network of stem cell transcription factors that act as repressors of adipogenesis. Nat Genet. 2019;51(4):716-727. [59] BORK S, HORN P, CASTOLDI M, et al. Adipogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stromal cells is down-regulated by microRNA-369-5p and up-regulated by microRNA-371. J Cell Physiol. 2011;226(9): 2226-2234. [60] SUN J, WANG Y, LI Y, et al. Downregulation of PPARγ by miR-548d-5p suppresses the adipogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and enhances their osteogenic potential. J Transl Med. 2014;12:168. [61] HAMAM D, ALI D, VISHNUBALAJI R, et al. microRNA-320/RUNX2 axis regulates adipocytic differentiation of human mesenchymal (skeletal) stem cells. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5(10):e1499. [62] KIM YJ, HWANG SJ, BAE YC, et al. MiR-21 regulates adipogenic differentiation through the modulation of TGF-beta signaling in mesenchymal stem cells derived from human adipose tissue. Stem Cells. 2009;27(12):3093-3102. [63] LIU Y, ZHANG ZC, QIAN SW, et al. MicroRNA-140 promotes adipocyte lineage commitment of C3H10T1/2 pluripotent stem cells via targeting osteopetrosis-associated transmembrane protein 1. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(12):8222-8230. [64] 汪建样,吴次虎,殷嫦嫦,等.Wnt信号通路调控干细胞成软骨分化[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2015,37(11):1554-1559. [65] AKIYAMA H, LYONS JP, MORI-AKIYAMA Y, et al. Interactions between Sox9 and beta-catenin control chondrocyte differentiation. Genes Dev. 2004;18(9):1072-1087. [66] JIN EJ, LEE SY, CHOI YA, et al. BMP-2-enhanced chondrogenesis involves p38 MAPK-mediated down-regulation of Wnt-7a pathway. Mol Cells. 2006;22(3):353-359. [67] CHURCH V, NOHNO T, LINKER C, et al. Wnt regulation of chondrocyte differentiation. J Cell Sci. 2002;115(Pt 24):4809-4818. [68] QU F, WANG J, XU N, et al. WNT3A modulates chondrogenesis via canonical and non-canonical Wnt pathways in MSCs. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2013;18:493-503. [69] 刘刚,张磊,扶世杰.Notch信号通路在软骨细胞分化过程中的作用[J].医学研究生学报,2016,29(10):1111-1115. [70] TIAN Y, XU Y, FU Q, et al. Notch inhibits chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal progenitor cells by targeting Twist1. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015;403:30-38. [71] ZANOTTI S, SMERDEL-RAMOYA A, CANALIS E. Reciprocal regulation of Notch and nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) c1 transactivation in osteoblasts. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(6):4576-4588. [72] KAMEI N, KWON SM, ISHIKAWA M, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells promote astrogliosis following spinal cord injury through Jagged1-dependent Notch signaling. J Neurotrauma. 2012;29(9):1758-1769. [73] DONG Y, JESSE AM, KOHN A, et al. RBPjkappa-dependent Notch signaling regulates mesenchymal progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation during skeletal development. Development. 2010;137(9):1461-1471. [74] CAO L, YANG F, LIU G, et al. The promotion of cartilage defect repair using adenovirus mediated Sox9 gene transfer of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials. 2011;32(16):3910-3920. [75] 吕学敏,杨庆铭,邓廉夫.调控软骨生成和软骨内骨化的转录因子及其相关机制研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2004,12(3):268-270. [76] TENCEROVA M, RENDINA-RUEDY E, NEESS D, et al. Metabolic programming determines the lineage-differentiation fate of murine bone marrow stromal progenitor cells. Bone Res. 2019;7:35. [77] LI Q, GAO Z, CHEN Y, et al. The role of mitochondria in osteogenic, adipogenic and chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Protein Cell. 2017;8(6):439-445. [78] LIU H, ZHONG L, YUAN T, et al. MicroRNA-155 inhibits the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells induced by BMP9 via downregulation of BMP signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(6): 3379-3393. [79] HUANG H, DOU L, SONG J, et al. CBFA2T2 is required for BMP-2-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;496(4):1095-1101. [80] ALMALKI SG, AGRAWAL DK. Key transcription factors in the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Differentiation. 2016;92(1-2):41-51. [81] LEE WC, GUNTUR AR, LONG F, et al. Energy Metabolism of the Osteoblast: Implications for Osteoporosis. Endocr Rev. 2017;38(3): 255-266. [82] MALEKZADEH BÖ, ERLANDSSON MC, TENGVALL P, et al. Effects of implant-delivered insulin on bone formation in osteoporotic rats. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106(9):2472-2480. [83] AGHEBATI-MALEKI L, DOLATI S, ZANDI R, et al. Prospect of mesenchymal stem cells in therapy of osteoporosis: A review. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(6):8570-8578. [84] HU L, YIN C, ZHAO F, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Cell Fate Decision to Osteoblast or Adipocyte and Application in Osteoporosis Treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(2):360. [85] CHO SW, SUN HJ, YANG JY, et al. Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing RANK-Fc or CXCR4 prevents bone loss in ovariectomized mice. Mol Ther. 2009;17(11):1979-1987. [86] TZOUVELEKIS A, TOONKEL R, KARAMPITSAKOS T, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for the Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018;5:142. [87] MANSOURI N, WILLIS GR, FERNANDEZ-GONZALEZ A, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell exosomes prevent and revert experimental pulmonary fibrosis through modulation of monocyte phenotypes. JCI Insight. 2019;4(21):e128060. |
| [1] | 蒲 锐, 陈子扬, 袁凌燕. 不同细胞来源外泌体保护心脏的特点与效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | 林清凡, 解一新, 陈婉清, 叶振忠, 陈幼芳. 人胎盘源间充质干细胞条件培养液可上调缺氧状态下BeWo细胞活力和紧密连接因子的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | 袁家威, 张海涛, 揭 珂, 曹厚然, 曾意荣. 基于网络药理学研究桃红四物汤治疗假体周围感染的潜在靶点和机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [4] | 张秀梅, 翟运开, 赵 杰, 赵 萌. 类器官模型国内外数据库近10年文献研究热点分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [5] | 汪显耀, 关亚琳, 刘忠山. 提高间充质干细胞治疗难愈性创面的策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [6] | 万 然, 史 旭, 刘京松, 王岩松. 间充质干细胞分泌组治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [7] | 廖成成, 安家兴, 谭张雪, 王 倩, 刘建国. 口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的治疗靶点及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [8] | 谢文佳, 夏天娇, 周卿云, 刘羽佳, 顾小萍. 小胶质细胞介导神经元损伤在神经退行性疾病中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [9] | 李珊珊, 郭笑霄, 尤 冉, 杨秀芬, 赵 露, 陈 曦, 王艳玲. 感光细胞替代治疗视网膜变性疾病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [10] | 焦 慧, 张一宁, 宋雨晴, 林 宇, 王秀丽. 乳腺癌类器官研究进展及临床应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [11] | 王诗琦, 张金生. 中医药调控缺血缺氧微环境对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖、分化及衰老的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [12] | 曾燕华, 郝延磊. 许旺细胞体外培养及纯化的系统性综述[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [13] | 孔德胜, 何晶晶, 冯宝峰, 郭瑞云, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, 吕 飞, 张舒涵, 张晓琳, 马 隽, 崔慧先. 间充质干细胞修复大动物模型脊髓损伤疗效评价的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [14] | 侯婧瑛, 于萌蕾, 郭天柱, 龙会宝, 吴 浩. 缺氧预处理激活HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞生存和血管再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [15] | 史洋洋, 秦英飞, 吴福玲, 何 潇, 张雪静. 胎盘间充质干细胞预处理预防小鼠毛细支气管炎[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
肝、黏膜、羊水、羊膜、脐血[2]。FRIEDENSTEIN 等[3]在1968年首次证实了骨髓中存在间充质干细胞,并利用贴壁法将骨髓间充质干细胞在体外进行分离培养。骨髓间充质干细胞是一类具有分化功能的多能干细胞,主要分化为脂肪细胞和骨骼细胞等。作为脂肪细胞和成骨细胞的祖细胞,骨髓间充质干细胞在分化平衡方面发挥至关重要的作用。大量的实验发现脂肪诱导因子可以抑制成骨,反之成骨诱导因子会阻碍脂肪的形成,在这个过程中骨髓间充质干细胞发挥了“指挥官”的作用,同时一些外部因子例如物理、化学、非编码RNA(微小RNA、长链非编码RNA等)、代谢(胰岛素)以及遗传基因也共同参与骨髓间充质干细胞分化的命运。骨髓间充质干细胞分化的失调与多种病理生理过程相关,例如骨质疏松、肥胖及肥胖引发的糖尿病、衰老等,因此骨髓间充质干细胞分化的命运越来越引起科学家们的广泛关注。作者查阅了关于骨髓间充质干细胞分化命运的相关文献进行综述,希望有助于人们更好地从骨髓间充质干细胞分化的角度来了解骨质疏松、肥胖及肥胖引发的糖尿病、衰老等一系列疾病,为这些疾病的治疗提供新的思路。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.2 纳入和排除标准
纳入标准:①原创性和创新性,论点和论据可靠;②权威性高的文献综述等。
排除标准:陈旧和不相关的文献。
1.3 数据提取 初步检索到1 972篇英文文献,756篇中文文献,最终纳入87篇文献进行综述。
骨髓间充质干细胞与新型材料的联合应用也是研究的热点,比如前面提到的整合素家族可以将机械信号转导到细胞骨架[32],用于促进成骨分化,这就提示整合素涂抹机械支架可以用于骨再生的治疗。另外还可以用于治疗发育缺陷或者面部美容需求的下颌骨缺损重建,通过三维打印金属钛支架后,在支架表层涂抹提前利用基质胶制备好的骨髓间充质干细胞混合物,体外培养得到新骨。研究还发现骨髓间充质干细胞可以作为治疗肺纤维化的候选药物[86]。内皮-间质转化是肺纤维化过程中的关键步骤。在肺纤维化小鼠模型中注射纳米颗粒标记的骨髓间充质干细胞,利用纳米颗粒示踪技术发现14 d左右骨髓间充质干细胞富集到了肺部,并减轻了肺纤维化程度[87]。
以上的应用主要集中在骨髓间充质干细胞的细胞治疗,由于骨髓间充质干细胞具有分化潜能,那么在体内的安全性就存在不稳定因素,如何控制其适宜注射量、采取恰当的移植方式及达到优化疗效的途径仍是现在亟需广大研究者解决的问题。
作者最近一直在关注骨髓间充质干细胞的提取物或者分泌物在各种治疗中的应用,研究发现骨髓间充质干细胞在外界微环境刺激作用下,可以通过自分泌或者旁分泌多种生长因子促进骨再生和修复。研究发现当植入外源性骨髓间充质干细胞后,机体会分泌生长因子激活损伤部位的干细胞,当外源性骨髓间充质干细胞不定植在损伤部位后,依然可以产生显著的治疗效果,这就提示骨髓间充质干细胞的提取物或者分泌物用于治疗骨质疏松或其他疾病的可行性。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程

文题释义:#br# 骨骼微环境:指的是骨骼在分子特征或细胞层面的相关骨细胞、基质细胞、微循环、信号转导通路、骨机械负荷、骨pH值环境等多方面、多组分构成的骨细胞或骨骼的生存环境,主要构成有骨髓基质、微血管、成骨细胞、破骨细胞、脂肪细胞、成软骨细胞、造血细胞及相关细胞因子等,是骨吸收、骨重建、造血、免疫的重要场所。骨骼微环境的改变和很多疾病密切相关,如骨质疏松、多发性骨髓瘤、骨髓增生异常综合征等。#br# 间充质干细胞:是来源于发育早期中胚层的一类多能干细胞,主要存在于各种结缔组织以及器官的间质中,以骨髓和脂肪组织中含量最丰富。骨髓间充质干细胞作为成骨细胞、脂肪细胞和软骨细胞的共同祖细胞,在分化平衡方面发挥至关重要的作用,同时外部因子如物化因素、非编码RNA、代谢等共同参与其分化的调控,而其分化失调与多种病理生理过程相关,例如骨质疏松、肥胖和衰老等。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
文章详细的总结了骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞、脂肪细胞和软骨细胞分化的机制,涵盖重要信号通路、转录因子、非编码RNA、整合素家族、激素和线粒体。目前对于骨髓间充质干细胞分化命运的研究主要集中在一些经典的信号通路和下游的转录因子,参与骨髓间充质干细胞分化命运调控的机制研究主要聚焦在遗传发育的改变、化学药物、物理刺激,以及一些非编码RNA、细胞因子、代谢物胰岛素等。在应用骨髓间充质干细胞治疗骨质疏松的临床试验中,其归巢数量的有限和较低的定植比例限制了治疗效果,如何通过加工修饰提高骨髓间充质干细胞归巢的数量以及定植的比例,进一步提高治疗效果,是目前研究的难点热点。骨髓间充质干细胞与新型材料的联合应用也是研究的热点。骨髓间充质干细胞的分化潜能在带来疾病治疗新思路的同时也带来体内安全性的问题,如何控制其适宜注射量、采取恰当的移植方式及达到优化疗效的途径亟需广大研究者解决。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||